| 学习笔记 | 您所在的位置:网站首页 › signature注解 › 学习笔记 |
学习笔记
|
1、设计的类图
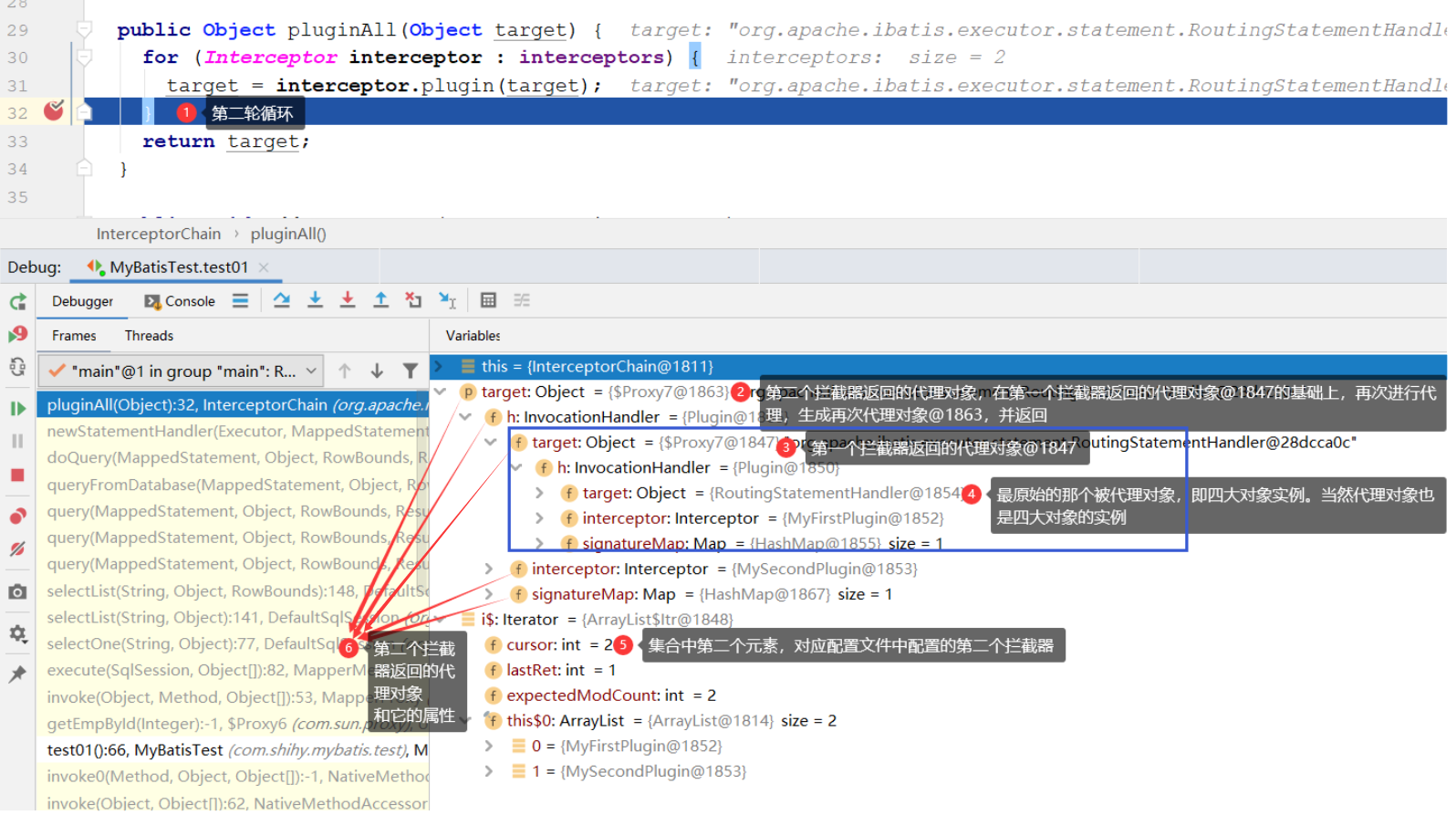
MyBatis 允许用户使用自定义拦截器(即:插件) 对 SQL 语句执行过程中的某一点进行拦截 。 默认情况 下, MyBatis允许拦截器拦截 Executor的方法 、 ParameterHandler 的方法 、 ResultSetHandler 的 方法以及 StatementHandler 的方法,这个四个对象可称为Mybatis的四大对象 。 具体可拦截的方法如下 : Executor 中 的 update()方法、 query()方法 、 flushStatements()方法 、 commit()方法 、 rollback()方法、getTransaction()方法 、 close()方法、 isClosed()方法 。 ParameterHandler 中的 getParameterObject()方法 、setParameters()方法 。 ResultS etHandler 中的 handleResultSets()方法 、 handleOu飞putParameters()方法 。 StatementHandler 中的 prepare()方法、 parameterize()方法 、 batch()方法、 update()方法 、 query()方法 。 2、Interceptor接口 MyBatis中使用的拦截器已经我们自定义的拦截器都需要实现 Interceptor 接口 。 Interceptor 接口是 MyBatis 插件模块的核心。源码:org.apache.ibatis.plugin.Interceptor代码如下: /** 子类实现该接口,重写以下方法 **/ public interface Interceptor { //执行拦截逻辑的方法 Object intercept(Invocation var1) throws Throwable; //决定是否触发intercept()方法。该方法会根据被拦截的对象来绝对是否要创建四大对象的代理对象 Object plugin(Object var1); //根据mybatis-config.xml配置文件中配置的property属性,初始Interceptor对象 void setProperties(Properties var1); } 复制代码自定义拦截器: 用户自定义的拦截器除了实现Interceptor 接口,还需要使用==@Intercepts== 和==@Signature== 两个 注解进行标识。@Intercepts 注解中指定了一个@Signature 注解列表,每个@Signature 注解中都 标识了该插件需要拦截的方法信息,其中@Signature 注解的type属性指定需要拦截的类型, method 属性指定需要拦截的方法 ,args 属性指定了被拦截方法的参数列表。通过这三个属性值, @Signature 注解就可 以表示一个方法签名, 唯一确定一个方法。 /** * 完成插件签名: * 告诉MyBatis当前插件用来拦截哪个对象的哪个方法 */ @Intercepts( { @Signature(type=StatementHandler.class,method="parameterize",args=java.sql.Statement.class) }) public class MyFirstPlugin implements Interceptor{ /** * intercept:拦截: * 拦截目标对象的目标方法的执行; */ @Override public Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable { // TODO Auto-generated method stub System.out.println("MyFirstPlugin...intercept:"+invocation.getMethod()); //动态的改变一下sql运行的参数:以前1号员工,实际从数据库查询11号员工 Object target = invocation.getTarget(); System.out.println("当前拦截到的对象:"+target); //拿到:StatementHandler==>ParameterHandler===>parameterObject //拿到target的元数据 MetaObject metaObject = SystemMetaObject.forObject(target); Object value = metaObject.getValue("parameterHandler.parameterObject"); System.out.println("sql语句用的参数是:"+value); //修改完sql语句要用的参数 metaObject.setValue("parameterHandler.parameterObject", 11); //执行目标方法 Object proceed = invocation.proceed(); //返回执行后的返回值 return proceed; } /** * plugin: * 包装目标对象:为目标对象(即:四大对象)创建一个代理对象。注:返回的不一定就是代理对象,在Plugin.wrap()方 *法中会进行判断是否进行包装。 */ @Override public Object plugin(Object target) { //我们可以借助Plugin的wrap方法来使用当前Interceptor包装我们目标对象 System.out.println("MyFirstPlugin...plugin:mybatis将要包装的对象"+target); Object wrap = Plugin.wrap(target, this); //返回为当前target创建的动态代理 return wrap; } /** * setProperties: * 将插件注册时的property属性设置进来 */ @Override public void setProperties(Properties properties) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub System.out.println("插件配置的信息:"+properties); } } 复制代码 自定义拦截器的配置 复制代码 拦截器的加载和初始化流程:在 MyBatis 初 始 化时, 会通过 XMLConfigBuilder.puginElement()方法解析 mybatis-config .xml 配置文件中 定义的<plugin>节点 , 得到相应的 Interceptor 对象以及配置的相应属性,之后会调用 Interceptor.setProperties(properties) 方法完成对 Interceptor 对象的初始化配 置 , 最后将 Interceptor 对象添加到Configuration. interceptorChain字段(该字段是个InterceptorChain对象的引用)中保存 。 前面说了拦截器可以拦截的四大对象的方法,那么拦截器如何以及在哪里对四大对象进行拦截呢?:在 MyBatis 中使用的这四类的对象 , 都是通过 Configuration .new*()系列方法创建的 ,在这些new*()系列方法中都会调用InterceptorChain .pluginAll(),在该方法以及后续方法中完成拦截,可以理解为在创建四大对象的时候拦截。 如果配置了用户自定义拦截器,则会在该系列方法中 , 通过 InterceptorChain .pluginAll()方法为目标对象创建代理对象 ,所以通过 Configuration . new *()系列方法得到的对象实际是一个代理对象。 如:Executor 对象在我们获取SqlSession对象的时候会被创建,然后被拦截。 //获取连接 SqlSession openSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); //org.apache.ibatis.session.defaults.DefaultSqlSessionFactory public SqlSession openSession() { return openSessionFromDataSource(configuration.getDefaultExecutorType(), null, false); } //org.apache.ibatis.session.defaults.DefaultSqlSessionFactory private SqlSession openSessionFromDataSource(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) { .......省略部分代码 //这里就会调用了newExecutor方法 final Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType); return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit); .......省略部分代码 } //org.apache.ibatis.session.Configuration public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType) { executorType = executorType == null ? defaultExecutorType : executorType; executorType = executorType == null ? ExecutorType.SIMPLE : executorType; Executor executor; if (ExecutorType.BATCH == executorType) { executor = new BatchExecutor(this, transaction); } else if (ExecutorType.REUSE == executorType) { executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction); } else { executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction); } if (cacheEnabled) { executor = new CachingExecutor(executor); } //调用pluginAll方法 executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor); return executor; } 复制代码如:StatementHandler 对象,在我们执行和数据库交互的方法的时候被创建,然后被拦截。 //利用动态mapper查询 EmployeeMapper mapper = openSession.getMapper(EmployeeMapper.class); Employee employee = mapper.getEmpById(1); //多步骤以后会调用到一下方法: public List doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException { .......省略部分代码 //这里就会调用了newStatementHandler方法 StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(wrapper, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql); stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog()); return handler.query(stmt, resultHandler); .......省略部分代码 } //org.apache.ibatis.session.Configuration public StatementHandler newStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) { StatementHandler statementHandler = new RoutingStatementHandler(executor, mappedStatement, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql); //调用pluginAll方法 statementHandler = (StatementHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(statementHandler); return statementHandler; } 复制代码记录了 mybatis-config.xml 文件中配置的拦截器 源码:org.apache.ibatis.plugin.InterceptorChain 大名鼎鼎的pluginAll方法 //org.apache.ibatis.plugin.InterceptorChain //InterceptorChain 中使用 interceptors 字段( ArrayListConfiguration #addInterceptor(Interceptor interceptor)--->InterceptorChain #addInterceptor(Interceptor interceptor) 。 