| 爱可可AI前沿推介(3.24) | 您所在的位置:网站首页 › senator记忆 › 爱可可AI前沿推介(3.24) |
爱可可AI前沿推介(3.24)
|
LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 1、[LG] Hardness of Independent Learning and Sparse Equilibrium Computation in Markov Games2、[LG] Reflexion: an autonomous agent with dynamic memory and self-reflection3、[CV] Affordance Diffusion: Synthesizing Hand-Object Interactions4、[LG] Sparks of Artificial General Intelligence: Early experiments with GPT-45、[CL] Large Language Models Can Be Used to Estimate the Ideologies of Politicians in a Zero-Shot Learning Setting[CV] Pix2Video: Video Editing using Image Diffusion[CV] Instruct-NeRF2NeRF: Editing 3D Scenes with Instructions[CV] Compositional 3D Scene Generation using Locally Conditioned Diffusion[CV] NUWA-XL: Diffusion over Diffusion for eXtremely Long Video Generation 摘要:Markov博弈自主学习与稀疏均衡计算之难、基于动态记忆和自我反思的自主智能体、手-物品交互合成、面向通用智能评估的GPT-4前期实验、大型语言模型可以用来零样本评估政治家的意识形态 、基于图像扩散的视频编辑、用指令编辑3D场景、基于局部条件扩散的合成3D场景生成、面向超长视频生成的扩散超扩散技术 1、[LG] Hardness of Independent Learning and Sparse Equilibrium Computation in Markov GamesD J. Foster, N Golowich, S M. Kakade[Microsoft & MIT & Harvard] Markov博弈自主学习与稀疏均衡计算之难 要点: 在Markov博弈中,独立学习是否存在无遗憾的算法是一个基本问题。在被广泛认为的PPAD难题不能在多项式时间内解决的情况下,没有多项式时间的算法可以在通观的Markov博弈中实现无遗憾。当博弈是未知的,无论计算效率如何,没有算法可以在观察次数为指数级别的情况下实现无遗憾。一句话总结:考虑了马尔可夫博弈中的分散式多智能体强化学习问题,证明了在一般的马尔可夫博弈中不存在独立无遗憾学习的算法,即使是玩家人数为常数、博弈内容也已知的情况。 We consider the problem of decentralized multi-agent reinforcement learning in Markov games. A fundamental question is whether there exist algorithms that, when adopted by all agents and run independently in a decentralized fashion, lead to no-regret for each player, analogous to celebrated convergence results in normal-form games. While recent work has shown that such algorithms exist for restricted settings (notably, when regret is defined with respect to deviations to Markovian policies), the question of whether independent no-regret learning can be achieved in the standard Markov game framework was open. We provide a decisive negative resolution this problem, both from a computational and statistical perspective. We show that: - Under the widely-believed assumption that PPAD-hard problems cannot be solved in polynomial time, there is no polynomial-time algorithm that attains no-regret in general-sum Markov games when executed independently by all players, even when the game is known to the algorithm designer and the number of players is a small constant. - When the game is unknown, no algorithm, regardless of computational efficiency, can achieve no-regret without observing a number of episodes that is exponential in the number of players. Perhaps surprisingly, our lower bounds hold even for seemingly easier setting in which all agents are controlled by a a centralized algorithm. They are proven via lower bounds