| python cv2 绘制不规则形状的最小外接矩形、最大内接矩形、最大内接圆、最小外接圆、拟合椭圆 | 您所在的位置:网站首页 › python生成图形 › python cv2 绘制不规则形状的最小外接矩形、最大内接矩形、最大内接圆、最小外接圆、拟合椭圆 |
python cv2 绘制不规则形状的最小外接矩形、最大内接矩形、最大内接圆、最小外接圆、拟合椭圆
|
目录 一、最小外接矩形 二、最大内接矩形 三、最大内接圆 四、最小外接圆 五、拟合椭圆 一、最小外接矩形这里的图片是mask,类似于这样的:
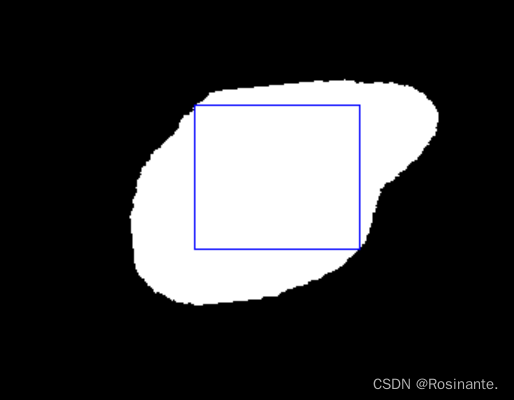
绘制如上图片的最小外接矩阵: def draw_min_rect_rectangle(mask_path): image = cv2.imread(mask_path) thresh = cv2.Canny(image, 128, 256) contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(thresh, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE) img = np.copy(image) for cnt in contours: x, y, w, h = cv2.boundingRect(cnt) # 绘制矩形 cv2.rectangle(img, (x, y+h), (x+w, y), (0, 255, 255))绘制结果:
也可以将矩形区域作成新的mask: # 将最小内接矩形填充为白色 white = [255, 255, 255] for col in range(x, x+w): for row in range(y, y+h): image[row, col] = white那么我们的最小内接矩阵mask就绘制好了:
也可以通过x,y,w,h对图片进行切割: pic = cv2.imread(original_img_path) # 读取mask对应的图片 cut = pic[y:y+h, x:x+w] # 根据内接矩形的顶点切割图片 cv2.imwrite(save_path, cut) # 保存切割好的图片
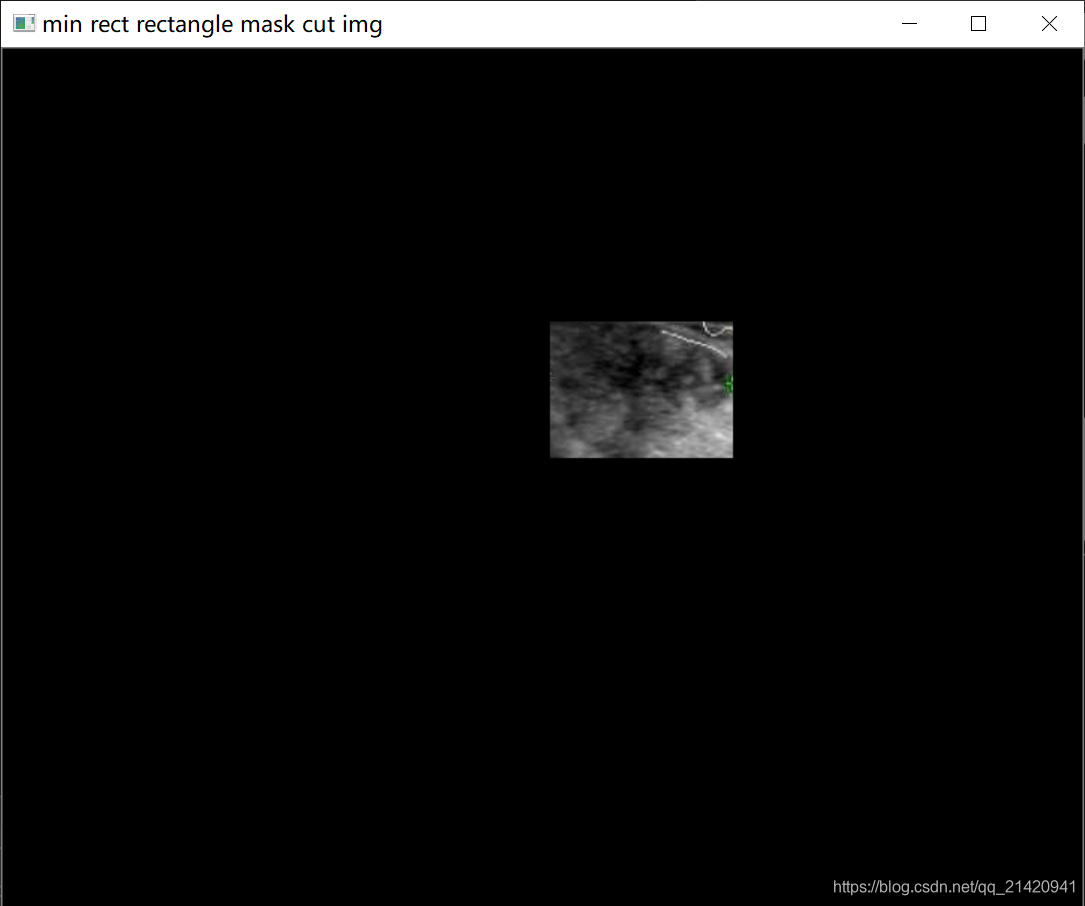
