| 数据结构回顾:最基本的数据结构 | 您所在的位置:网站首页 › 四大基本存储结构 › 数据结构回顾:最基本的数据结构 |
数据结构回顾:最基本的数据结构
|
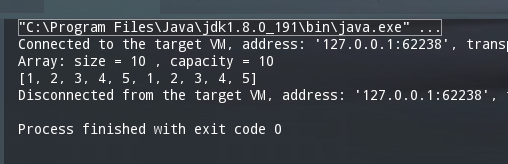
数组是数据结构中最基本,最基础的结构了,只要熟悉数据结构的属性,就可以利用数组构造出我们需要的数据结构。这里列出最常见的用法: package com.soecode.lyf.datastruct.array; /** 最基本的数据结构 数组 * @author 魏文思 * @date 2019/8/30$ 14:23$ */ public class Array { private E[] data; //假设初始长度 private int size; public Array(int capcity) { data = (E[]) new Object[capcity]; size = 0; } public Array() { } //获取数组的容量 public int getCapacity() { return data.length; } //获取数组中的元素个数 public int getSize() { return size; } // 返回数组是否为空 public boolean isEmpty() { return size == 0; } //向数组指定索引中添加新的元素 public void add(int index, E e) { if (size == data.length) { // throw new RuntimeException("容量超出限制"); //对数组进行扩容 resize(2 * data.length); } if (index < 0 || index > size) { throw new RuntimeException("参数输入错误"); } for (int i = size - 1; i >= index; i--) //将下标为index右面的数据整体进行右移,然后空出来一个我们需要的空间 data[i + 1] = data[i]; //将数据存储到指定位置 data[index] = e; size++; } // 从数组中删除index位置的元素, 返回删除的元素 public E remove(int index){ if(index < 0 || index >= size) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Remove failed. Index is illegal."); E ret = data[index]; for(int i = index + 1 ; i < size ; i ++) data[i - 1] = data[i]; size --; data[size] = null; //将最后一位数据置空,防止内存泄漏 if(size == data.length / 4 && data.length / 2 != 0) resize(data.length / 2); return ret; } // 从数组中删除第一个元素, 返回删除的元素 public E removeFirst(){ return remove(0); } // 从数组中删除最后一个元素, 返回删除的元素 public E removeLast(){ return remove(size - 1); } //在数组的后面追加一个元素 public void addLast(E e) { add(size, e); } //获取index索引位置的元素 public E get(int index) { if (index < 0 || index >= size) throw new RuntimeException("数组下标错误"); return data[index]; } //修改index数索引的元素 public void update(int index, E e) { if (index < 0 || index >= size) throw new RuntimeException(); data[index] = e; } // 查找数组中元素e所在的索引,如果不存在元素e,则返回-1 public int find(E e){ for(int i = 0 ; i < size ; i ++){ if(data[i] == e) return i; } return -1; } //获取数组最后一个数据 public E getLast(){ return get(size - 1); } //获取数组第一个数据 public E getFirst(){ return get(0); } // 查找数组中是否有元素e public boolean contains(E e){ for(int i = 0 ; i < size ; i ++){ if(data[i] == e) return true; } return false; } @Override public String toString() { StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder(); res.append(String.format("Array: size = %d , capacity = %d\n", size, data.length)); res.append('['); for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { res.append(data[i]); if (i != size - 1) res.append(", "); } res.append(']'); return res.toString(); } // 将数组空间的容量变成newCapacity大小 private void resize(int newCapacity){ E[] newData = (E[])new Object[newCapacity]; for(int i = 0 ; i < size ; i ++) newData[i] = data[i]; data = newData; } public static void main(String[] args) { Array array = new Array(5); array.addLast(1); array.addLast(2); array.addLast(3); array.addLast(4); array.addLast(5); array.addLast(1); array.addLast(2); array.addLast(3); array.addLast(4); array.addLast(5); System.out.println(array.toString()); } }结果:
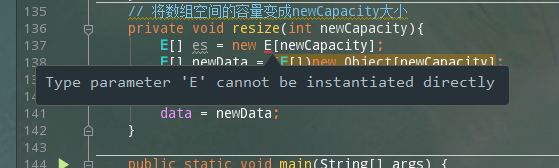
大部分注释都有,特别需要注意一下的是,当我们自己管理内存的时候这个时候就需要考虑内存泄漏的问题了,在前面的一篇文章中有写过内存泄漏相关的东西,感兴趣的可以看一下。 需要注意的问题 // 从数组中删除index位置的元素, 返回删除的元素 public E remove(int index){ if(index < 0 || index >= size) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Remove failed. Index is illegal."); E ret = data[index]; for(int i = index + 1 ; i < size ; i ++) data[i - 1] = data[i]; size --; data[size] = null; //将最后一位数据置空,防止内存泄漏 if(size == data.length / 4 && data.length / 2 != 0) resize(data.length / 2); return ret; }从数组中某个位置删除,就需要将需要删除元素的索引右面的位置的数据全部都左移一下,另外需要将腾出来的一个元素空间置空,消除对象的过期引用,防止内存泄漏。 看一下他的扩容方法: // 将数组空间的容量变成newCapacity大小 private void resize(int newCapacity){ E[] newData = (E[])new Object[newCapacity]; for(int i = 0 ; i < size ; i ++) newData[i] = data[i]; data = newData; }这里使用到了泛型,一开始我使用的是下面的方式
这种错误的原因 1.泛型擦除 这个涉及到jdk的语法糖,java的泛型在编译器有效,在运行时期被删除,也就是说所有的泛型类型在编译后都会被删除 2.因为编译器该类型是否有默认的构造器器 使用Object+类型转换的方式类的方式解决这种问题。 |
【本文地址】
公司简介
联系我们