for a simpler problem we refer to as SparseCCE, in which the goal is to compute a coarse correlated equilibrium that is sparse in the sense that it can be represented as a mixture of a small number of product policies. The crux of our approach is a novel application of aggregation techniques from online learning, whereby we show that any algorithm for the SparseCCE problem can be used to compute approximate Nash equilibria for non-zero sum normal-form games.https://arxiv.org/abs/2303.12287  2、[LG] Reflexion: an autonomous agent with dynamic memory and self-reflection 2、[LG] Reflexion: an autonomous agent with dynamic memory and self-reflectionN Shinn, B Labash, A Gopinath[Northeastern University & MIT] Reflexion: 基于动态记忆和自我反思的自主智能体 要点: 提出一种基于动态记忆和自我反思能力的自主决策智能体方法;提出一种简单而有效的启发式算法,使智能体能确定幻觉实例,避免行动序列中的重复,并在某些环境中构建给定环境的内部记忆图;通过 AlfWorld 和 HotPotQA 环境中的决策任务进行评估,观察到分别达到了 97% 和 51% 的成功率;Reflexion 是一种高度适用于提高决策和知识密集任务的表现的方法,因为它仅依赖于二元奖励模型。一句话总结:提出 Reflexion,一种基于动态记忆和自我反思能力的自主决策智能体,以提高其现有的推理轨迹和任务特定行动选择能力。 Recent advancements in decision-making large language model (LLM) agents have demonstrated impressive performance across various benchmarks. However, these state-of-the-art approaches typically necessitate internal model fine-tuning, external model fine-tuning, or policy optimization over a defined state space. Implementing these methods can prove challenging due to the scarcity of high-quality training data or the lack of well-defined state space. Moreover, these agents do not possess certain qualities inherent to human decision-making processes, specifically the ability to learn from mistakes. Self-reflection allows humans to efficiently solve novel problems through a process of trial and error. Building on recent research, we propose Reflexion, an approach that endows an agent with dynamic memory and self-reflection capabilities to enhance its existing reasoning trace and task-specific action choice abilities. To achieve full automation, we introduce a straightforward yet effective heuristic that enables the agent to pinpoint hallucination instances, avoid repetition in action sequences, and, in some environments, construct an internal memory map of the given environment. To assess our approach, we evaluate the agent's ability to complete decision-making tasks in AlfWorld environments and knowledge-intensive, search-based question-and-answer tasks in HotPotQA environments. We observe success rates of 97% and 51%, respectively, and provide a discussion on the emergent property of self-reflection.https://arxiv.org/abs/2303.11366     3、[CV] Affordance Diffusion: Synthesizing Hand-Object Interactions 3、[CV] Affordance Diffusion: Synthesizing Hand-Object InteractionsY Ye, X Li, A Gupta, S D Mello, S Birchfield, J Song, S Tulsiani, S Liu[NVIDIA & CMU] Affordance Diffusion: 手-物品交互合成 要点: 提出一种两步生成方法,用于合成人手与物体的交互图像,可以从中提取出可用性信息。