| springboot黑马 | 您所在的位置:网站首页 › jQuery实战pdf黑马程序员 › springboot黑马 |
springboot黑马
|
介绍
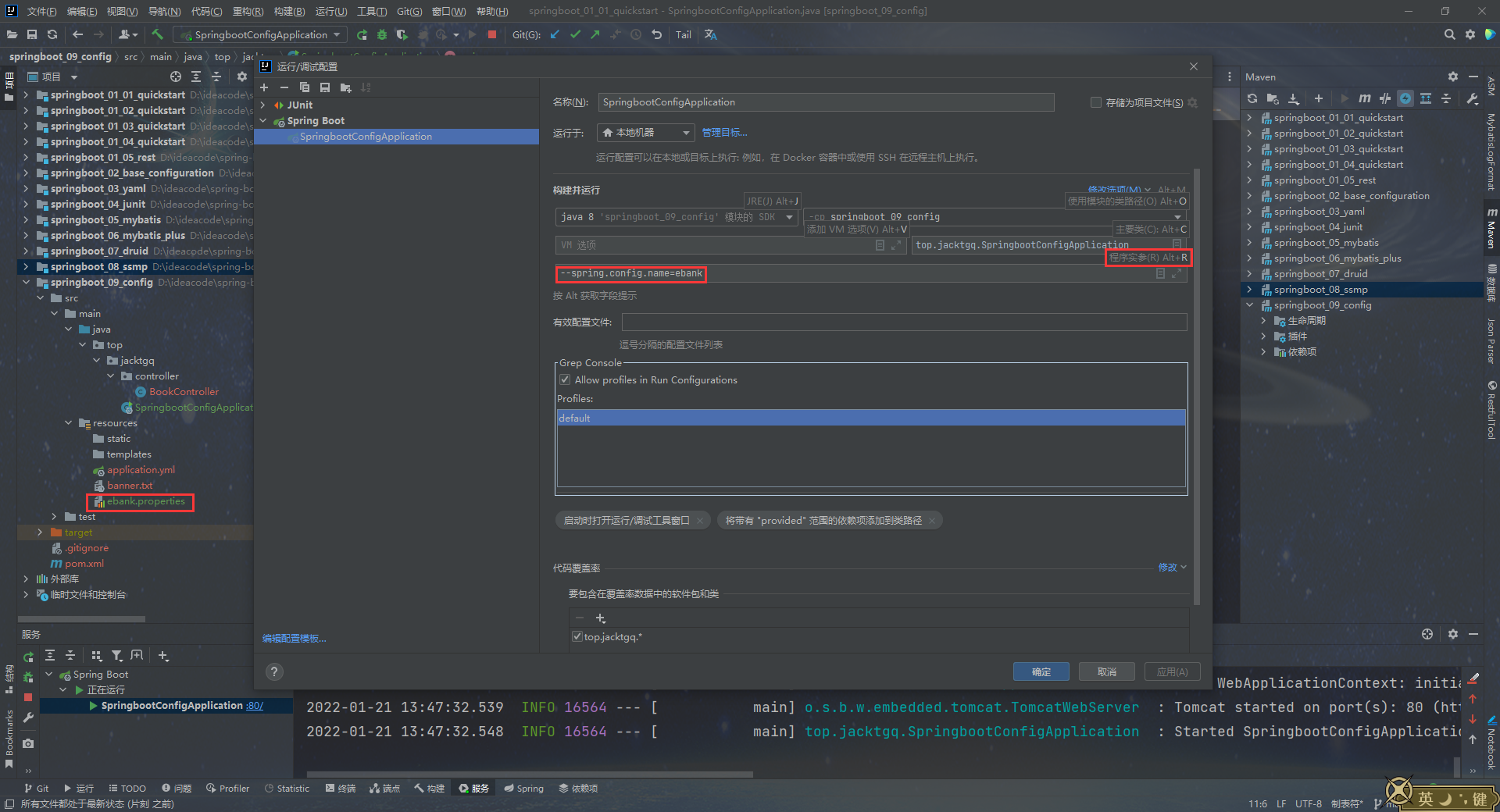
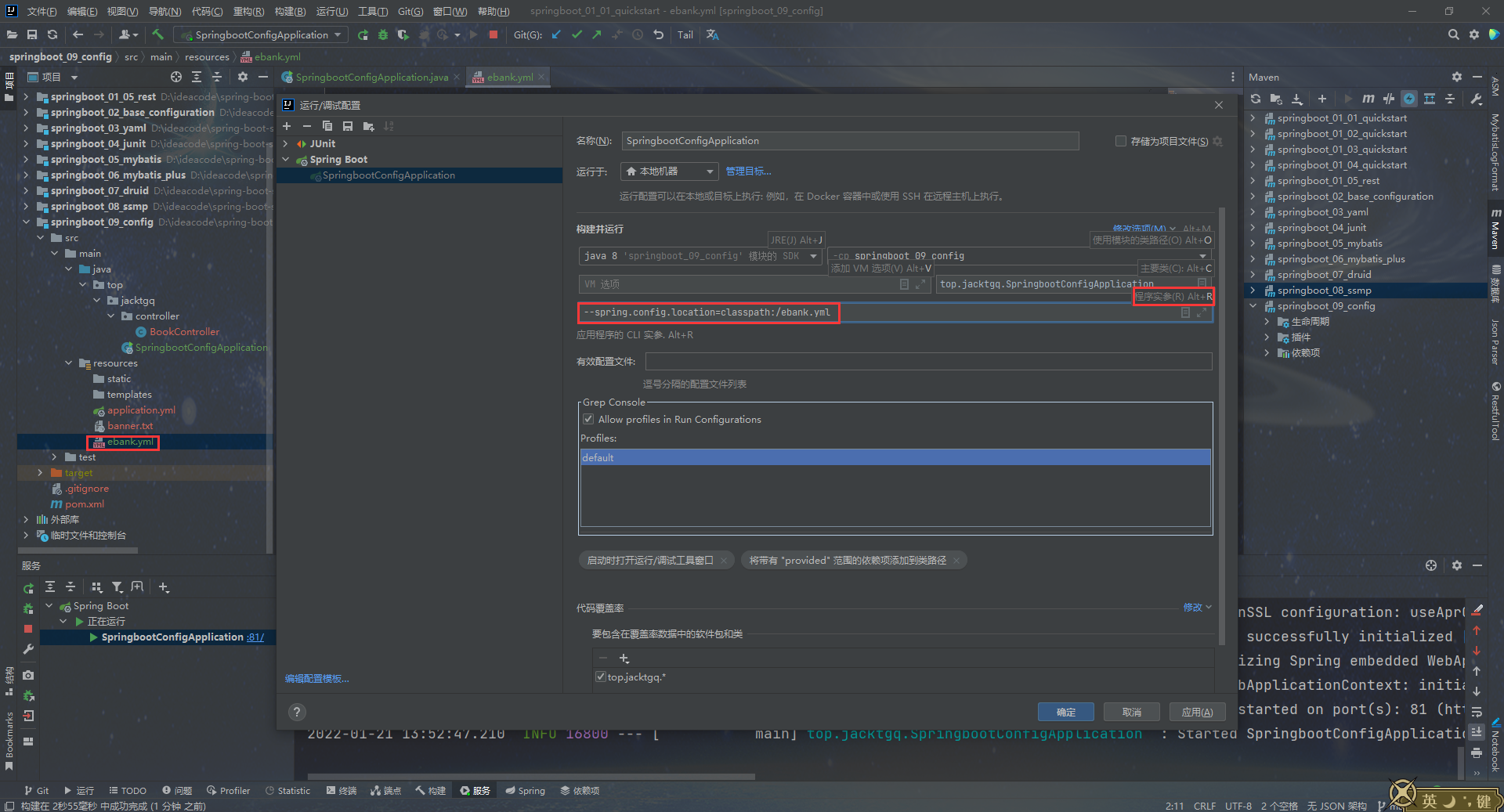
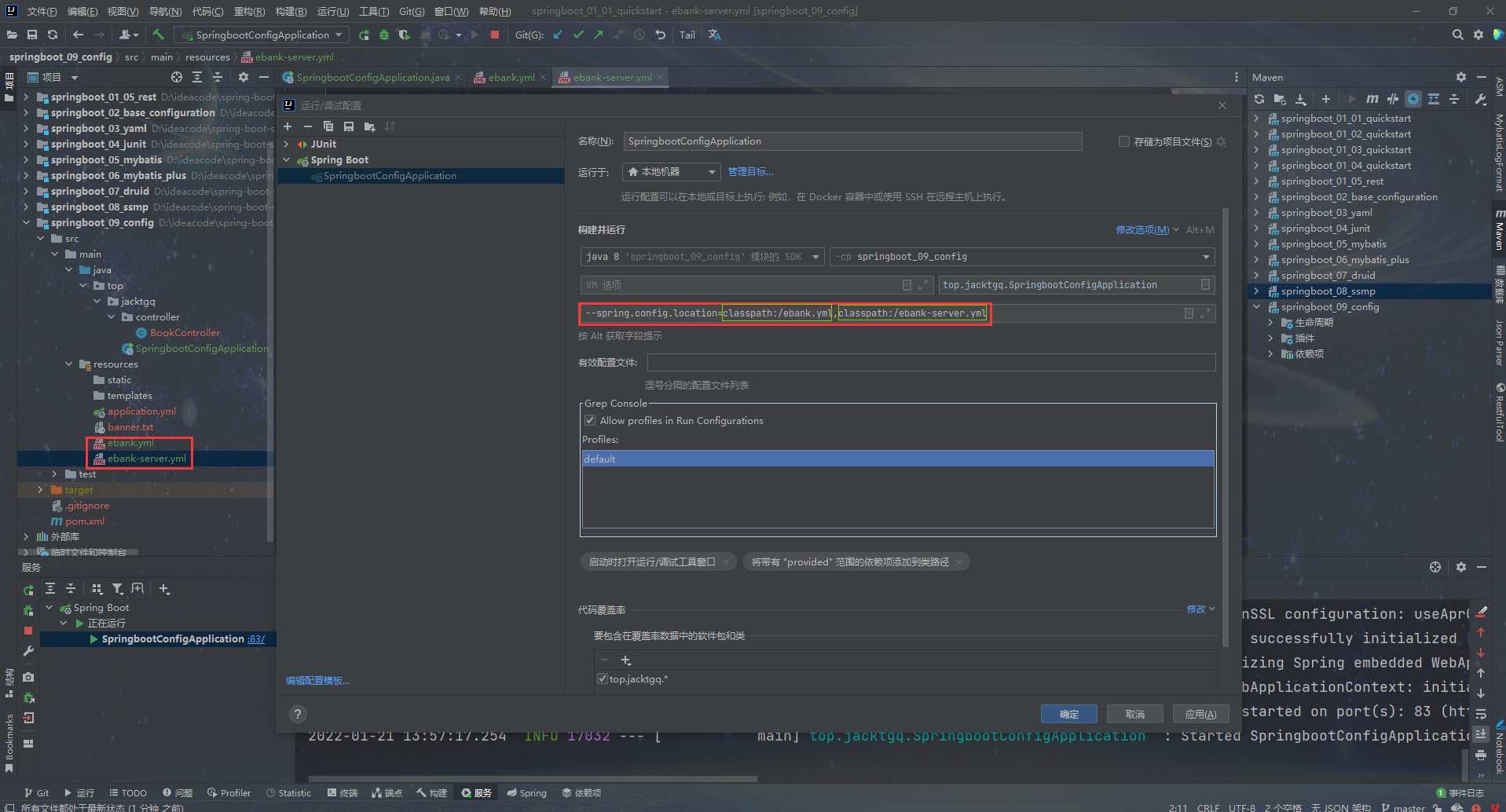
代码仓库地址:https://gitee.com/CandyWall/spring-boot-study 跟着黑马程序员spring boot教程做的学习笔记,本笔记跟视频内容的项目名称和代码略有不同,都是基于我自己的考量,代码都已经过运行验证过的,仅供参考。 视频教程地址:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV15b4y1a7yG 注:四级标题和部分5级标题是使用子项目名称命名的,和我代码仓库的项目是一一对应的。 每个子项目对应的视频链接以及一些重要内容的笔记 一、基础篇 1.入门案例 springboot_01_01_quickstartP3 基础篇-03-SpringBoot入门案例(Idea联网版)18:12 springboot_01_02_quickstartP4 基础篇-04-SpringBoot入门案例(官网创建版)06:21 springboot_01_03_quickstartP5 基础篇-05-SpringBoot入门案例(阿里云版)06:01 springboot_01_04_quickstartP6 基础篇-06-SpringBoot入门案例(手工制作版)08:34 P7 基础篇-07-教你一招:隐藏文件或文件夹 P8 基础篇-08-入门案例解析:parent P9 基础篇-09-入门案例解析:starter P10 基础篇-10-入门案例解析:引导类 P11 基础篇-11-入门案例:辅助功能:更换SpringBoot内嵌的默认的web容器从tomcat换成jetty 1.1 补充 springboot_01_05_restP12 知识加油站-01-REST风格简介 P13 知识加油站-02-RESTful入门案例 P14 知识加油站-03-RESTful快速开发 springboot_0x_02x_xxxxxxxx 2. 基础配置P15 基础篇-12-教你一招:复制模块 springboot_02_base_configurationP16 基础篇-13-属性配置方式 P17 基础篇-14-基础配置 P18 基础篇-15-3种配置文件类型 properties yml(主流格式) yaml P19 基础篇-16-配置文件加载优先级 三种格式共存,优先级从先到后为properties、yml、yaml P20 基础篇-17-教你一招:属性提示消失解决方案 3. yaml配置文件 springboot_03_yamlP21 基础篇-18-yaml数据格式 P22 基础篇-19-读取yaml单一属性数据 P23 基础篇-20-yaml文件中的变量引用 P24 基础篇-21-读取yaml全部属性数据 P25 基础篇-22-读取yaml引用类型属性数据 4. 整合Junit springboot_04_junitP27基础篇-24-整合JUnit——classes属性 5. 