| 如何使用Python在Pandas数据框架列上进行模糊匹配 | 您所在的位置:网站首页 › 如何模糊匹配两个excel数据表格 › 如何使用Python在Pandas数据框架列上进行模糊匹配 |
如何使用Python在Pandas数据框架列上进行模糊匹配
|
如何使用Python在Pandas数据框架列上进行模糊匹配
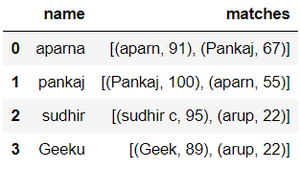
在本教程中,我们将学习如何使用Python对pandas DataFrame列进行模糊匹配。模糊匹配是一个过程,它可以让我们识别那些不准确但在我们的目标项目中找到一个给定模式的匹配。模糊匹配是搜索引擎的基础。这就是为什么我们在任何浏览器中输入搜索查询时,会得到许多推荐或建议。 用到的方法 pd.DataFrame(dict)。将 python 字典转换为 pandas 数据框架 dataframe[‘column_name’].tolist()。在Python中,将pandas数据框架的某一列转换成一个项目列表 append()。将项目追加到一个列表中 process.extract(query, choice, limit)。fuzzywuzzy库的处理模块中的一个函数,用于从选择列表中提取符合给定查询的项目。被提取的最接近的选择的数量由我们设定的限制来决定。 process.extractOne(query, choice, scorer)。从选择列表中提取与给定查询相匹配的唯一最接近的匹配,scorer是可选参数,使其使用特定的评分器,如fuzz.token_sort_ratio、fuzz.token_set_ratio。 fuzz.ratio:基于Levenshtein距离计算两个字符串之间的相似性比率 fuzz.partial_ratio:计算最小的字符串与长字符串的所有n个长度的子字符串之间的部分字符串比率 fuzz.token_sort_ratio:在对每个字符串中的标记进行排序后,计算出相似性比率 fuzz.token_set_ratio。它试图排除字符串中的差异,它在python中计算了三个特定的子字符串集的比率后返回最大的比率。 示例例子1:(基本方法) 首先,我们将创建两个字典。然后,我们将把它转换为pandas数据框架,并创建两个空的列表,以便以后存储匹配结果,如下图所示。 from fuzzywuzzy import fuzz from fuzzywuzzy import process import pandas dict1 = {'name': ["aparna", "pankaj", "sudhir", "Geeku"]} dict2 = {'name': ["aparn", "arup", "Pankaj", "sudhir c", "Geek", "abc"]} # converting to pandas dataframes dframe1 = pd.DataFrame(dict1) dframe2 = pd.DataFrame(dict2) # empty lists for storing the # matches later mat1 = [] mat2 = [] # printing the pandas dataframes dframe1.show() dframe2.show()dframe1:
dframe2:
输出:
输出:
输出:
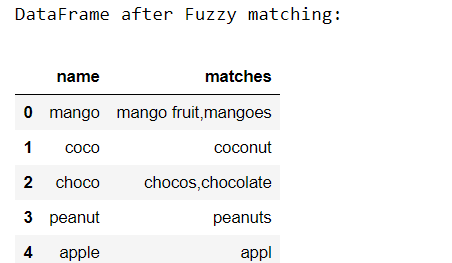
示例 2: 在这个例子中,步骤与例子一相同。唯一不同的是,一个特定的行项目有多个匹配项,比如 “芒果 “和 “巧克力”。我们设置阈值=82,以提高模糊匹配的准确性。 import pandas as pd from fuzzywuzzy import fuzz from fuzzywuzzy import process # creating the dictionaries dict1 = {'name': ["mango", "coco", "choco", "peanut", "apple"]} dict2 = {'name': ["mango fruit", "coconut", "chocolate", "mangoes", "chocos", "peanuts", "appl"]} # converting to pandas dataframes dframe1 = pd.DataFrame(dict1) dframe2 = pd.DataFrame(dict2) # empty lists for storing the matches later mat1 = [] mat2 = [] p = [] # printing the pandas dataframes print("First dataframe:\n", dframe1, "\nSecond dataframe:\n", dframe2) # converting dataframe column to list # of elements # to do fuzzy matching list1 = dframe1['name'].tolist() list2 = dframe2['name'].tolist() # taking the threshold as 82 threshold = 82 # iterating through list1 to extract # it's closest match from list2 for i in list1: mat1.append(process.extract(i, list2, limit=2)) dframe1['matches'] = mat1 # iterating through the closest matches # to filter out the maximum closest match for j in dframe1['matches']: for k in j: if k[1] >= threshold: p.append(k[0]) mat2.append(",".join(p)) p = [] # storing the resultant matches back to dframe1 dframe1['matches'] = mat2 print("\nDataFrame after Fuzzy matching:") dframe1输出:
现在我们将使用process.extractOne()方法,只匹配两个数据帧之间最接近的部分。在这个方法中,我们将应用不同的模糊匹配函数,如下所示。 例子3:使用fuzz.ratio()。 import pandas as pd from fuzzywuzzy import fuzz from fuzzywuzzy import process # creating the dictionaries dict1 = {'name': ["aparna", "pankaj", "sudhir", "Geeku", "geeks for geeks"]} dict2 = {'name': ["aparn", "arup", "Pankaj", "for geeks geeks", "sudhir c", "geeks geeks"]} # converting to pandas dataframes dframe1 = pd.DataFrame(dict1) dframe2 = pd.DataFrame(dict2) # empty lists for storing the matches # later mat1 = [] mat2 = [] p = [] # printing the pandas dataframes print("First dataframe:\n", dframe1, "\nSecond dataframe:\n", dframe2) # converting dataframe column to # list of elements # to do fuzzy matching list1 = dframe1['name'].tolist() list2 = dframe2['name'].tolist() # taking the threshold as 80 threshold = 80 # iterating through list1 to extract # it's closest match from list2 for i in list1: mat1.append(process.extractOne(i, list2, scorer=fuzz.ratio)) dframe1['matches'] = mat1 # iterating through the closest matches # to filter out the maximum closest match for j in dframe1['matches']: if j[1] >= threshold: p.append(j[0]) mat2.append(",".join(p)) p = [] # storing the resultant matches back to dframe1 dframe1['matches'] = mat2 print("\nDataFrame after Fuzzy matching using fuzz.ratio():") dframe1输出:
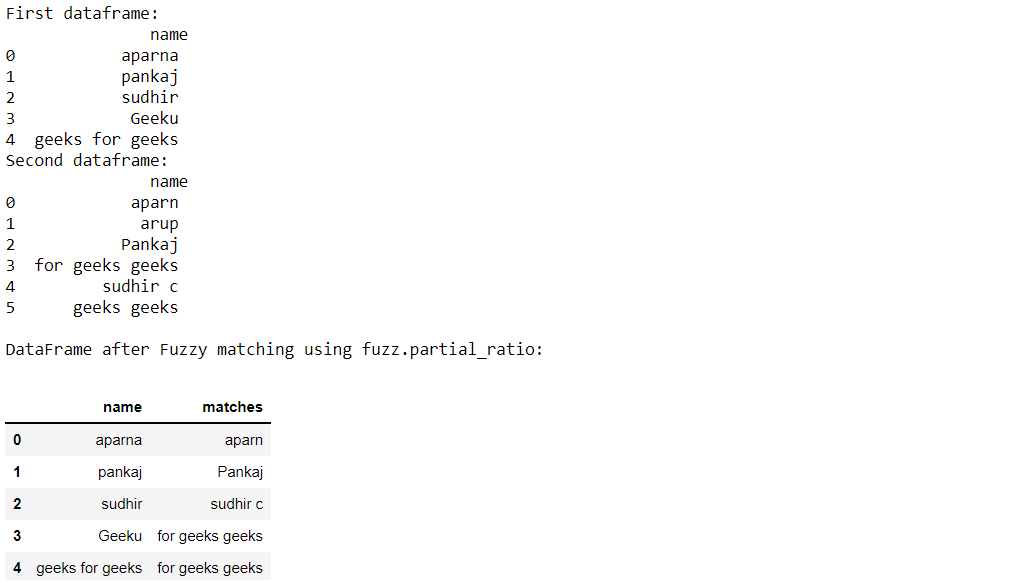
例子4:使用fuzz.partial_ratio()。 import pandas as pd from fuzzywuzzy import fuzz from fuzzywuzzy import process # creating the dictionaries dict1 = {'name': ["aparna", "pankaj", "sudhir", "Geeku", "geeks for geeks"]} dict2 = {'name': ["aparn", "arup", "Pankaj", "for geeks geeks", "sudhir c", "geeks geeks"]} # converting to pandas dataframes dframe1 = pd.DataFrame(dict1) dframe2 = pd.DataFrame(dict2) # empty lists for storing the matches # later mat1 = [] mat2 = [] p = [] # printing the pandas dataframes print("First dataframe:\n", dframe1, "\nSecond dataframe:\n", dframe2) # converting dataframe column to # list of elements # to do fuzzy matching list1 = dframe1['name'].tolist() list2 = dframe2['name'].tolist() # taking the threshold as 80 threshold = 80 # iterating through list1 to extract # it's closest match from list2 for i in list1: mat1.append(process.extractOne( i, list2, scorer=fuzz.partial_ratio)) dframe1['matches'] = mat1 # iterating through the closest matches # to filter out the maximum closest match for j in dframe1['matches']: if j[1] >= threshold: p.append(j[0]) mat2.append(",".join(p)) p = [] # storing the resultant matches back to dframe1 dframe1['matches'] = mat2 print("\nDataFrame after Fuzzy matching using fuzz.partial_ratio:") dframe1输出:
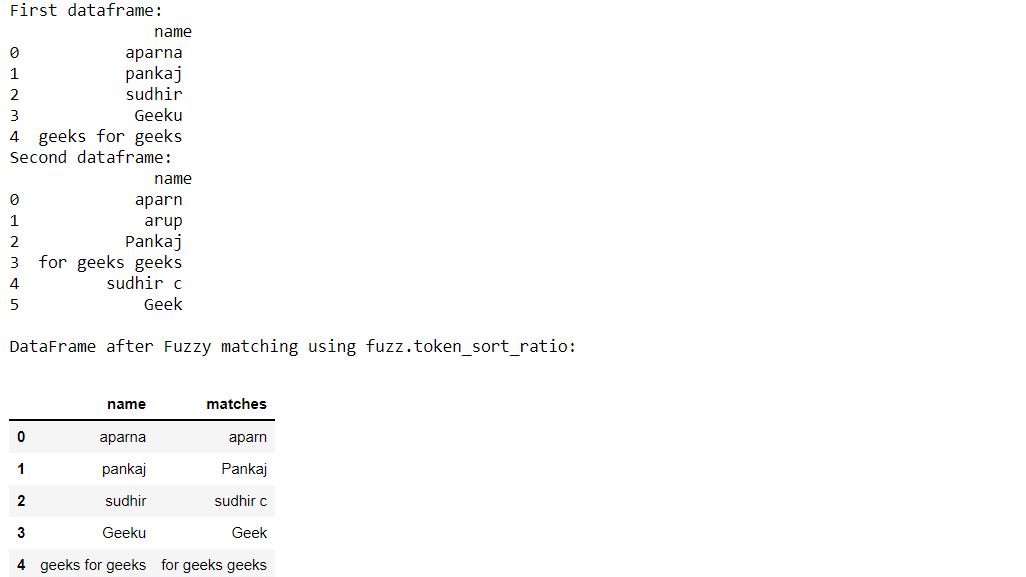
示例5:使用fuzz.token_sort_ratio()。 import pandas as pd from fuzzywuzzy import fuzz from fuzzywuzzy import process # creating the dictionaries dict1 = {'name': ["aparna", "pankaj", "sudhir", "Geeku", "geeks for geeks"]} dict2 = {'name': ["aparn", "arup", "Pankaj", "for geeks geeks", "sudhir c", "Geek"]} # converting to pandas dataframes dframe1 = pd.DataFrame(dict1) dframe2 = pd.DataFrame(dict2) # empty lists for storing the matches # later mat1 = [] mat2 = [] p = [] # printing the pandas dataframes print("First dataframe:\n", dframe1, "\nSecond dataframe:\n", dframe2) # converting dataframe column to # list of elements # to do fuzzy matching list1 = dframe1['name'].tolist() list2 = dframe2['name'].tolist() # taking the threshold as 80 threshold = 80 # iterating through list1 to extract # it's closest match from list2 for i in list1: mat1.append(process.extractOne( i, list2, scorer=fuzz.token_sort_ratio)) dframe1['matches'] = mat1 # iterating through the closest matches # to filter out the maximum closest match for j in dframe1['matches']: if j[1] >= threshold: p.append(j[0]) mat2.append(",".join(p)) p = [] # storing the resultant matches back # to dframe1 dframe1['matches'] = mat2 print("\nDataFrame after Fuzzy matching using fuzz.token_sort_ratio:") dframe1输出:
实例6:使用fuzz.token_set_ratio() import pandas as pd from fuzzywuzzy import fuzz from fuzzywuzzy import process # creating the dictionaries dict1 = {'name': ["aparna", "pankaj", "Geeku", "geeks for geeks"]} dict2 = {'name': ["aparn", "arup", "Pankaj", "geeks for for geeks", "geeks for geeks", "Geek"]} # converting to pandas dataframes dframe1 = pd.DataFrame(dict1) dframe2 = pd.DataFrame(dict2) # empty lists for storing the matches # later mat1 = [] mat2 = [] p = [] # printing the pandas dataframes print("First dataframe:\n", dframe1, "\nSecond dataframe:\n", dframe2) # converting dataframe column # to list of elements # to do fuzzy matching list1 = dframe1['name'].tolist() list2 = dframe2['name'].tolist() # taking the threshold as 80 threshold = 80 # iterating through list1 to extract # it's closest match from list2 for i in list1: mat1.append(process.extractOne( i, list2, scorer=fuzz.token_set_ratio)) dframe1['matches'] = mat1 # iterating through the closest matches # to filter out the maximum closest match for j in dframe1['matches']: if j[1] >= threshold: p.append(j[0]) mat2.append(",".join(p)) p = [] # storing the resultant matches back # to dframe1 dframe1['matches'] = mat2 print("\nDataFrame after Fuzzy matching using token_set_ratio():") dframe1输出:
|
【本文地址】
公司简介
联系我们