采用修复技术来监督模型,提出一种新的数据增强方法,以减轻对工件的过拟合。展示了所提出方法生成了真实的HOI图像以及合理的3D姿态,并在分布不均的场景中表现出惊人的普遍性。一句话总结:提出了从物品图像合成人手与物品交互图像的方法。 Recent successes in image synthesis are powered by large-scale diffusion models. However, most methods are currently limited to either text- or image-conditioned generation for synthesizing an entire image, texture transfer or inserting objects into a user-specified region. In contrast, in this work we focus on synthesizing complex interactions (ie, an articulated hand) with a given object. Given an RGB image of an object, we aim to hallucinate plausible images of a human hand interacting with it. We propose a two-step generative approach: a LayoutNet that samples an articulation-agnostic hand-object-interaction layout, and a ContentNet that synthesizes images of a hand grasping the object given the predicted layout. Both are built on top of a large-scale pretrained diffusion model to make use of its latent representation. Compared to baselines, the proposed method is shown to generalize better to novel objects and perform surprisingly well on out-of-distribution in-the-wild scenes of portable-sized objects. The resulting system allows us to predict descriptive affordance information, such as hand articulation and approaching orientation.https://arxiv.org/abs/2303.12538   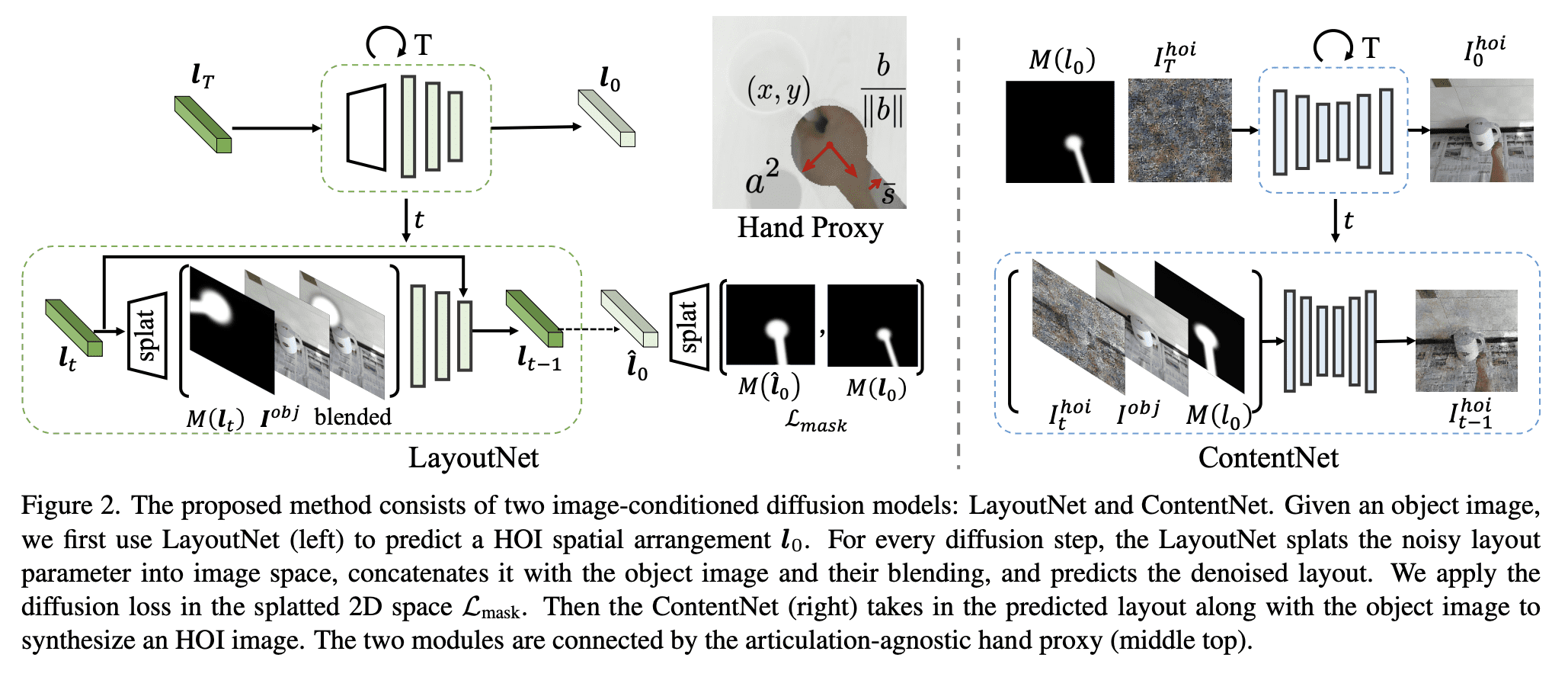  4、[LG] Sparks of Artificial General Intelligence: Early experiments with GPT-4 4、[LG] Sparks of Artificial General Intelligence: Early experiments with GPT-4S Bubeck, V Chandrasekaran, R Eldan, J Gehrke, E Horvitz, E Kamar...[Microsoft Research] 通用人工智能的火花: GPT-4的前期实验 要点: 报告了对OpenAI开发的GPT-4的早期版本的调研结果。GPT-4是展现更通用智能的大型语言模型(LLM)的一部分,其能力和影响正在不断上升。GPT-4可以解决数学、编程、视觉、医学、法律、心理学等多种难题,而且往往接近人类水平,甚至超过ChatGPT等之前的模型。我们相信GPT-4是一个早期(仍然不完整)的通用人工智能系统,所得到的研究结果激发了对GPT-4和类似系统的进一步研究。一句话总结:人工智能研究者正在开发和完善具有多种领域和任务能力的大型语言模型,挑战了我们对学习和认知的理解。 Artificial intelligence (AI) researchers have been developing and refining large language models (LLMs) that exhibit remarkable capabilities across a variety of domains and tasks, challenging our understanding of learning and cognition. The latest model developed by OpenAI, GPT-4, was trained using an unprecedented scale of compute and data. In this paper, we report on our investigation of an early version of GPT-4, when it was still in active development by OpenAI. We contend that (this early version of) GPT-4 is part of a new cohort of LLMs (along with ChatGPT and Google's PaLM for example) that exhibit more general intelligence than previous AI models. We discuss the rising capabilities and implications of these models. We demonstrate that, beyond its mastery of language, GPT-4 can solve novel and difficult tasks that span mathematics, coding, vision, medicine, law, psychology