整合mybatis springboot_05_mybatisP28基础篇-25-SpringBoot整合MyBatis 课程中使用到的数据库脚本 /* Navicat MySQL Data Transfer Source Server : localhost Source Server Type : MySQL Source Server Version : 80023 Source Host : localhost:3306 Source Schema : springboot_db Target Server Type : MySQL Target Server Version : 80023 File Encoding : 65001 Date: 20/01/2022 11:50:34 */ SET NAMES utf8mb4; SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS = 0; -- ---------------------------- -- Table structure for tbl_book -- ---------------------------- DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `tbl_book`; CREATE TABLE `tbl_book` ( `id` int NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `name` varchar(50) CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL, `type` varchar(100) CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL, `description` varchar(100) CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`) USING BTREE ) ENGINE = InnoDB CHARACTER SET = utf8mb4 COLLATE = utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci ROW_FORMAT = Dynamic; -- ---------------------------- -- Records of tbl_book -- ---------------------------- INSERT INTO `tbl_book` VALUES (1, '三体', '科幻', '大刘的巅峰之作,将中国科幻推向世界舞台。总共分为三部曲:《地球往事》、《黑暗森林》、《死神永生》。'); INSERT INTO `tbl_book` VALUES (2, '格林童话', '童话', '睡前故事。'); INSERT INTO `tbl_book` VALUES (3, 'Spring 5设计模式', '计算机理论', '深入Spring源码剖析Spring源码中蕴含的10大设计模式'); INSERT INTO `tbl_book` VALUES (4, 'Spring MVC+ MyBatis开发从入门到项目实战', '计算机理论', '全方位解析面向Web应用的轻量级框架,带你成为Spring