也可以通过最小内接矩形mask来进行切割: rectangle_mask_gray = cv2.cvtColor(rectangle_mask, cv2.COLOR_RGB2GRAY) # 此处的image是我们之前获取的最小内接矩形的mask pic = cv2.imread(original_img_path) # 读取mask对应的图像 out = cv2.bitwise_and(pic, pic, mask=rectangle_mask) # 根据mask切割 cv2.imshow("min rect rectangle mask cut img", out)效果如下:
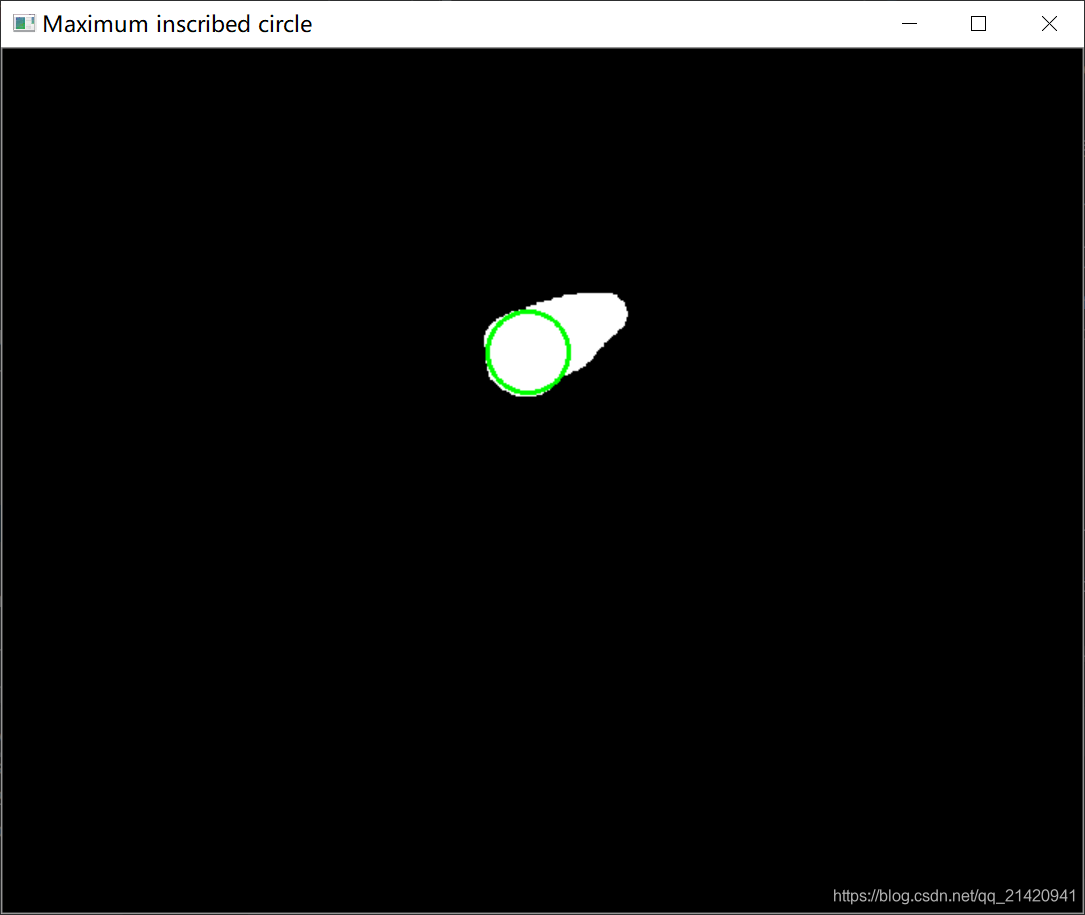
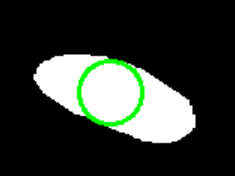
先看效果:
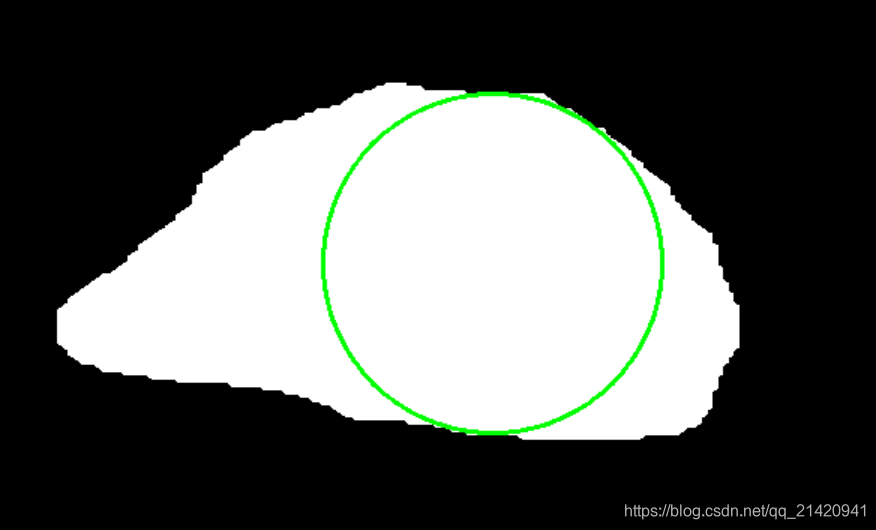
再放代码: # 读取图片,转灰度 mask = cv2.imread(mask_path) mask_gray = cv2.cvtColor(mask, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) # 识别轮廓 contours, _ = cv2.findContours(mask_gray, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE) # 计算到轮廓的距离 raw_dist = np.empty(mask_gray.shape, dtype=np.float32) for i in range(mask_gray.shape[0]): for j in range(mask_gray.shape[1]): raw_dist[i, j] = cv2.pointPolygonTest(contours[0], (j, i), True) # 获取最大值即内接圆半径,中心点坐标 minVal, maxVal, _, maxDistPt = cv2.minMaxLoc(raw_dist) minVal = abs(minVal) maxVal = abs(maxVal) # 画出最大内接圆 result = cv2.cvtColor(mask_gray, cv2.COLOR_GRAY2BGR) radius = np.int(maxVal) center_of_circle = maxDistPt cv2.circle(result, maxDistPt, radius, (0, 255, 0), 2, 1, 0) cv2.imshow('Maximum inscribed circle', result) cv2.waitKey(0) 四、最小外接圆效果:
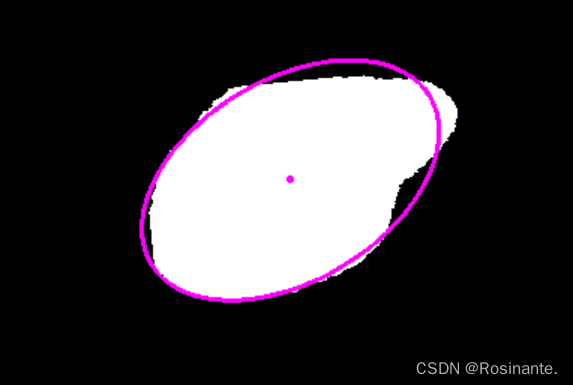
代码: def minimum_external_circle(mask_path): img = cv2.imread(mask_path) img_gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) contours, _ = cv2.findContours(img_gray, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE) cnt = contours[0] (x, y), radius = cv2.minEnclosingCircle(cnt) center = (int(x), int(y)) # 最小内接圆圆心 radius = int(radius) cv2.circle(img, center, radius, (0, 255, 0), 2) cv2.circle(img, center, 1, (0, 255, 0), 2) cv2.imshow('ret', img) cv2.waitKey(0) 五、拟合椭圆效果:
代码: def fit_ellipse(mask_path): img = cv2.imread(mask_path) img_gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) contours, _ = cv2.findContours(img_gray, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE) # 拟合椭圆 ellipse = cv2.fitEllipse(contours[0]) cv2.ellipse(img, ellipse, (255, 0, 255), 2) ellipse_center = (int(ellipse[0][0]), int(ellipse[0][1])) # 椭圆圆心坐标 cv2.circle(img, ellipse_center, 1, (255, 0, 255), 2) cv2.imshow('ellipse', img) cv2.waitKey(0) |
【本文地址】
公司简介
联系我们