and more, without needing any special prompting. Moreover, in all of these tasks, GPT-4's performance is strikingly close to human-level performance, and often vastly surpasses prior models such as ChatGPT. Given the breadth and depth of GPT-4's capabilities, we believe that it could reasonably be viewed as an early (yet still incomplete) version of an artificial general intelligence (AGI) system. In our exploration of GPT-4, we put special emphasis on discovering its limitations, and we discuss the challenges ahead for advancing towards deeper and more comprehensive versions of AGI, including the possible need for pursuing a new paradigm that moves beyond next-word prediction. We conclude with reflections on societal influences of the recent technological leap and future research directions.https://arxiv.org/abs/2303.12712     5、[CL] Large Language Models Can Be Used to Estimate the Ideologies of Politicians in a Zero-Shot Learning Setting 5、[CL] Large Language Models Can Be Used to Estimate the Ideologies of Politicians in a Zero-Shot Learning SettingP Y. Wu, J A. Tucker, J Nagler, S Messing[New York University] 大型语言模型可以用来零样本评估政治家的意识形态 要点: 通过比较大语言模型,证明了大型语言模型(LLM)可以用于零样本估算政治家的意识形态。LLM在反复迭代中产生了稳定的答案,没有产生幻觉,也不是简单地从单一来源转述信息。ChatGPT 得出的意识形态评分与其他意识形态评分相关性很高,但也有重要的不同之处。研究表明,生成式大型语言模型可以用于社会科学的评分问题。一句话总结:通过比较大语言模型,本研究证明了大型语言模型可以用于零样本估算政治家的意识形态。 The mass aggregation of knowledge embedded in large language models (LLMs) holds the promise of new solutions to problems of observability and measurement in the social sciences. We examine the utility of one such model for a particularly difficult measurement task: measuring the latent ideology of lawmakers, which allows us to better understand functions that are core to democracy, such as how politics shape policy and how political actors represent their constituents. We scale the senators of the 116th United States Congress along the liberal-conservative spectrum by prompting ChatGPT to select the more liberal (or conservative) senator in pairwise comparisons. We show that the LLM produced stable answers across repeated iterations, did not hallucinate, and was not simply regurgitating information from a single source. This new scale strongly correlates with pre-existing liberal-conservative scales such as NOMINATE, but also differs in several important ways, such as correctly placing senators who vote against their party for far-left or far-right ideological reasons on the extreme ends. The scale also highly correlates with ideological measures based on campaign giving and political activists' perceptions of these senators. In addition to the potential for better-automated data collection and information retrieval, our results suggest LLMs are likely to open new avenues for measuring latent constructs like ideology that rely on aggregating large quantities of data from public sources.https://arxiv.org/abs/2303.12057     另外几篇值得关注的论文: [CV] Pix2Video: Video Editing using Image DiffusionD Ceylan, C P Huang, N J. Mitra[Adobe Research] Pix2Video: 基于图像扩散的视频编辑 要点: Pix2Video使用预训练的图像生成模型编辑视频片段。