MVC开发高手'); INSERT INTO `tbl_book` VALUES (5, '轻量级Java Web企业应用实战', '计算机理论', '源码级剖析Spring框架,适合已掌握Java基础的读者'); INSERT INTO `tbl_book` VALUES (6, 'Java核心技术卷|基础知识(原书第11版)', '计算机理论', 'Core Java第11版,Jolt大奖获奖作品,针对Java SE9、10、 11全面更新'); INSERT INTO `tbl_book` VALUES (7, '深入理解Java虚拟机', '计算机理论', '5个维度全面剖析JVM,面试知识点全覆盖'); INSERT INTO `tbl_book` VALUES (8, 'Java编程思想(第4版)', '计算机理论', 'Java学习必读经典殿堂级著作!赢得了全球程序员的广泛赞誉'); INSERT INTO `tbl_book` VALUES (9, '零基础学Java (全彩版)', '计算机理论', '零基础自学编程的入门]图书,由浅入深,详解Java语言的编程思想和核心技术'); INSERT INTO `tbl_book` VALUES (10, '直播就该这么做:主播高效沟通实战指南', '市场营销', '李子柒、李佳琦、薇娅成长为网红的秘密都在书中'); INSERT INTO `tbl_book` VALUES (11, '直播销讲实战一本通', '市场营销', '和秋叶一起学系列网络营销书籍'); INSERT INTO `tbl_book` VALUES (12, '直播带货:淘宝、天猫直播从新手到高手', '市场营销', '一本教你如何玩转直播的书, 10堂课轻松实现带货月入3W+'); INSERT INTO `tbl_book` VALUES (13, 'Spring实战第5版', '计算机理论', 'Spring入门经典教程,深入理解Spring原理技术内幕'); INSERT INTO `tbl_book` VALUES (14, 'Spring 5核心原理与30个类手写实战', '计算机理论', '十年沉淀之作,写Spring精华思想'); SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS = 1;P29 基础篇-26-SpringBoot整合MyBatis常见问题处理 6. 整合mybatis-plus springboot_06_mybatis_plusP30 基础篇-27-SpringBoot整合MyBatisPlus 7. 整合druid数据库连接池 springboot_07_druidP31 基础篇-28-SpringBoot整合Druid 8. springboot基础篇综合案例 springboot_08_ssmpP32 基础篇-29-SSMP整合案例制作分析 P33 基础篇-30-模块创建 P34 基础篇-31-实体类快速开发(lombok) P35 基础篇-32-数据层标准开发(基础CRUD) P36 基础篇-33-开启MP运行日志 P38 基础篇-35-数据层标准开发(条件查询) P39 基础篇-36-业务层标准开发(基础CRUD) P40 基础篇-37-业务层快速开发(基于MyBatisPlus构建) P41 基础篇-38-表现层标准开发 P42 基础篇-39-表现层数据一致性处理(R对象) P43 