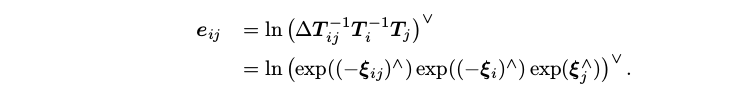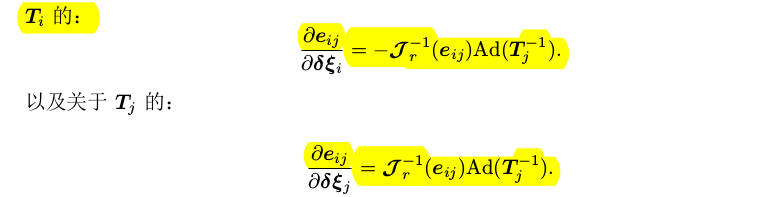| Ceres用法及Ceres | 您所在的位置:网站首页 › 以践行楷模精神为主题的作文800字 › Ceres用法及Ceres |
Ceres用法及Ceres
|
(一)Ceres-Solver的一般用法
简述:
Ceres Solver is an open source C++ library for modeling and solving large, complicated optimization problems. 使用 Ceres Solver 求解非线性优化问题,主要包括以下几部分: 构建代价函数(cost function)或残差(residual)构建优化问题(ceres::Problem):通过 AddResidualBlock 添加代价函数(cost function)、损失函数(loss function核函数) 和 待优化状态量配置求解器(ceres::Solver::Options)运行求解器(ceres::Solve(options, &problem, &summary))注意:与g2o优化中直接在边上添加information(信息矩阵)不同,Ceres无法直接实现此功能。由于Ceres只接受最小二乘优化就,即 (1)AutoDiffCostFunction(自动求导) 构造 代价函数结构体或代价函数类(例如:struct CostFunctor),在其结构体内对模板括号() 重载用来定义残差;在重载的 () 函数形参中,最后一个为残差,前面几个为待优化状态量,注意:形参类型必须是模板类型。 struct CostFunctor { template bool operator()(const T *const x, T *residual) const { residual[0] = 10.0 - x[0]; // r(x) = 10 - x return true; } };利用ceres::CostFunction *cost_function=new ceres::AutoDiffCostFunction(new costFunc),获得Cost Function 模板参数分别是:代价结构体仿函数类型名,残差维度,第一个优化变量维度,第二个....;函数参数(new costFunc)是代价结构体(或类)对象,即此对象重载的 () 函数的函数指针 (2)NumericDiffCostFunction(数值求导) 数值求导法 也是构造 代价函数结构体,也需要重载括号()来定义残差,但在重载括号() 时没有用模板; struct CostFunctorNum { bool operator()(const double *const x, double *residual) const { residual[0] = 10.0 - x[0]; // r(x) = 10 - x return true; } }; 并且在实例化代价函数时也稍微有点区别,多了一个模板参数 ceres::CENTRAL ceres::CostFunction *cost_function; cost_function =new ceres::NumericDiffCostFunction(new CostFunctorNum);(3)自定义CostFunction 构建一个 继承自 ceres::SizedCostFunction 的类,同样,对于模板参数的数字,第一个为残差的维度,后面几个为待优化状态量的维度 ;重载虚函数virtual bool Evaluate(double const* const* parameters, double *residuals, double **jacobians) const,根据 待优化变量,实现 残差和雅克比矩阵的计算(雅克比矩阵计算需要提供公式); class PoseGraphCFunc : public ceres::SizedCostFunction { public: EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW; PoseGraphCFunc(const Sophus::SE3 measure,const Matrix6d covariance):_measure(measure),_covariance(covariance){} ~PoseGraphCFunc(){} virtual bool Evaluate(double const* const* parameters, double *residuals, double **jacobians)const { Sophus::SE3 pose_i=Sophus::SE3::exp(Vector6d(parameters[0]));//Eigen::MtatrixXd可以通过double指针来构造 Sophus::SE3 pose_j=Sophus::SE3::exp(Vector6d(parameters[1])); Eigen::Map residual(residuals);//Eigen::Map(ptr)函数的作用是通过传入指针将c++数据映射为Eigen上的Matrix数据,有点与&相似 residual=(_measure.inverse()*pose_i.inverse()*pose_j).log(); Matrix6d sqrt_info=Eigen::LLT(_covariance).matrixLLT().transpose(); if(jacobians) { if(jacobians[0]) { Eigen::Map jacobian_i(jacobians[0]); Matrix6d Jr=JRInv(Sophus::SE3::exp(residual)); jacobian_i=(sqrt_info)*(-Jr)*pose_j.inverse().Adj(); } if(jacobians[1]) { Eigen::Map jacobian_j(jacobians[1]); Matrix6d J = JRInv(Sophus::SE3::exp(residual)); jacobian_j = sqrt_info * J * pose_j.inverse().Adj(); } } residual=sqrt_info*residual; return true; } private: const Sophus::SE3 _measure; const Matrix6d _covariance; }; 如果待优化变量处于流形上则需自定义 一个继承于LocalParameterization的类,重载其中的Plus()函数实现迭代递增,重载computeJacobian()定义流形到切平面的雅克比矩阵 class Parameterization:public ceres::LocalParameterization { public: Parameterization(){} virtual ~Parameterization(){} virtual bool Plus(const double* x, const double * delta, double *x_plus_delta)const { Vector6d lie(x); Vector6d lie_delta(delta); Sophus::SE3 T=Sophus::SE3::exp(lie); Sophus::SE3 T_delta=Sophus::SE3::exp(lie_delta); Eigen::Map x_plus(x_plus_delta); x_plus=(T_delta*T).log(); return true; } //流形到其切平面的雅克比矩阵 virtual bool ComputeJacobian(const double *x, double * jacobian) const { ceres::MatrixRef(jacobian,6,6)=ceres::Matrix::Identity(6,6);//ceres::MatrixRef()函数也类似于Eigen::Map,通过模板参数传入C++指针将c++数据映射为Ceres::Matrix return true; } //定义流形和切平面维度:在本问题中是李代数到李代数故都为6 virtual int GlobalSize()const{return 6;} virtual int LocalSize()const {return 6;} }; Step2:AddResidualBlock 声明 ceres::Problem problem;通过 AddResidualBlock 将 代价函数(cost function)、损失函数(loss function) 和 待优化状态量 添加到 problem ceres::LossFunction *loss = new ceres::HuberLoss(1.0); ceres::CostFunction *costfunc = new PoseGraphCFunc(measurement, covariance);//定义costfunction problem.AddResidualBlock(costfunc, loss, param[vertex_i].se3, param[vertex_j].se3);//为整体代价函数加入快,ceres的优点就是直接在param[vertex_i].se3上优化 problem.SetParameterization(param[vertex_i].se3, local_param);//为待优化的两个位姿变量定义迭代递增方式 problem.SetParameterization(param[vertex_j].se3, local_param); Step3:配置优化参数并优化Config&solve 定义ceres::Solver::Options options;对options成员进行赋值以配置优化参数;定义ceres::Solver::Summary summary;用来存储优化输出;求解:ceres::Solve(options, &problem, &summary); ceres::Solver::Options options;//配置优化设置 options.linear_solver_type = ceres::SPARSE_NORMAL_CHOLESKY; options.trust_region_strategy_type=ceres::LEVENBERG_MARQUARDT; options.max_linear_solver_iterations = 50; options.minimizer_progress_to_stdout = true; ceres::Solver::Summary summary;//summary用来存储优化过程 ceres::Solve(options, &problem, &summary);//开始优化 (二)Ceres-Sophus在位姿优图化的应用 残差及雅克比矩阵推导:(1)基于李代数的公式推导 残差(运动方程):
(2)基于四元数或其他空间转换表达形式的公式推导(暂省后补) 代码实现: #include #include #include #include #include #include #include using namespace std; using namespace Eigen; //using namespace ceres; typedef Matrix Matrix6d; typedef Matrix Vector6d; typedef struct { int id = 0; double param[7] = {0}; double se3[6] = {0};//(t,r) } param_type; Matrix6d JRInv(const Sophus::SE3 &e){ Matrix6d J; J.block(0,0,3,3) = Sophus::SO3::hat(e.so3().log()); J.block(0,3,3,3) = Sophus::SO3::hat(e.translation()); J.block(3,0,3,3) = Matrix3d::Zero(3,3); J.block(3,3,3,3) = Sophus::SO3::hat(e.so3().log()); J = 0.5 * J + Matrix6d::Identity(); return J; // return Matrix6d::Identity(); } class Parameterization:public ceres::LocalParameterization { public: Parameterization(){} virtual ~Parameterization(){} virtual bool Plus(const double* x, const double * delta, double *x_plus_delta)const { Vector6d lie(x); Vector6d lie_delta(delta); Sophus::SE3 T=Sophus::SE3::exp(lie); Sophus::SE3 T_delta=Sophus::SE3::exp(lie_delta); Eigen::Map x_plus(x_plus_delta); x_plus=(T_delta*T).log(); return true; } //流形到其切平面的雅克比矩阵 virtual bool ComputeJacobian(const double *x, double * jacobian) const { ceres::MatrixRef(jacobian,6,6)=ceres::Matrix::Identity(6,6);//ceres::MatrixRef()函数也类似于Eigen::Map,通过模板参数传入C++指针将c++数据映射为Ceres::Matrix return