该方法不需要预处理,推理阶段也不需要额外的开销。Pix2Video 与基线相当或优于基线,但也存在一些局限性。Pix2Video的方法为使用图像生成模型的可控图像编辑带来了令人兴奋的进展,而不需要任何成本。一句话总结:Pix2Video是一种利用预训练和固定文本到图像生成模型编辑视频片段的方法。 Image diffusion models, trained on massive image collections, have emerged as the most versatile image generator model in terms of quality and diversity. They support inverting real images and conditional (e.g., text) generation, making them attractive for high-quality image editing applications. We investigate how to use such pre-trained image models for text-guided video editing. The critical challenge is to achieve the target edits while still preserving the content of the source video. Our method works in two simple steps: first, we use a pre-trained structure-guided (e.g., depth) image diffusion model to perform text-guided edits on an anchor frame; then, in the key step, we progressively propagate the changes to the future frames via self-attention feature injection to adapt the core denoising step of the diffusion model. We then consolidate the changes by adjusting the latent code for the frame before continuing the process. Our approach is training-free and generalizes to a wide range of edits. We demonstrate the effectiveness of the approach by extensive experimentation and compare it against four different prior and parallel efforts (on ArXiv). We demonstrate that realistic text-guided video edits are possible, without any compute-intensive preprocessing or video-specific finetuning.https://arxiv.org/abs/2303.12688     [CV] Instruct-NeRF2NeRF: Editing 3D Scenes with Instructions [CV] Instruct-NeRF2NeRF: Editing 3D Scenes with InstructionsA Haque, M Tancik, A A. Efros, A Holynski, A Kanazawa[UC Berkeley] Instruct-NeRF2NeRF: 用指令编辑3D场景 要点: 提出一种用文本指令编辑NeRF场景的方法。使用图像辅助扩散模型(InstructPix2Pix)进行迭代编辑,以维持3D一致性。能编辑大规模的真实世界场景,并实现更逼真、更有针对性的编辑。所提方法为日常用户提供了一种简单直观的3D场景编辑方法。一句话总结:提出了一种用文本指令编辑NeRF场景的方法。 We propose a method for editing NeRF scenes with text-instructions. Given a NeRF of a scene and the collection of images used to reconstruct it, our method uses an image-conditioned diffusion model (InstructPix2Pix) to iteratively edit the input images while optimizing the underlying scene, resulting in an optimized 3D scene that respects the edit instruction. We demonstrate that our proposed method is able to edit large-scale, real-world scenes, and is able to accomplish more realistic, targeted edits than prior work.https://arxiv.org/abs/2303.12789     [CV] Compositional 3D Scene Generation using Locally Conditioned Diffusion [CV] Compositional 3D Scene Generation using Locally Conditioned DiffusionR Po, G Wetzstein[Stanford University] 基于局部条件扩散的合成3D场景生成 要点: 引入了局部条件扩散,提供了对现有2D扩散模型的更好的组合控制。