基础篇-40-前后端调用(axios发送异步请求) P44 基础篇-41-列表功能 P45 基础篇-42-添加功能 P46 基础篇-43-删除功能 P47 基础篇-44修改功能(加载数据) P48 基础篇-45-修改功能 P49 基础篇-46-异常消息处理 P50 基础篇-47-分页 P51 基础篇-48-分页功能维护(删除BUG) P52 基础篇-49-条件查询 P53 基础篇-50-基础篇完结 二、运维实用篇P54 运维实用篇-51-工程打包与运行 P55 运维实用篇-52-打包插件 P56 运维实用篇-53-Boot工程快速启动(Linux版) # 后台启动springboot项目jar包 nohup java -jar springboot_08_ssmp-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar > server.log 2>&1 & # 终止程序 # 查看java -jar 命令对应的进程号 ps -ef | grep "java -jar" # 终止对应进程 kill -9P57 运维实用篇-54-临时属性 P58 运维实用篇-55-临时属性(开发环境) P59 运维实用篇-56-配置文件4级分类 9. 使用自定义配置 springboot_09_configP60 运维实用篇-57-自定义配置文件 方法1:设置程序参数,指定文件名(不包含后缀),如:--spring.config.name=ebank
P61 运维实用篇-58-多环境开发(yaml版) 单文件版: application.yml文件: # 应用环境 # 公共配置 spring: profiles: active: dev --- # 生产环境 spring: config: activate: on-profile: pro server: port: 80 --- spring: config: activate: on-profile: dev server: port: 8080 --- # 测试环境 spring: config: activate: on-profile: test server: port: 8888P62 运维实用篇-59-多环境开发多文件版(yaml版) yaml多文件版application.yml # 应用环境 # 公共配置 spring: profiles: active: testapplication-dev.yml # 开发环境 server: port: 8080application-pro.yml # 生产环境 server: port: 80application-test.yml # 测试环境 server: port: 8888P63 运维实用篇-60-多环境开发多文件版(properties版) properties多文件版application.properties # 应用环境 spring.profiles.active=testapplication-dev.properties # 开发环境 server.port=80application-pro.properties # 生产环境 server.port=8080application-test.properties # 测试环境 server.port=8888P64 运维实用篇-61-多环境分组管理 