| TIKZ | 您所在的位置:网站首页 › tikzcd箭头 › TIKZ |
TIKZ
|
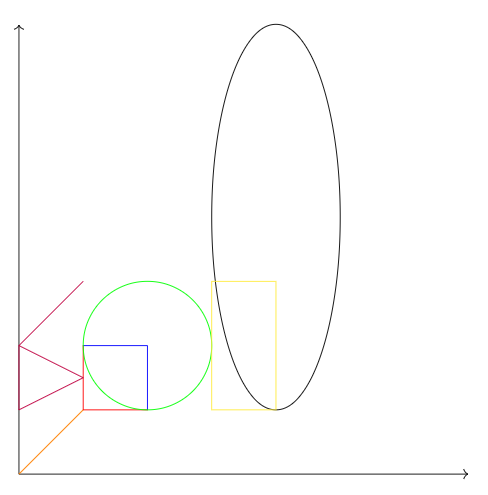
TIKZ是LaTeX的一个绘图包,可以绘制其他软件很难画出来的图像。 基本用法 直线、垂足、矩形、椭圆代码: \documentclass{article} \usepackage{tikz} \usetikzlibrary{arrows.meta}%画箭头用的包 \begin{document} \begin{tikzpicture} \draw[->] (0,0)--(7,0); \draw[->] (0,0)--(0,7); %箭头线 \draw[red] (2,1) -| (1,2);%直角1 \draw[blue] (2,1)|-(1,2);%直角2 \draw[green] (2,2) circle (1);%圆:圆心、半径 \draw[black] (4,4) ellipse (1 and 3);%椭圆:短、长半轴 \draw[yellow] (3,3) rectangle (4,1);%矩形 \draw[orange] (0,0) -- (2,1-|1,2);%找到垂点并与(0,0)连线 \draw[purple] (0,1)--(1,1.5)--(0,2)--cycle %封闭的线段 (0,2)--(1,3);%不加分号的连写 \end{tikzpicture} \end{document}效果图:
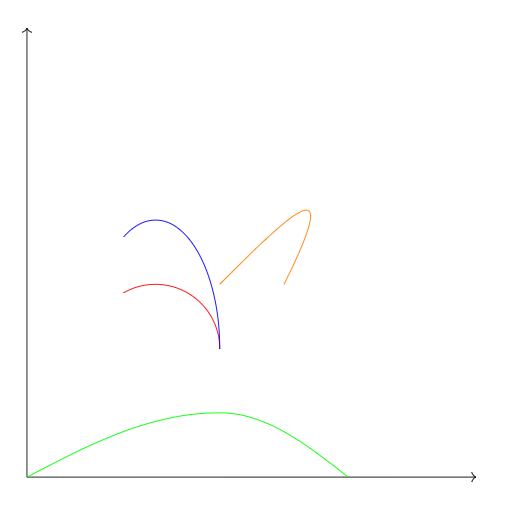
代码: \documentclass{article} \usepackage{tikz} \usetikzlibrary{arrows.meta}%画箭头用的包 \begin{document} \begin{tikzpicture} \draw[->] (0,0)--(7,0); \draw[->] (0,0)--(0,7); %箭头线 \draw[red] (3,2) arc (0:120:1);%圆弧:起始点,开始角度:结束角度:半径 \draw[blue] (3,2) arc (0:120:1 and 2);%椭圆弧 \draw[green] (0,0) sin (3,1) cos (5,0);%画pi/2的正弦、余弦 \draw[orange] (3,3)..controls (4,4)and(5,5) .. (4,3); %贝塞尔曲线:起点..controls 控制点 and 控制点..终点 \end{tikzpicture} \end{document}效果图:
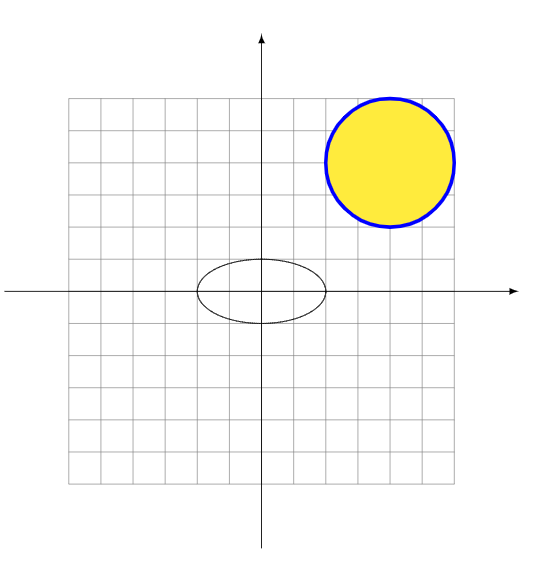
代码: \documentclass{article} \usepackage{tikz} \usetikzlibrary{arrows.meta}%画箭头用的包 \begin{document} \begin{tikzpicture} \draw[help lines,step = 0.5] (-3,-3) grid (3,3); %辅助线格子 \draw[-latex] (-4,0) -- (4,0); \draw[-latex] (0,-4) -- (0,4);%实心箭头 \draw[domain = -2:360][samples = 200] plot({cos(\x)}, {0.5*sin(\x)});%函数图像,参数方程,内有小括号,外面必须用花括号括起来,samples是画函数图时列出的点 \filldraw[fill = yellow,draw = blue][ultra thick] (2,2) circle (1);%填色,还可以设置线宽 \end{tikzpicture} \end{document}效果图:
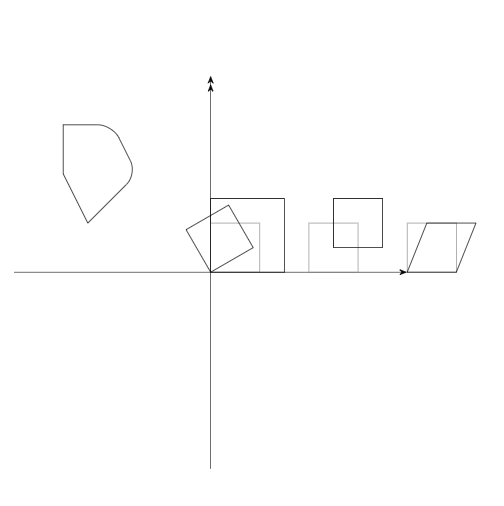
代码: \documentclass{article} \usepackage{tikz} \usetikzlibrary{arrows.meta}%画箭头用的包 \begin{document} \begin{tikzpicture}[>=Stealth]%设置箭头,环境中所有箭头都用这个库 \draw[->] (-4,0) -- (4,0); \draw[->>] (0,-4) -- (0,4); \draw(-3,2)--(-3,3)[rounded corners = 0.3cm] -- (-2,3)--(-1.5,2)[sharp corners]--(-2.5,1)--cycle;%圆角多边形 \draw[help lines](0,0) rectangle (1,1);%辅助线 \draw[scale=1.5] (0,0) rectangle (1,1);%缩放 \draw[rotate=30] (0,0) rectangle (1,1);%扰起点旋转 \draw[help lines](2,0) rectangle (3,1); \draw[shift={(0.5,0.5)}](2,0) rectangle (3,1);%平移 \draw[help lines](4,0) rectangle (5,1); \draw[xslant=0.4](4,0) rectangle (5,1);%倾斜 \end{tikzpicture} \end{document}效果图:
代码: \documentclass{article} \usepackage{tikz} \usetikzlibrary{arrows.meta}%画箭头用的包 \begin{document} \begin{tikzpicture} \draw[->] (-4,0) -- (4,0); \draw[->>] (0,-4) -- (0,4); \node (A) at (2,2) {$A_1$}; \node[draw] (B) at (3,2) {B};%draw属性添加自适应大小的方框 \node[draw] (C) at (2.5,3) {}; \draw (A) -- (B.center) -- (C.north) -- (A);%连线可以连到字母方框的某个位置:center/north/south/east/west \node[draw,anchor=east] (a) at (A) {$a_0$};%定义A的锚点在A位置的东部,然后定义a,并将其位置定义为A位置的中心 \node[draw,below right=4pt] (b) at (B) {b};%在相对于B的位置右下方4pt的地方定义b \node[circle,fill=blue,text=white,font={\bfseries}] (A) at (0,0) {A node};%填充、各种可自定义的参数 \node[rectangle,rounded corners,draw=gray,font={\sffamily\slshape}] (B) at (2,0) {B node}; \node[draw] (P) at (-3,3){center}; \draw[dotted] (0,0)--(P.south);%画某点到某点的南边的线 \end{tikzpicture} \end{document}效果图:
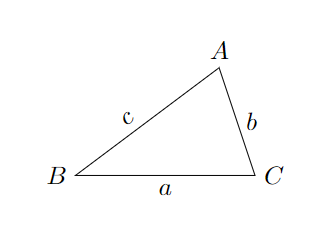
代码: \documentclass{article} \usepackage{tikz} \usetikzlibrary{arrows.meta}%画箭头用的包 \begin{document} \begin{tikzpicture} \draw (2,1.5)coordinate (A)node[above] {$A$}%定义点A并标注A --node[above left,sloped] {$c$}%给线标注c (0,0)coordinate (B)node[left] {$B$} --node[below]{$a$} (2.5,0)coordinate (C)node[right]{$C$} --node[right]{$b$} cycle; \end{tikzpicture} \end{document}效果图:
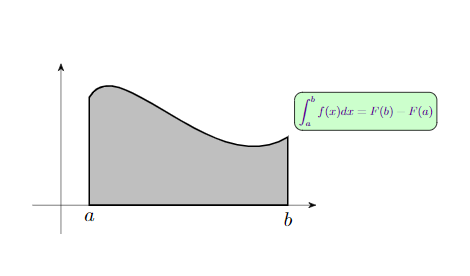