介绍了通过将局部条件扩散应用于分数蒸馏采样的3D生成管线的组合3D合成方法。介绍了关键摄像机姿态采样策略,对复合3D生成至关重要。一句话总结:提出基于局部条件扩散的复合3D场景生成方法。 Designing complex 3D scenes has been a tedious, manual process requiring domain expertise. Emerging text-to-3D generative models show great promise for making this task more intuitive, but existing approaches are limited to object-level generation. We introduce extbf{locally conditioned diffusion} as an approach to compositional scene diffusion, providing control over semantic parts using text prompts and bounding boxes while ensuring seamless transitions between these parts. We demonstrate a score distillation sampling--based text-to-3D synthesis pipeline that enables compositional 3D scene generation at a higher fidelity than relevant baselines.https://arxiv.org/abs/2303.12218  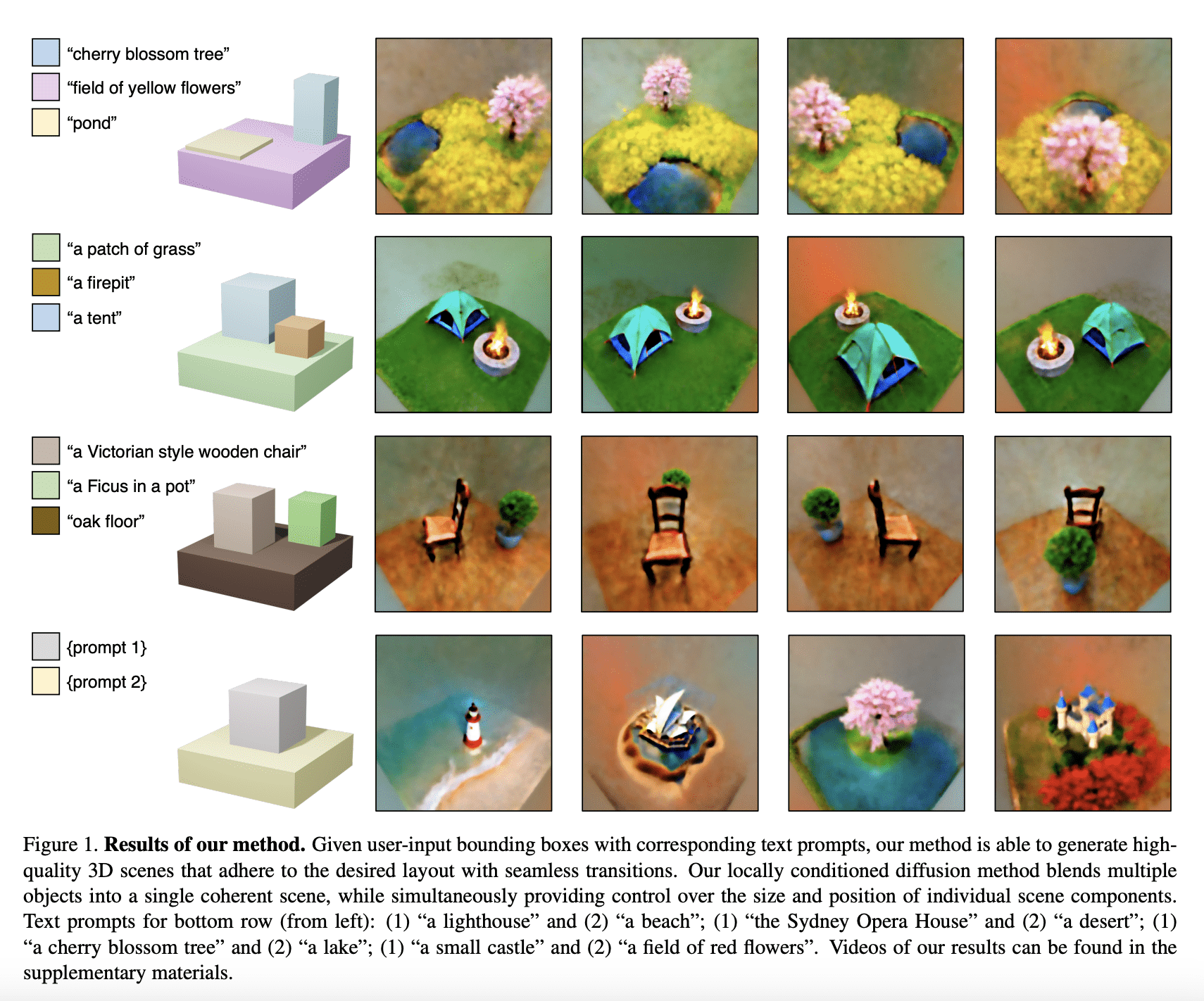   [CV] NUWA-XL: Diffusion over Diffusion for eXtremely Long Video Generation [CV] NUWA-XL: Diffusion over Diffusion for eXtremely Long Video GenerationS Yin, C Wu, H Yang, J Wang, X Wang, M Ni, Z Yang...[Microsoft Research Asia & University of Science and Technology of China] NUWA-XL: 面向超长视频生成的扩散超扩散技术 要点: 提出NUWA-XL,采用“Diffusion over Diffusion”架构。NUWA-XL 是第一个直接在长视频(3376帧)上进行训练的模型,解决了长视频生成的训练-推理差距问题。NUWA-XL 支持并行推理,在生成1024帧视频时,推理速度提高了94.26%。建立了FlintstonesHD数据集,以证明NUWA-XL的有效性,并为长视频生成提供了一个基准。一句话总结:NUWA-XL是一种新的视频生成方法,采用“Diffusion over Diffusion”架构,以“从粗到细”的过程并行生成高度一致的长视频,能直接在长视频(3376帧)上进行训练,从而消除训练-推理差距。 In this paper, we propose NUWA-XL, a novel Diffusion over Diffusion architecture for eXtremely Long video generation. Most current work generates long videos segment by segment sequentially, which normally leads to the gap between training on short videos and inferring long videos, and the sequential generation is inefficient. Instead, our approach adopts a ``coarse-to-fine'' process, in which the video can be generated in parallel at the same granularity. A global diffusion model is applied to generate the keyframes across the entire time range, and then local diffusion models recursively fill in the content between nearby frames. This simple yet effective strategy allows us to directly train on long videos (3376 frames) to reduce the training-inference gap, and makes it possible to generate all segments in parallel. To evaluate our model, we build FlintstonesHD dataset, a new benchmark for long video generation. Experiments show that our model not only generates high-quality long videos with both global and local coherence, but also decreases the average inference time from 7.55min to 26s (by 94.26%) at the same hardware setting when generating 1024 frames.https://arxiv.org/abs/2303.12346    
|
【本文地址】
| 今日新闻 |
| 推荐新闻 |
| 专题文章 |