使用group属性配置同组的配置文件,active可以直接使一组配置文件同时生效 application.yml #spring: # profiles: # active: dev # include: devDB, devMVC spring: profiles: active: dev group: "dev": devDB, devMVC "pro": proDB, proMVC "test": testDB, TestMVCapplication-dev.yml server: port: 80application-devDB.yml server: port: 81application-devMVCyml server: servlet: context-path: /ebank port: 82观察启动日志,配置文件加载的顺序为 : The following profiles are active: dev,devDB,devMVC P65 运维实用篇-62-多环境开发控制 maven中使用多环境,然后在springboot中读取maven中的配置 pom.xml中的配置 env_dev dev true env_pro pro env_test test trueapplication.yml中的配置 #spring: # profiles: # active: dev # include: devDB, devMVC spring: profiles: active: @profile.active@ group: "dev": devDB, devMVC "pro": proDB, proMVC "test": testDB, TestMVC 11. 记录日志 springboot_11_logP66 运维实用篇-63-日志基础操作 P67 运维实用篇-64-教你一招:快速创建日志对象 P68 运维实用篇-65-日志输出格式控制 P69 运维实用篇-66-文件记录日志(运维实用篇完结) 三、开发实用篇 12. 热部署 springboot_12_hot_deployP70 开发实用篇-67-手工启动热部署 想要拥有热部署的功能,需要在pom.xml文件中添加如下依赖: org.springframework.boot spring-boot-devtools trueP71 开发实用篇-68-自动启动热部署 自动启动热部署,即,CTRL + F9编译的操作操作由程序自动完成,需要进行如下配置: 在设置中勾选
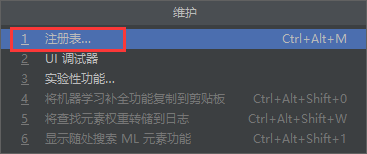
 idea新版本2021.3.1中在注册表中找不到改选项,需要在高级设置中进行设置。 [外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-PA8pixRs-1644940136019)(C:\Users\CandyWall\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20220122193933991.png)] idea新版本2021.3.1中在注册表中找不到改选项,需要在高级设置中进行设置。 [外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-PA8pixRs-1644940136019)(C:\Users\CandyWall\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20220122193933991.png)]
