|
第一种 是在class内部,方法之间的互相调用
举一个简单的例子
class cat():
def __init__(self,age):
cat.age = age
def show_color(self):
print("The color of the cat is white")
def show_age(self):
self.show_color()
print("The age of the cat is "+str(self.age))
Ragdoll = cat(2)
Ragdoll.show_age()
结果为  这里我只用实例Ragdoll调用了show_age方法,但因为在show_age中调用了show_color方法,所以两个方法最后都执行了 这里我只用实例Ragdoll调用了show_age方法,但因为在show_age中调用了show_color方法,所以两个方法最后都执行了
类里面的方法想调用另外一个方法,需要在方法体中用self.方法名的方式来调用
同样,类里面的方法想调用类的属性,需要用self.属性名的方式
第二种 是在类的外面,def函数之间的彼此调用
还是来看一个简单的例子
def show_num(num):
print(num)
def test(num):
if num>3:
show_num(num)
test(4)
结果为  在类外面的函数之间,只需要函数名就可以调用彼此 在类外面的函数之间,只需要函数名就可以调用彼此
另外要记得参数列表保持一致,如果你要调用的函数参数列表中有多个参数,那么自身这个函数的参数列表中也要有那些参数
以下是错误示范
def create_cat(color,age):
print("The age and color of the cat are"+str(age)+color)
def show_cat():
create_cat(color,age)
show_cat()
结果是  正确的函数调用是这样 正确的函数调用是这样
def create_cat(color,age):
print("The age and color of the cat are "+str(age)+" and "+color)
def show_cat(color,age):
create_cat(color,age)
show_cat("white",3)
结果是 
第三种 是在类外面的函数,调用在类里面的方法
class cat():
def __init__(self,age):
self.age = age
def age_increase(self):
self.age += 1
print("the age of the cat is "+str(self.age))
def year():
Ragdoll = cat(3)
Ragdoll.age_increase()
year()
结果为 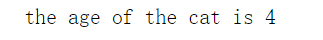 创建该类的实例对象,再通过实例调用方法,最后运行函数即可 创建该类的实例对象,再通过实例调用方法,最后运行函数即可
class cat():
def __init__(self,age):
self.age = age
self.color = "white"
def age_increase(self):
self.age += 1
print("the age of the cat is "+str(self.age))
def year():
Ragdoll = cat(3)
Ragdoll.age_increase()
print(Ragdoll.color)
year()
在函数中直接用实例调用属性,获取属性值也是可以的 结果为 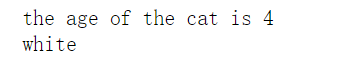
第四种 是不同的类之间的方法的彼此调用
class cat():
def __init__(self,age1):
self.age1 = age1
def show_age(self):
print("the age of the cat is "+str(self.age1))
class dog():
def __init__(self,age2):
self.age2 = age2
def show_cat_age(self):
Ragdoll = cat(3)
Ragdoll.show_age()
Husky = dog(2)
Husky.show_cat_age()
结果为  而如果想在这个类里面调用其他类里面的属性值,则需要这样做 而如果想在这个类里面调用其他类里面的属性值,则需要这样做
class cat():
def __init__(self,age1):
self.age1 = age1
self.color = "white"
def show_age(self):
print("the age of the cat is "+str(self.age1))
class dog():
def __init__(self,age2,Ragdoll):
self.age2 = age2
self.Ragdoll = Ragdoll
def show_cat_age(self,Ragdoll):
Ragdoll = cat(3)
Ragdoll.show_age()
print(self.Ragdoll.color)
if self.Ragdoll.age1 > self.age2:
print("the cat is older than the dog")
def run():
Ragdoll = cat(3)
Husky = dog(2,Ragdoll)
Husky.show_cat_age(Ragdoll)
run()
结果为 
需要将对象作为参数放入类里面
|  这里我只用实例Ragdoll调用了show_age方法,但因为在show_age中调用了show_color方法,所以两个方法最后都执行了
这里我只用实例Ragdoll调用了show_age方法,但因为在show_age中调用了show_color方法,所以两个方法最后都执行了 在类外面的函数之间,只需要函数名就可以调用彼此
在类外面的函数之间,只需要函数名就可以调用彼此 正确的函数调用是这样
正确的函数调用是这样
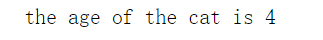 创建该类的实例对象,再通过实例调用方法,最后运行函数即可
创建该类的实例对象,再通过实例调用方法,最后运行函数即可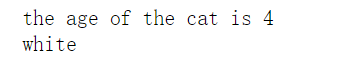
 而如果想在这个类里面调用其他类里面的属性值,则需要这样做
而如果想在这个类里面调用其他类里面的属性值,则需要这样做