| 基于Python+tensorflow深度学习VGG | 您所在的位置:网站首页 › 风格迁移代码 › 基于Python+tensorflow深度学习VGG |
基于Python+tensorflow深度学习VGG
|
目录
前言总体设计系统整体结构图系统流程图
运行环境Python 环境TensorFlow 环境
模块实现1. 图片处理2. 模型构造
系统测试工程源代码下载其它资料下载
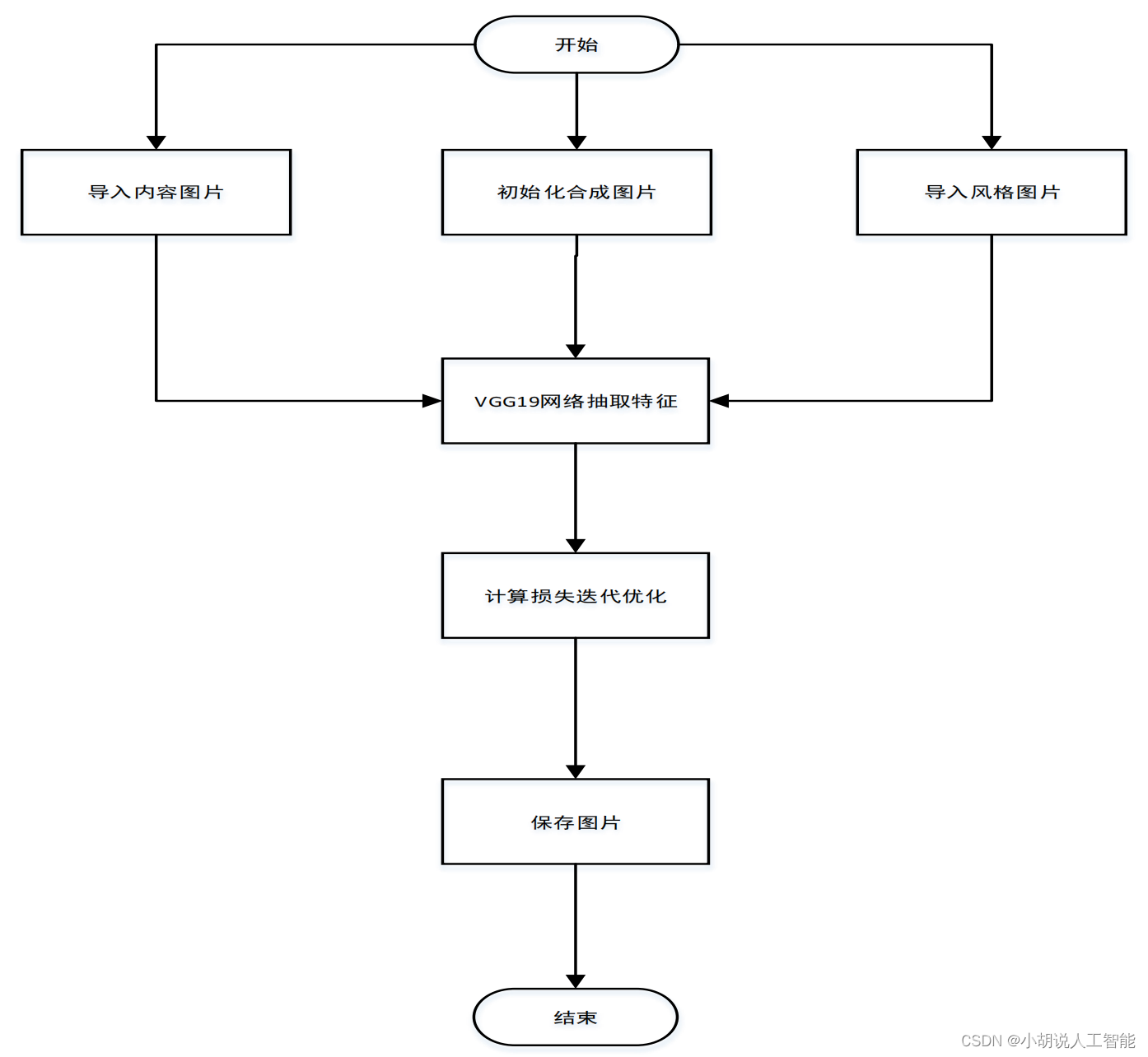
本项目基于 MNIST 数据集,使用 VGG-19 网络模型,将图像进行风格迁移,实现去噪功能。 VGG-19是一种深度卷积神经网络模型,具有较强的图像特征提取能力。在本项目中,我们利用VGG-19模型的卷积层,提取输入图像的特征表示。 图像风格迁移是一种通过将图像的内容与另一个图像的风格相结合,生成新图像的技术。通过将待处理的图像输入VGG-19模型,我们可以获得图像的内容特征和风格特征。然后,利用风格迁移算法,将图像的内容特征与一个风格图像的风格特征进行融合。这样,我们可以生成一张具有原始图像内容但具有去除噪声的新图像。 这项技术可以应用于图像处理领域,提高图像质量,去除噪声干扰,从而改善图像的视觉效果和可用性。 总体设计本部分包括系统整体结构图和系统流程图。 系统整体结构图系统整体结构如图所示。
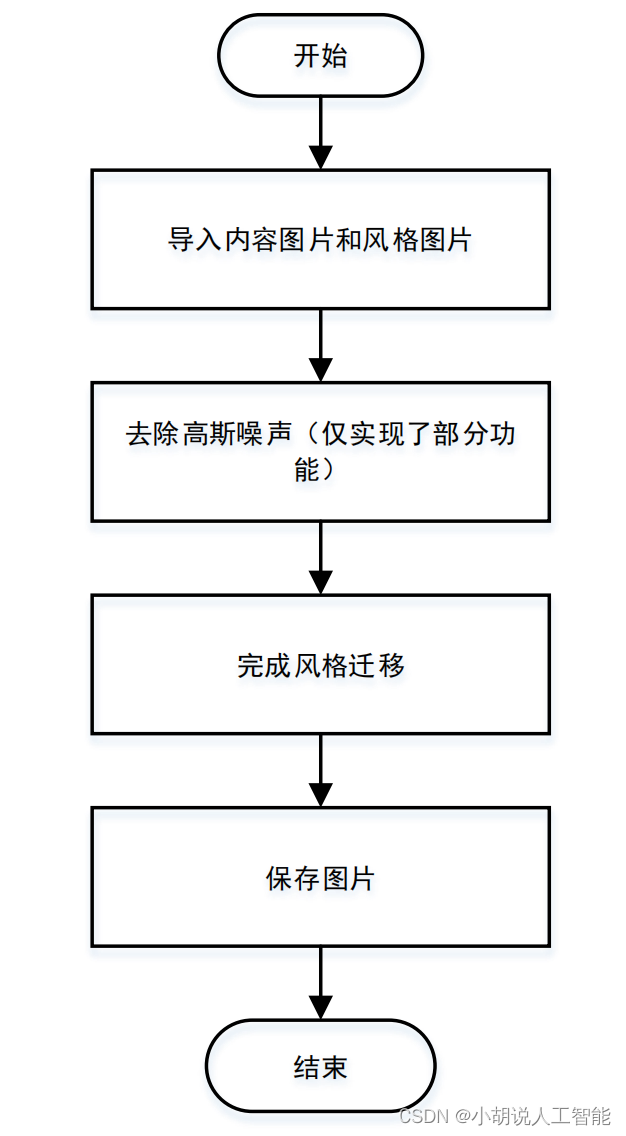
系统流程如图所示。
本部分包括 Python 和 TensorFlow 运行环境。 Python 环境需要 Python 3.6 及以上配置,在 Windows 环境下推荐下载 Anaconda 完成 Python 所需的配置,下载地址:https://www.anaconda.com/。也可以下载虚拟机在 Linux 环境下运行代码。 TensorFlow 环境打开 Anaconda Prompt,输入清华仓库镜像。 conda config --add channels https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/pkgs/free/ conda config –set show_channel_urls yes创建 Python 3.5 环境,名称为 TensorFlow: conda create -n tensorflow python=3.5有需要确认的地方,都输入 y。 在 Anaconda Prompt 中激活 TensorFlow 环境: activate tensorflow安装 CPU 版本的 TensorFlow: pip install –upgrade --ignore-installed tensorflow 模块实现本项目包括3 个模块:图片处理、模型构造、迭代更新,下面分别给出各模块的功能介绍及相关代码。 1. 图片处理图片风格迁移会涉及到图片处理,主要为图片的大小裁剪、导入和保存。由于图片尺寸参差不齐,在风格迁移之前,将图片大小调为一致以降低难度。图像风格迁移过程中会迭代更新很多张图片,这些图片放一起做成动图。 def get_resized_image(img_path, width, height, save=True): #改变图片大小 image = Image.open(img_path) image = ImageOps.fit(image, (width, height), Image.ANTIALIAS) if save: image_dirs = img_path.split('/') image_dirs[-1] = 'resized_' + image_dirs[-1] out_path = '/'.join(image_dirs) if not os.path.exists(out_path): image.save(out_path) image = np.asarray(image, np.float32) return np.expand_dims(image, 0) def generate_noise_image(content_image, width, height, noise_ratio=0.6): #给图片加噪声 noise_image = np.random.uniform(-20, 20, (1, height, width, 3)).astype(np.float32) return noise_image * noise_ratio + content_image * (1 - noise_ratio) def save_image(path, image): #保存图片 image = image[0] image = np.clip(image, 0, 255).astype('uint8') scipy.misc.imsave(path, image) def safe_mkdir(path): #生成路径 try: os.mkdir(path) except OSError: pass def create_gif(root_dir, duration=0.3): #创建GIF动图 img_list = os.listdir(root_dir) img_list.sort(key=lambda x: int(x[6:-4])) frames = list() gif_name = GIF_PATH + '/' + root_dir.split('/')[-1] + '.gif' for i in img_list: i = root_dir + '/' + i frames.append(imageio.imread(i)) imageio.mimsave(gif_name, frames, 'GIF', duration=duration) return gif_name 2. 模型构造本部分包括定义模型结构和优化损失函数。 1)定义模型结构 项目用到的网络模型为预训练好的 VGG-19,使用过程中抛弃最后三个全连接层,取出前面各层的参数,构建网络结构。 def download(download_link, file_name, expected_bytes): #下载VGG-19 print(file_name) if os.path.exists(file_name): print("VGG-19 pre-trained model is ready") return print("Downloading the VGG pre-trained model. This might take a while ...") file_name, _ = urllib.request.urlretrieve(download_link, file_name) file_stat = os.stat(file_name) if file_stat.st_size == expected_bytes: print('Successfully downloaded VGG-19 pre-trained model', file_name) else: raise Exception('File ' + file_name + ' might be corrupted.You should try downloading it with a browser.') class VGG(object): def __init__(self, input_img): #下载文件 utils.download(VGG_DOWNLOAD_LINK, VGG_FILENAME, EXPECTED_BYTES) #加载文件 self.vgg_layers = scipy.io.loadmat(VGG_FILENAME)["layers"] self.input_img = input_img #VGG在处理图像时将图片进行mean-center,所以要计算RGB三个通道上的mean值 #为训练集每个通道求和的均值,统一减去,使得均值为0,模型收敛更快 self.mean_pixels=np.array([123.68,116.779,103.939]).reshape((1,1,1, 3)) def _weights(self, layer_idx, expected_layer_name): #参数特定存储位置 W = self.vgg_layers[0][layer_idx][0][0][2][0][0] b = self.vgg_layers[0][layer_idx][0][0][2][0][1] #当前层的名称 layer_name = self.vgg_layers[0][layer_idx][0][0][0][0] assert layer_name==expected_layer_name, print("Layer name error!") return W, b.reshape(b.size) def conv2d_relu(self, prev_layer, layer_idx, layer_name): with