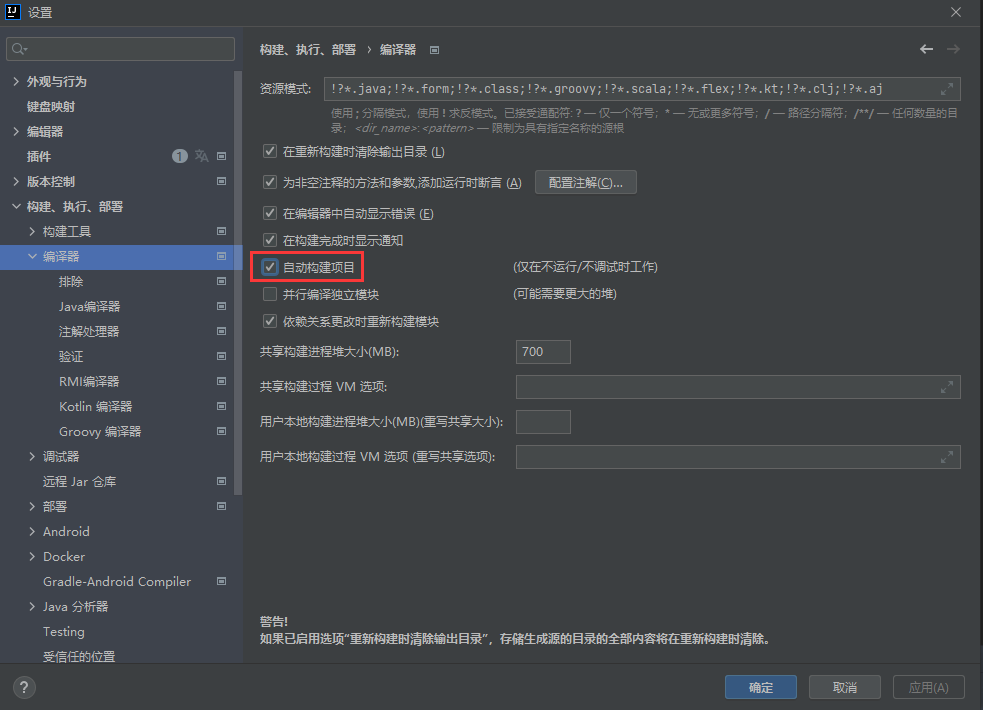
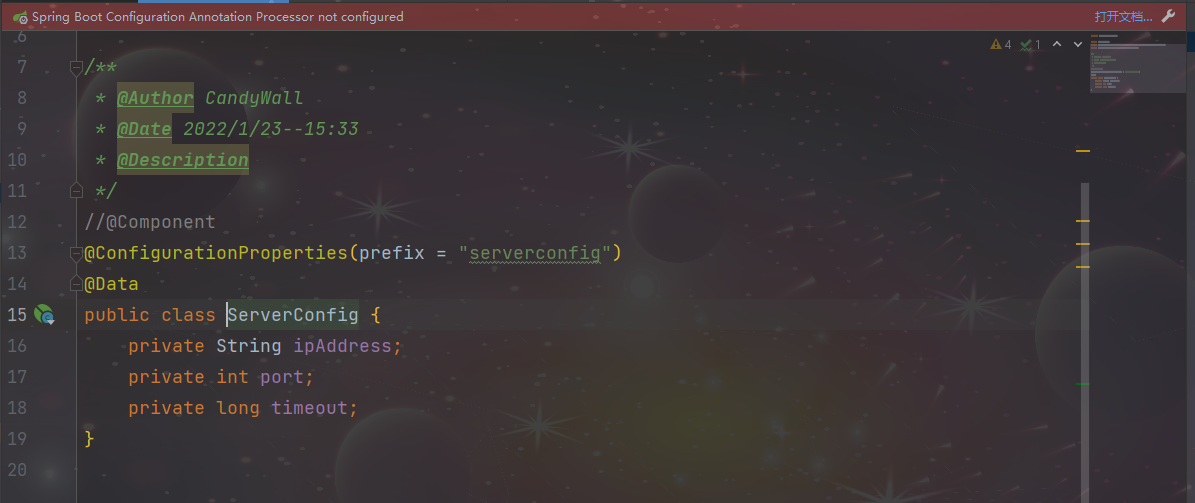
P72 开发实用篇-69-热部署范围配置 P73 开发实用篇-70-关闭热部署功能 application.yml spring: # 热部署范围配置 devtools: restart: # 设置不参与热部署的文件和文件夹(即修改后不重启) exclude: static/**,public/**,config/application.yml #是否可用 enabled: false如果配置文件比较多的时候找热部署对应配置比较麻烦,可以在springboot启动类的main方法中设置,此处设置的优先级将比配置文件高,一定会生效。 System.setProperty("spring.devtools.restart.enabled", "false"); 13. 属性绑定 springboot_13_configurationP74 实用开发篇-71-第三方bean属性绑定 先在要配置的类上面加@Component注解将该类交由spring容器管理; @ConfigurationProperties(prefix="xxx"),xxx跟application.yml配置文件中的属性对应; 如果多个配置类想统一管理也可以通过@EnableConfigurationProperties({xxx.class, yyy.class})的方式完成配置,不过该注解会与@Component配置发生冲突,二选一即可; 第三方类对象想通过配置进行属性注入,可以通过创建一个方法,在方法体上加@Bean和@ConfigurationProperties(prefix="xxx")注解,然后方法返回这个第三方对象的方式。 使用@ConfigurationProperties(prefix="xxx")注解后idea工具会报一个警告Spring Boot Configuration Annotation Processor not configured
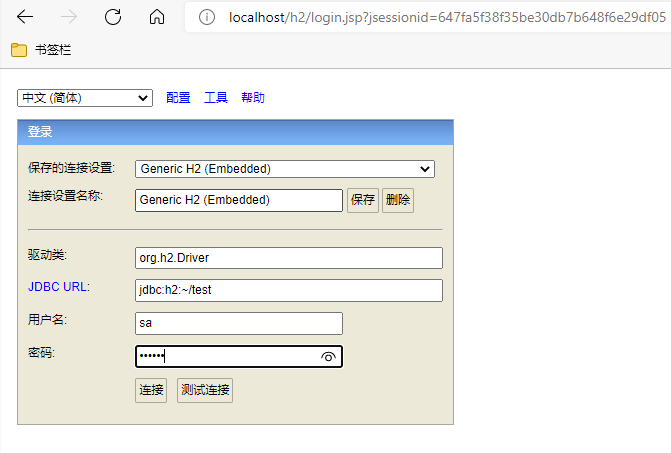
只需要在pom.xml中加上如下依赖刷新即可消除该警告 org.springframework.boot spring-boot-configuration-processorP75 实用开发篇-72-松散绑定 @ConfigurationProperties绑定属性支持属性名宽松绑定,又叫松散绑定。 比如要将ServerConfig.class作为配置类,并通过配置文件application.yml绑定属性 ServerConfig.class @Component @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "serverconfig") @Data public class ServerConfig { private String ipAddress; private int port; private long timeout; }application.yml serverConfig: # ipAddress: 192.168.0.1 # 驼峰模式 # ipaddress: 192.168.0.1 # IPADDRESS: 192.168.0.1 ip-address: 192.168.0.1 # 主流配置方式,烤肉串模式 # ip_address: 192.168.0.1 # 下划线模式 # IP_ADDRESS: 192.168.0.1 # 常量模式 # ip_Add_rEss: 192.168.0.1 # ipaddress: 192.168.0.1 port: 8888 timeout: -1以ipAddress属性为例,上面的多种配置方式皆可生效,这就是松散绑定。而@Value不支持松散绑定,必须一一对应。 @ConfigurationProperties(prefix="serverconfig")中的prefix的值为serverconfig或者server-config,如果是serverConfig就会报错,这与松散绑定的前缀命名规范有关:仅能使用纯小写字母、数字、中划线作为合法的字符 P76 实用开发篇-73-常用计量单位应用 //@Component @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "server-config") @Data public class ServerConfig { private String ipAddress; private int port; @DurationUnit(ChronoUnit.MINUTES) private Duration timeout; @DataSizeUnit(DataUnit.MEGABYTES) private DataSize dataSize; }P77 实用开发篇-74-bean属性校验 引入Bean属性校验框架的步骤: 在pom.xml中添加JSR303规范和hibernate校验框架的依赖: javax.validation validation-api org.hibernate.validator hibernate-validator 在要校验的类上加@Validated注解设置具体的校验规则,如:@Max(value=8888, message="最大值不能超过8888") @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "server-config") @Data // 2.开启对当前bean的属性注入校验 @Validated public class ServerConfig { private String ipAddress; // 设置具体的规则 @Max(value = 8888, message = "最大值不能超过8888") @Min(value = 1000, message = "最小值不能低于1000") private int port; @DurationUnit(ChronoUnit.MINUTES) private Duration timeout; @DataSizeUnit(DataUnit.MEGABYTES) private DataSize dataSize; }P78 实用开发篇-75-进制数据转换规则 进制转换中的一些问题: 如application.yml文件中对数据库有如下配置: datasource: driverClassName: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver123 # 不加引号读取的时候默认解析为了8进制数,转成十进制就是87 # 所以想让这里正确识别,需要加上引号 # password: 0127 password: "0127" 14. 