true; } //定义流形和切平面维度:在本问题中是李代数到李代数故都为6 virtual int GlobalSize()const{return 6;} virtual int LocalSize()const {return 6;} }; class PoseGraphCFunc : public ceres::SizedCostFunction { public: EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW; PoseGraphCFunc(const Sophus::SE3 measure,const Matrix6d covariance):_measure(measure),_covariance(covariance){} ~PoseGraphCFunc(){} virtual bool Evaluate(double const* const* parameters, double *residuals, double **jacobians)const { Sophus::SE3 pose_i=Sophus::SE3::exp(Vector6d(parameters[0]));//Eigen::MtatrixXd可以通过double指针来构造 Sophus::SE3 pose_j=Sophus::SE3::exp(Vector6d(parameters[1])); Eigen::Map residual(residuals);//Eigen::Map(ptr)函数的作用是通过传入指针将c++数据映射为Eigen上的Matrix数据,有点与&相似 residual=(_measure.inverse()*pose_i.inverse()*pose_j).log(); Matrix6d sqrt_info=Eigen::LLT(_covariance).matrixLLT().transpose(); if(jacobians) { if(jacobians[0]) { Eigen::Map jacobian_i(jacobians[0]); Matrix6d Jr=JRInv(Sophus::SE3::exp(residual)); jacobian_i=(sqrt_info)*(-Jr)*pose_j.inverse().Adj(); } if(jacobians[1]) { Eigen::Map jacobian_j(jacobians[1]); Matrix6d J = JRInv(Sophus::SE3::exp(residual)); jacobian_j = sqrt_info * J * pose_j.inverse().Adj(); } } residual=sqrt_info*residual; return true; } private: const Sophus::SE3 _measure; const Matrix6d _covariance; }; void Convert2se3(param_type &_p){ Quaterniond q(_p.param[6], _p.param[3], _p.param[4], _p.param[5]); Vector3d t(_p.param[0], _p.param[1], _p.param[2]); Vector6d se = Sophus::SE3(q.normalized(),t).log(); // auto tmp = Sophus::SE3(q,t).log(); // auto tmp1 = Sophus::SE3::exp(tmp); for(int i = 0; i < 6; i++){ _p.se3[i] = se(i, 0); } } int main(int argc, char **argv) { google::InitGoogleLogging(argv[0]); string fin_path = "./sphere.g2o"; ceres::Problem problem; vector param; ifstream fin; fin.open(fin_path); assert(fin.is_open()); ceres::LocalParameterization *local_param = new Parameterization(); while(!fin.eof()){ string name; fin >> name; if(name == "VERTEX_SE3:QUAT"){ param_type p; fin >> p.id; for(int i = 0; i < 7; i++) fin >> p.param[i]; Convert2se3(p); param.push_back(p); // problem.AddParameterBlock(param.back().se3, 6, local_param); } else if(name == "EDGE_SE3:QUAT"){ int vertex_i, vertex_j; fin >> vertex_i >> vertex_j; //输入观测值 double m[7];//temporary measurement result for(int i = 0; i < 7; i++) fin >> m[i]; Sophus::SE3 measurement(Quaternion(m[6], m[3], m[4], m[5]).normalized(), Vector3d(m[0], m[1], m[2])); //输入信息矩阵 Matrix6d covariance; for(int i = 0; i < 6 && fin.good(); i++){ for(int j = i; j < 6 && fin.good(); j++){ fin >> covariance(i,j); if(j != i) covariance(j,i) = covariance(i,j); } } ceres::LossFunction *loss = new ceres::HuberLoss(1.0); ceres::CostFunction *costfunc = new PoseGraphCFunc(measurement, covariance);//定义costfunction problem.AddResidualBlock(costfunc, loss, param[vertex_i].se3, param[vertex_j].se3);//为整体代价函数加入快,ceres的优点就是直接在param[vertex_i].se3上优化 problem.SetParameterization(param[vertex_i].se3, local_param);//为待优化的两个位姿变量定义迭代递增方式 problem.SetParameterization(param[vertex_j].se3, local_param); } } fin.close(); cout |
【本文地址】
公司简介
联系我们