tf.variable_scope(layer_name): #获取当前权重(numpy格式) W, b = self._weights(layer_idx, layer_name) #将权重转化为tensor(由于不需要重新训练VGG的权重,初始化为常数) W = tf.constant(W, name="weights") b = tf.constant(b, name="bias") #卷积操作 conv2d = tf.nn.conv2d(input=prev_layer, filter=W, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding="SAME") #激活 out = tf.nn.relu(conv2d + b) setattr(self, layer_name, out) def avgpool(self, prev_layer, layer_name): with tf.variable_scope(layer_name): out = tf.nn.avg_pool(value=prev_layer, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding="SAME") setattr(self, layer_name, out) def load(self): self.conv2d_relu(self.input_img, 0, "conv1_1") self.conv2d_relu(self.conv1_1, 2, "conv1_2") self.avgpool(self.conv1_2, "avgpool1") self.conv2d_relu(self.avgpool1, 5, "conv2_1") self.conv2d_relu(self.conv2_1, 7, "conv2_2") self.avgpool(self.conv2_2, "avgpool2") self.conv2d_relu(self.avgpool2, 10, "conv3_1") self.conv2d_relu(self.conv3_1, 12, "conv3_2") self.conv2d_relu(self.conv3_2, 14, "conv3_3") self.conv2d_relu(self.conv3_3, 16, "conv3_4") self.avgpool(self.conv3_4, "avgpool3") self.conv2d_relu(self.avgpool3, 19, "conv4_1") self.conv2d_relu(self.conv4_1, 21, "conv4_2") self.conv2d_relu(self.conv4_2, 23, "conv4_3") self.conv2d_relu(self.conv4_3, 25, "conv4_4") self.avgpool(self.conv4_4, "avgpool4") self.conv2d_relu(self.avgpool4, 28, "conv5_1") self.conv2d_relu(self.conv5_1, 30, "conv5_2") self.conv2d_relu(self.conv5_2, 32, "conv5_3") self.conv2d_relu(self.conv5_3, 34, "conv5_4") self.avgpool(self.conv5_4, "avgpool5")2)优化损失函数 搭建好网络模型,需要定义损失函数,由内容损失、风格损失构成。内容损失采用 L2范数损失,风格损失用 Gram 矩阵计算各通道的相关性,以便更好的捕捉笔触、纹理等细节信息,利用 adam 梯度下降算法进行优化。 def create_input(self): #初始化图片tensor with tf.variable_scope("input"): self.input_img = tf.get_variable("in_img", shape=([1, self.img_height, self.img_width, 3]), dtype=tf.float32, initializer=tf.zeros_initializer()) def load_vgg(self): #加载VGG模型并对图片进行预处理 self.vgg = load_vgg.VGG(self.input_img) self.vgg.load() #mean-center