| MySQL数据库基础(多表关联查询、内外全连接、复合条件查询、子查询) | 您所在的位置:网站首页 › 多表多条件查询 › MySQL数据库基础(多表关联查询、内外全连接、复合条件查询、子查询) |
MySQL数据库基础(多表关联查询、内外全连接、复合条件查询、子查询)
|
文章目录
一、笛卡尔积查询二、内、外、全连接查询三、复合条件查询四、子查询五、EXIST判断
本篇文章主要介绍MySQL里的多表关联查询,其中包括了笛卡尔积查询、内连接查询、外连接查询、全连接查询,另外还会介绍复合条件查询和子查询。
一、笛卡尔积查询
1、首先创建表并插入数据 1)doctor表 --创建一个doctor表 create table doctor( doc_id int auto_increment primary key not null, doc_name varchar(50), age int, dept_id int ); --给doctor插入数据 insert into doctor(doc_name,age,dept_id) values ('A',19,200), ('B',26,201), ('C',30,201), ('D',24,202), ('E',20,200), ('F',38,204);2)department表 create table department( dept_id int, dept_name varchar(100) ); --给department插入数据 insert into department values (200,'Lin'), (201,'Cure'), (202,'Check'), (203,'Found');3)参考结果 2、笛卡尔积表 简单来说就是将两张表合在一起显示出来,该表成为笛卡尔积表(用处不大); 也就是说,如果A表里有m条记录,B表里有n条记录,那这样取出来的表将有m✖n条记录 SELECT * from doctor, department;
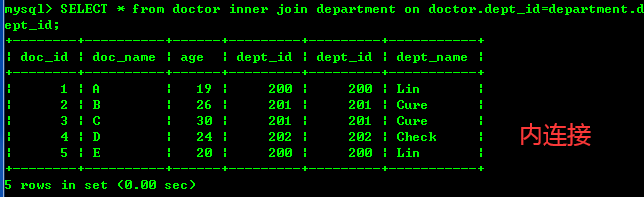
1、内外全连接查询关键字 内连接:inner join外连接:left join, right join全连接:full join2、内连接查询(inner join): 通过对笛卡尔积表筛选后得到的表 --筛选doctor里的dept_id与department里的dept_id相对应的部分 SELECT * from doctor, department where doctor.dept_id=department.dept_id; --如上例子,使用内连接查询 --格式为:(A inner join B on A.C=B.D) SELECT * from doctor inner join department on doctor.dept_id=department.dept_id;
4、全连接查询(full join): 但是在MySQL里不支持这种写法; 最主要的是,全连接基本用不上。不过可以用左右连接的拼接(UNION)来模拟全连接的效果 -- 模拟全连接 select * from doctor RIGHT JOIN department on doctor.dept_id = department.dept_id UNION select * from doctor LEFT JOIN department on doctor.dept_id = department.dept_id;
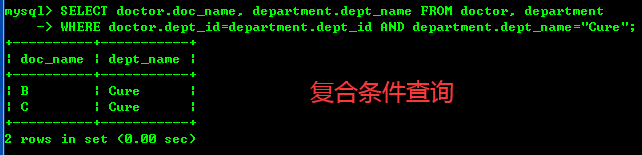
简单来说就是多条件复合成一条复杂的select查询语句 --查找所有Cure部(编号201)的doctor名字 SELECT doctor.doc_name, department.dept_name FROM doctor, department WHERE doctor.dept_id=department.dept_id AND department.dept_name="Cure"; --找出大于25的doctor的名字和所在的部门 SELECT doctor.doc_name,department.dept_name FROM doctor, department WHERE doctor.dept_id=department.dept_id AND doctor.age>25;
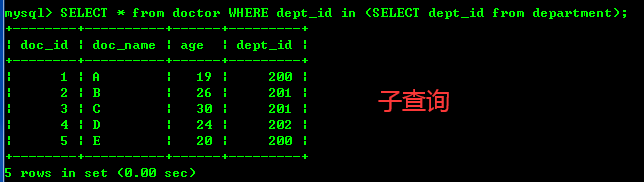
1、查询内容在A表,查询条件在B表 --查询doctor的dep_id在department的dep_id中出现过的doctor SELECT * from doctor WHERE dept_id in (201,202,203,204);但是以上把(201,202,203,204)给写死了,不灵活,因此可以再查询一遍得到department中所有的dep_id,也就是用到子查询 2、子查询 其实就是嵌套查询,查询里面嵌套查询(select里套着select) SELECT * from doctor WHERE dept_id in (SELECT dept_id from department);两种查询结果当然也是一样的:
|
【本文地址】
公司简介
联系我们


 3、外连接查询(left join, right join):
3、外连接查询(left join, right join):

 这里还有另外一些练习:
这里还有另外一些练习: