| 第五章 C语言:预处理 | 您所在的位置:网站首页 › 在一个c语言的源程序中 › 第五章 C语言:预处理 |
第五章 C语言:预处理
|
一、源文件到可执行程序的过程
预处理:去注释,宏替换,头文件展开,条件编译 编译:c语言 ---> 汇编语言(语法分析、词法分析、语义分析、符号汇总) 汇编:汇编语言 ---> 二进制指令,形成符号表 链接:合并段表,符号表的合并和重定位 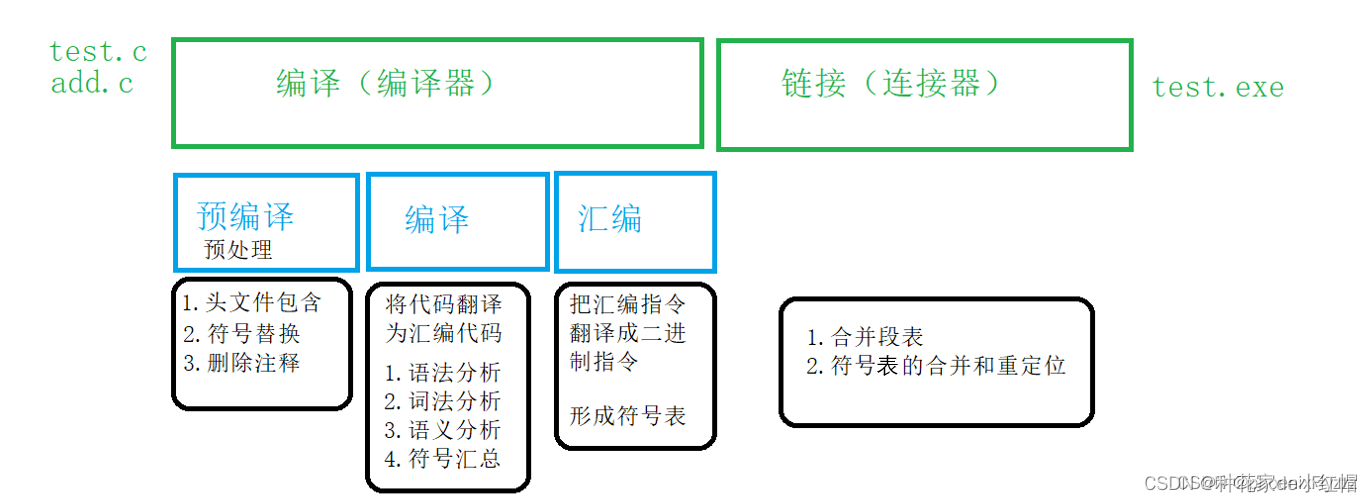 二、预处理详解
预定义符号
二、预处理详解
预定义符号
__FILE__ 进行编译的源文件 __LINE__ 文件当前的行号 __DATE__ 文件被编译的日期 __TIME__ 文件被编译的时间 __func__ 当前的函数名 void Test() { printf("name:%s file:%s line:%d date:%s time:%s\n", __func__, __FILE__, __LINE__, __DATE__, __TIME__); //name:Test file:test.c line:5 date:Mar 10 2023 time:16:27:41 } int main() { Test(); return 0; } #define符号替换 宏替换 #include #define PRINT(N, format) printf("the value of "#N" is "format"\n", N) int main() { int a = 10; float pai = 3.1415926; PRINT(a, "%d"); //the value of a is 10 PRINT(pai, "%.2f"); //the value of pai is 3.14 return 0; }##:将两端的符号合成一个符号 #include #define CAT(x, y) x##y int main() { int ABC = 10; printf("%d\n", CAT(A, BC)); //10 return 0; }宏的参数可以出现类型,函数不行 #define MALLOC(num, type) (type*)malloc(sizeof(type) * num)用宏定义将一个整数的二进制位的奇数位和偶数位交换 #define SwapIntBit(n) (((n) & 0x55555555) > 1)用一个宏定义计算一个结构体中某成员变量相对于首地址的偏移 #include #define offsetof(StructType, MemberName) (size_t)&(((StructType*)0)->MemberName) typedef struct Student { char name[20]; int age; float score; }Student; int main() { Student stu; int n = offsetof(Student, score); printf("%d\n", n); //24 return 0; } 条件编译 #include #define a 2 int main() { #if (a == 1) printf("hello world\n"); #elif (a == 2) printf("hello hdu\n"); #else printf("hello china\n"); #endif return 0; } #include #define MAX 0 int main() { #if defined(MAX) printf("haha\n"); #endif #ifdef MAX //判断该符号是否定义 printf("haha\n"); #endif #if !defined(max) printf("hehe\n"); #endif #ifndef max printf("hehe\n"); #endif return 0; }#pragma once 避免头文件的重复引用 |
【本文地址】
公司简介
联系我们