代码: \documentclass{article} \usepackage{tikz} \usetikzlibrary{arrows.meta}%画箭头用的包 \begin{document} \begin{tikzpicture}[>=Stealth] \draw[->,line width=0.2pt](-0.5,0)--(4.5,0); \draw[->,line width=0.2pt](0,-0.5)--(0,2.5); \coordinate (a) at (0.5,1.9); \coordinate (b) at (4,1.2); \coordinate (a0) at (a |- 0,0); \coordinate (b0) at (b |- 0,0); \node[below] at (a0) {$a$}; \node[below] at (b0) {$b$}; \filldraw[fill=gray!50,draw,thick] (a0)--(a)..controls(1,2.8)and(2.7,0.4)..(b)--(b0)--cycle; \node[above right,outer sep=0.2cm,rounded corners,fill = green!20,draw = black,text = blue!60!red,scale = 0.6] %blue60,red40 at (b) {$\displaystyle\int_a^bf(x)dx = F(b)-F(a)$};%写标注,draw边框,fill填充,scale字体大小 \end{tikzpicture} \end{document}效果图:
代码: \documentclass{article} \usepackage{tikz} \usepackage{pgffor}%可以使用foreach的包 \usepackage{ifthen}%可以使用ifthenelse的包,还能使用whiledo \begin{document} \begin{tikzpicture} \foreach \i in {0,...,5}{ \foreach \j in {0,...,\i}{ \ifthenelse{\i > 3}{%if成立 \node[fill = green!20,rounded corners]at (\i,\j) {(\i,\j)}; }{%if不成立 \node[fill = red!20,rounded corners]at (\i,\j) {(\i,\j)}; } } } \end{tikzpicture} \end{document}效果图:
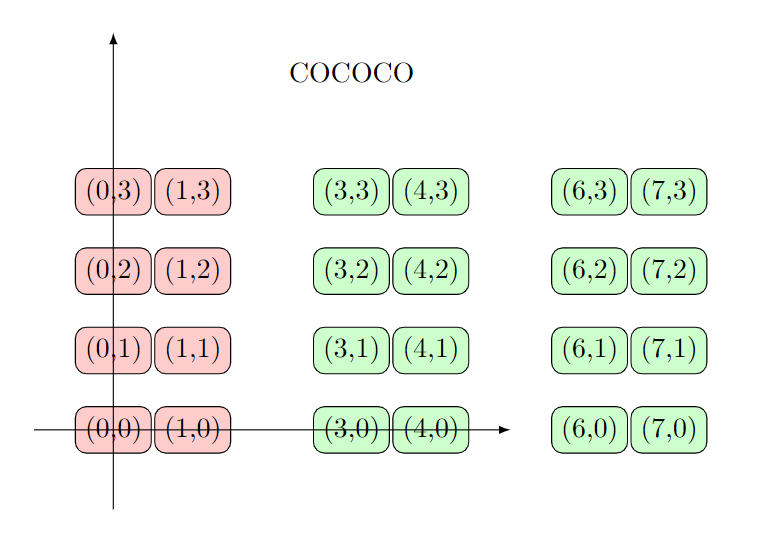
这个库可以让你使用过程语言结合LaTeX的画图脚本的来画图,十分方便。主要就是导入math库: \usetikzlibrary{math}%使用数学程序 \usetikzlibrary{fpu}%修理不能使用ifthenelse的错误 代码: \documentclass{article} \usepackage{tikz} \usetikzlibrary{fpu}%修理不能使用ifthenelse的错误!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! \usetikzlibrary{math}%使用数学程序 \begin{document} \begin{tikzpicture} \tikzmath{ %数学程序编写,定义的变量可以在其外部使用,里面所有语句都要加分号; 并且不能有多余的回车 function paint_loop(\x,\y){ %函数中只能使用局部变量,外部变量不能用 for \i in {0,1,...,\x}{ for \j in {0,...,\y}{ int \ii,\jj; \ii = \i*1.5; \jj = \j; if \ii > 2 then {%条件分支语句 {%绘图代码在数学程序内部使用,要用画括号括起来!!!! \node[draw,fill = green!20,rounded corners] at (\ii,\jj) {(\ii,\jj)}; }; }else{ { \node[draw,fill = red!20,rounded corners] at (\ii,\jj) {(\ii,\jj)}; }; }; }; }; }; \a = 5; %和python一样,加个.就是实数,不加点就是小数 \b = 3; paint_loop(\a,\b); coordinate \co;%能自定义的变量有int、real、coordinate(坐标),不能在定义的时候赋值 \co = (3,4.5); } \draw[-latex] (-1,0) -- (5,0); \draw[-latex] (0,-1) -- (0,5); \node at (\co) {COCOCO}; %在tikzmath中定义的变量在能外部使用 \end{tikzpicture} \end{document}效果图:
代码: \documentclass{article} \usepackage{tikz} \usetikzlibrary{fpu}%修理不能使用ifthenelse的错误!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! \usetikzlibrary{math}%使用数学程序 \begin{document} \begin{tikzpicture} \tikzmath{ function paint_nodes(\radius,\gapy,\posx,\num){ \gapy = \gapy+\radius*2; \starty = \gapy*(\num-1)/2; for \i in {0,...,\num-1}{ \drawy = \starty - \i*\gapy; { \filldraw[line width = 0.5pt,fill = white] (\posx,\drawy) circle (\radius); }; }; }; function paint_lines(\radius,\gapy,\posx,\num,\nextposx,\nextnum){ \gapy = \gapy+\radius*2; \starty = \gapy*(\num-1)/2; \startyy = \gapy*(\nextnum-1)/2; for \i in {0,...,\num-1}{ \drawy = \starty - \i*\gapy; for \j in {0,...,\nextnum-1}{ \drawyy = \startyy - \j*\gapy; { \draw (\posx,\drawy) -- (\nextposx,\drawyy); }; }; }; }; function paint_x_lines(\radius,\gapy,\posx,\num,\ifright,\len){ \gapy = \gapy+\radius*2; \starty = \gapy*(\num-1)/2; for \i in {0,...,\num-1}{ \drawy = \starty - \i*\gapy; if \ifright == 1 then{ { \draw[-latex] (\posx,\drawy) -- (\posx+\len,\drawy); }; }else{ { \draw[-latex] (\posx,\drawy)--(\posx-\len,\drawy); }; }; }; }; function paint_net(\x0,\x1,\x2,\x3){ \gapx = 2; \radius = 0.3; \gapy = 0.2; paint_lines(\radius,\gapy,0*\gapx,\x0,1*\gapx,\x1); paint_lines(\radius,\gapy,1*\gapx,\x1,2*\gapx,\x2); paint_lines(\radius,\gapy,2*\gapx,\x2,3*\gapx,\x3); paint_x_lines(\radius,\gapy,3*\gapx,\x3,1,1.8); paint_x_lines(\radius,\gapy,0*\gapx-1,\x0,1,1); paint_nodes(\radius,\gapy,1*\gapx,\x1); paint_nodes(\radius,\gapy,2*\gapx,\x2); paint_nodes(\radius,\gapy,3*\gapx,\x3); }; paint_net(7,9,10,5); } \node[scale = 0.9] at (0,-4.2) {Feature}; \node[scale = 0.9] at (2,-4.2) {Input layer}; \node[scale = 0.9] at (4,-4.2) {Hide layer}; \node[scale = 0.9] at (6,-4.2) {Output layer}; \end{tikzpicture} \end{document}效果图:
|
【本文地址】
公司简介
联系我们