self.content_img -= self.vgg.mean_pixels self.style_img -= self.vgg.mean_pixels def _content_loss(self, P, F): #计算内容损失 self.content_loss = tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(F - P))/(4.0 * P.size) def _gram_matrix(self, F, N, M): F = tf.reshape(F, (M, N)) return tf.matmul(tf.transpose(F), F) def _single_style_loss(self, a, g): N = a.shape[3] M = a.shape[1] * a.shape[2] #生成特征图的gram_matrix A = self._gram_matrix(a, N, M) G = self._gram_matrix(g, N, M) return tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(G - A)) / ((2 * N * M) ** 2) def _style_loss(self, A): #层数(用conv1_1, conv2_1, conv3_1, conv4_1, conv5_1) n_layers = len(A) #计算损失 E=[self.single_style_loss(A[i],getattr(self.vgg,self.style_layers[i])) for i in range(n_layers)] #加权求和 self.style_loss = sum(self.style_layer_w[i] * E[i] for i in range(n_layers)) def losses(self): #模型总体损失 with tf.variable_scope("losses"): #内容损失 with tf.Session() as sess: sess.run(self.input_img.assign(self.content_img)) gen_img_content = getattr(self.vgg, self.content_layer) content_img_content = sess.run(gen_img_content) self._content_loss(content_img_content, gen_img_content) #风格损失 with tf.Session() as sess: sess.run(self.input_img.assign(self.style_img)) style_layers = sess.run([getattr(self.vgg, layer) for layer in self.style_layers]) self._style_loss(style_layers) #加权求得最终的损失 self.total_loss = self.content_w * self.content_loss + self.style_w * self.style_loss def optimize(self): self.optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(self.lr).minimize(self.total_loss, global_step=self.gstep)3)迭代更新 训练过程中,每 10 个 epoch 生成一张图片。当 epoch > 20 时,每 20 个 epoch 生成一张图片,以免生成过多。 def train(self, epoches=20): skip_step = 1 with tf.Session() as sess: sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer()) sess.run(self.input_img.assign(self.initial_img)) initial_step = self.gstep.eval() for epoch in range(initial_step, epoches): #前面几轮每隔10个epoch生成一张图片 if 5 |
【本文地址】