XMLConfigBuilder的pluginElement(XNode parent)方法 //org.apache.ibatis.builder.xml.XMLConfigBuilder private void pluginElement(XNode parent) throws Exception { if (parent != null) { // 遍历 标签 for (XNode child : parent.getChildren()) { String interceptor = child.getStringAttribute("interceptor"); Properties properties = child.getChildrenAsProperties(); //创建 Interceptor 对象,并设置属性 Interceptor interceptorInstance = (Interceptor) resolveClass(interceptor).newInstance(); interceptorInstance.setProperties(properties); //添加到 configuration 中 configuration.addInterceptor(interceptorInstance); } } } 复制代码Configuration 的addInterceptor(Interceptor interceptor)方法 //org.apache.ibatis.session.Configuration public void addInterceptor(Interceptor interceptor) { interceptorChain.addInterceptor(interceptor); } 复制代码拦截器记录过程图解: SqlSessionFactoryBuilder #build(InputStream inputStream)----> SqlSessionFactoryBuilder #SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream, String environment, Properties properties)----> XMLConfigBuilder #parse()----> XMLConfigBuilder#parseConfiguration(XNode root)----> XMLConfigBuilder#pluginElement(XNode parent)----> Configuration #addInterceptor(Interceptor interceptor)----> InterceptorChain #addInterceptor(Interceptor interceptor) 源码:org.apache.ibatis.plugin.Plugin Plugin.wrap() 方法 //org.apache.ibatis.plugin.Plugin //注意:该方法返回的并不是一定就是target的代理对象,也可能返回原有的对象target本身 public static Object wrap(Object target, Interceptor interceptor) { //获取用户自定义 Interceptor中@Signature注解的信息,getSignatureMap()方法负责处理 //@Signature注解。获取该拦截器要拦截的类和对应的方法。key-->类全限定名,value-->一个包含Method对象的HashSet Map type = target.getClass(); //getAllInterfaces方法中堆type实现的接口和拦截器要拦截的类进行匹配,返回一个数组 Class[] interfaces = getAllInterfaces(type, signatureMap); //若数组的长度大于0,则表示target对象的类型,正是该拦截器要拦截的类型。 if (interfaces.length > 0) { //返回一个代理了target对象的代理对象 return Proxy.newProxyInstance( type.getClassLoader(), interfaces, //创建一个Plugin对象 new Plugin(target, interceptor, signatureMap)); } //返回原有的target对象本身 return target; } 复制代码,若有接口,则创建目标对象的 JDK Proxy 对象。 ,若无接口,则返回原始的目标对象。 signatureMap的具体值:由此即可见,@Signature 注解的 type 属性,必须是接口。 下面来看看Plugin对象的其他方法和属性。 Plugin 中各个字段 的含义如下: //org.apache.ibatis.plugin.Plugin // 目标对象 private Object target; //拦截器对象 private Interceptor interceptor; //获取该拦截器要拦截的类和对应的方法。key-->类全限定名,value-->一个包含Method对象的HashSet private Map type(); /** * @return 方法名 */ String method(); /** * @return 参数类型 */ Class[] args(); } 复制代码 8、流程总结 拦截器原理的流程图 1.x表示初始化拦截器对象,放入拦截器链对象InterceptorChain中 2.x表示拦截器在四大对象实例被创建时候进行拦截,并决定是否生成代理对象。以及后续调用代理对象的方法,决定该方法是否是该拦截器要拦截的方法(该代理对象有该拦截器的引用,方便后续调用intercept()方法)。
多个拦截器拦截同一个四大对象实例图解 |
【本文地址】