| [MATLAB]中meshgrid函数的用法与实践(学习笔记) | 您所在的位置:网站首页 › matlab中sound函数用法 › [MATLAB]中meshgrid函数的用法与实践(学习笔记) |
[MATLAB]中meshgrid函数的用法与实践(学习笔记)
|
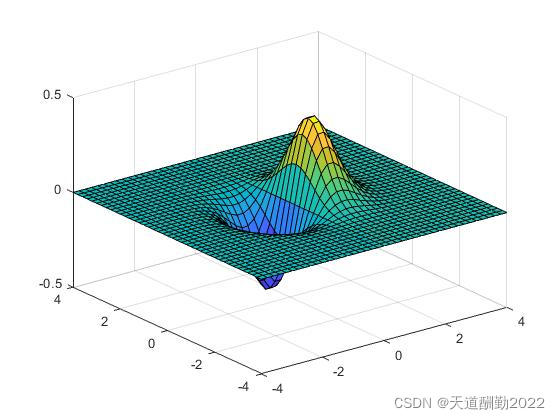
今天在看点目标成像仿真程序的时候,看到了meshgrid函数,看了matlab的帮助文档后理解了一点,特此记录学习过程。 目录 一、meshgrid函数二、举例验证 三、创建二维网格绘制曲面图四、总结五、meshgrid函数源代码(仅供参考): 一、meshgrid函数meshgrid函数是MATLAB中用于生成网格采样点数的函数,通常进行2D、3D图形的绘制。 1、【X,Y】 = meshgrid(x,y) :基于向量x和y中包含的坐标返回二维网格坐标。X是一个矩阵,每一行是x的一个副本,Y也是一个矩阵,每一列是y的一个副本。坐标X和Y表示的网格有length(y)个行和length(x)个列。 2 、[X,Y] = meshgrid(x) 与 [X,Y] = meshgrid(x,x)相同,返回网格大小为length(x)*length(x)的方形网格矩阵。 3、 [X,Y,Z] = meshgrid(x,y,z),返回由向量x,y,z定义的三维网格坐标,X,Y和Z表示的网格大小为length(x)*length(y)*length(z)。 二、举例验证1.【X,Y】 = meshgrid(x,y) , 代码如下: a 、b矩阵个数相同: a = [1 2 3 4]; b = [5 6 7 8]; [A,B] = meshgrid(a,b)结果: A = 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 B = 5 5 5 5 6 6 6 6 7 7 7 7 8 8 8 8 >>a 、b矩阵数量不同: a = [1 2 3]; b = [4 5 6 7]; [A,B] = meshgrid(a,b) A = 1 2 3 1 2 3 1 2 3 1 2 3 B = 4 4 4 5 5 5 6 6 6 7 7 7 >>2、【X,Y】 = meshgrid(x), 代码如下: x = [1 2 3]; [X,Y] = meshgrid(x) X = 1 2 3 1 2 3 1 2 3 Y = 1 1 1 2 2 2 3 3 3 >> x = [1 2 3]; >> [X,Y] = meshgrid(x,x) X = 1 2 3 1 2 3 1 2 3 Y = 1 1 1 2 2 2 3 3 3 >> 三、创建二维网格绘制曲面图使用均匀分布的x和y坐标在-4到4之间创建二维网格: 代码如下: x = -4:0.2:4; y = x; [X,Y] = meshgrid(x); F = X.*exp(-X.^2 - Y.^2); surf(X,Y,F);
为什么要使用meshgrid? matlab使用矩阵的方式进行运算,对于2D而言,如果采样10个点(指x,y轴),那么对于x=第一个采样点,反映到矩阵就是10个,即不管y是哪个值,x的第一采样点保持不变;对y是同理。因此,2D产生的x和y都是两维矩阵。 五、meshgrid函数源代码(仅供参考): 源代码: function [xx,yy,zz] = meshgrid(x,y,z) %MESHGRID Cartesian grid in 2-D/3-D space % [X,Y] = MESHGRID(xgv,ygv) replicates the grid vectors xgv and ygv to % produce the coordinates of a rectangular grid (X, Y). The grid vector % xgv is replicated numel(ygv) times to form the columns of X. The grid % vector ygv is replicated numel(xgv) times to form the rows of Y. % % [X,Y,Z] = MESHGRID(xgv,ygv,zgv) replicates the grid vectors xgv, ygv, zgv % to produce the coordinates of a 3D rectangular grid (X, Y, Z). The grid % vectors xgv,ygv,zgv form the columns of X, rows of Y, and pages of Z % respectively. (X,Y,Z) are of size numel(ygv)-by-numel(xgv)-by(numel(zgv). % % [X,Y] = MESHGRID(gv) is equivalent to [X,Y] = MESHGRID(gv,gv). % [X,Y,Z] = MESHGRID(gv) is equivalent to [X,Y,Z] = MESHGRID(gv,gv,gv). % % The coordinate arrays are typically used for the evaluation of functions % of two or three variables and for surface and volumetric plots. % % MESHGRID and NDGRID are similar, though MESHGRID is restricted to 2-D % and 3-D while NDGRID supports 1-D to N-D. In 2-D and 3-D the coordinates % output by each function are the same, the difference is the shape of the % output arrays. For grid vectors xgv, ygv and zgv of length M, N and P % respectively, NDGRID(xgv, ygv) will output arrays of size M-by-N while % MESHGRID(xgv, ygv) outputs arrays of size N-by-M. Similarly, % NDGRID(xgv, ygv, zgv) will output arrays of size M-by-N-by-P while % MESHGRID(xgv, ygv, zgv) outputs arrays of size N-by-M-by-P. % % Example: Evaluate the function x*exp(-x^2-y^2) % over the range -2 |
【本文地址】
公司简介
联系我们