| ASPP 详解 | 您所在的位置:网站首页 › 池化是什么 › ASPP 详解 |
ASPP 详解
文章目录
1. ASPP Conv2. ASPP Pooling3. ASPP4. 完整代码
ASPP(Atrous Spatial Pyramid Pooling),空洞空间卷积池化金字塔。简单理解就是个至尊版池化层,其目的与普通的池化层一致,尽可能地去提取特征。ASPP 的结构如下:
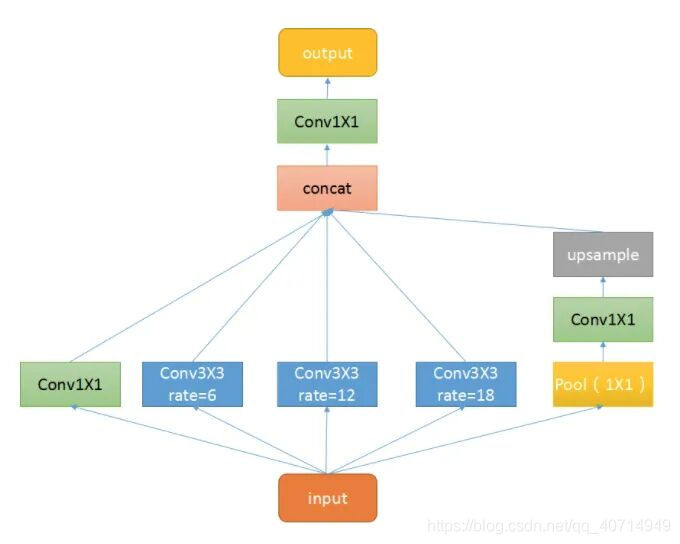
如图所示,ASPP 本质上由一个1×1的卷积(最左侧绿色) + 池化金字塔(中间三个蓝色) + ASPP Pooling(最右侧三层)组成。而池化金字塔各层的膨胀因子可自定义,从而实现自由的多尺度特征提取。 1. ASPP Conv class ASPPConv(nn.Sequential): def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, dilation): modules = [ nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, 3, padding=dilation, dilation=dilation, bias=False), nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels), nn.ReLU() ] super(ASPPConv, self).__init__(*modules)空洞卷积层与一般卷积间的差别在于膨胀率,膨胀率控制的是卷积时的 padding 以及 dilation。通过不同的填充以及与膨胀,可以获取不同尺度的感受野,提取多尺度的信息。注意卷积核尺寸始终保持 3×3 不变。 2. ASPP Pooling class ASPPPooling(nn.Sequential): def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels): super(ASPPPooling, self).__init__( nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1), nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, 1, bias=False), nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels), nn.ReLU()) def forward(self, x): size = x.shape[-2:] for mod in self: x = mod(x) return F.interpolate(x, size=size, mode='bilinear', align_corners=False)ASPP Polling 首先是一个 AdaptiveAvgPool2d 层。所谓自适应均值池化,其自适应的地方在于不需要指定 kernel size 和 stride,只需指定最后的输出尺寸(此处为 1×1)。通过将各通道的特征图分别压缩至 1×1,从而提取各通道的特征,进而获取全局的特征。然后是一个 1×1 的卷积层,对上一步获取的特征进行进一步的提取,并降维。需要注意的是,在 ASPP Polliing 的网络结构部分,只是对特征进行了提取;而在 forward 方法中,除了顺序执行网络的各层外,最终还将特征图从1×1 上采样回原来的尺寸。 3. ASPP class ASPP(nn.Module): def __init__(self, in_channels, atrous_rates, out_channels=256): super(ASPP, self).__init__() modules = [] # 注释 1 modules.append(nn.Sequential( nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, 1, bias=False), nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels), nn.ReLU())) # 注释 2 rates = tuple(atrous_rates) for rate in rates: modules.append(ASPPConv(in_channels, out_channels, rate)) # 注释 3 modules.append(ASPPPooling(in_channels, out_channels)) self.convs = nn.ModuleList(modules) # 注释 4 self.project = nn.Sequential( nn.Conv2d(len(self.convs) * out_channels, out_channels, 1, bias=False), nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels), nn.ReLU(), nn.Dropout(0.5)) # 注释 5 def forward(self, x): res = [] for conv in self.convs: res.append(conv(x)) res = torch.cat(res, dim=1) return self.project(res)注释: 最开始是一个 1×1 的卷积层,进行降维;构建 “池化金字塔”。对于给定的膨胀因子 atrous_rates,叠加相应的空洞卷积层,提取不同尺度下的特征;添加空洞池化层;出层,用于对ASPP各层叠加后的输出,进行卷积操作,得到最终结果;forward() 方法,其顺序执行ASPP的各层,将各层的输出按通道叠加,并通过输出层的 conv -> bn -> relu -> dropout 降维至给定通道数,获取最终结果。 4. 完整代码 # 空洞卷积 class ASPPConv(nn.Sequential): def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, dilation): modules = [ nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, 3, padding=dilation, dilation=dilation, bias=False), nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels), nn.ReLU() ] super(ASPPConv, self).__init__(*modules) # 池化 -> 1*1 卷积 -> 上采样 class ASPPPooling(nn.Sequential): def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels): super(ASPPPooling, self).__init__( nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1), # 自适应均值池化 nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, 1, bias=False), nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels), nn.ReLU()) def forward(self, x): size = x.shape[-2:] for mod in self: x = mod(x) # 上采样 return F.interpolate(x, size=size, mode='bilinear', align_corners=False) # 整个 ASPP 架构 class ASPP(nn.Module): def __init__(self, in_channels, atrous_rates, out_channels=256): super(ASPP, self).__init__() modules = [] # 1*1 卷积 modules.append(nn.Sequential( nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, 1, bias=False), nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels), nn.ReLU())) # 多尺度空洞卷积 rates = tuple(atrous_rates) for rate in rates: modules.append(ASPPConv(in_channels, out_channels, rate)) # 池化 modules.append(ASPPPooling(in_channels, out_channels)) self.convs = nn.ModuleList(modules) # 拼接后的卷积 self.project = nn.Sequential( nn.Conv2d(len(self.convs) * out_channels, out_channels, 1, bias=False), nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels), nn.ReLU(), nn.Dropout(0.5)) def forward(self, x): res = [] for conv in self.convs: res.append(conv(x)) res = torch.cat(res, dim=1) return self.project(res)【转载自】Pytorch-torchvision源码解读:ASPP |
【本文地址】
公司简介
联系我们