测试相关P79 实用开发篇-76-加载测试专用属性 springboot_14_test@SpringBootTest注解中可以设置properties和args属性,这里的args属性的作用跟idea工具中自带的程序参数类似,只不过这里的配置是源码级别的,会随着源码的移动而跟随,而idea中的程序参数的配置会丢失。并且这里的args属性的配置的作用范围比较小,仅在当前测试类生效。 application.yml test: prop: testValuePropertiesAndArgsTest.java // properties属性可以为当前测试用例添加临时的属性配置 //@SpringBootTest(properties = {"test.prop=testValue1"}) // args属性可以为当前测试用例添加临时的命令行参数 //@SpringBootTest(args = {"--test.prop=testValue2"}) // 优先级排序: args > properties > 配置文件 @SpringBootTest(args = {"--test.prop=testValue2"}, properties = {"test.prop=testValue1"}) class PropertiesAndArgsTest { @Value("${test.prop}") private String prop; @Test public void testProperties() { System.out.println("prop = " + prop); } }P80 实用开发篇-77-加载测试专用配置 某些测试类中需要用到第三方的类,而其他测试类则不需要用到,这里可以在类上加载@Import({xxx.class, yyy.class}) P81 实用开发篇-78-测试类中启动web环境 P82 实用开发篇-79-发送虚拟请求 P83 实用开发篇-80-匹配响应执行状态 P84 实用开发篇-81-匹配响应体 P85 实用开发篇-82-匹配响应体(json) P86 实用开发篇-83-匹配响应头 表现层BookController.java @RestController @RequestMapping("/books") public class BookController { /*@GetMapping("/{id}") public String getById(@PathVariable int id) { System.out.println("id = " + id); return "getById..."; }*/ @GetMapping("/{id}") public Book getById(@PathVariable int id) { System.out.println("id = " + id); Book book = new Book(); book.setId(5); book.setName("神秘岛"); book.setType("科幻"); book.setDescription("《神秘岛》是法国科幻小说家儒勒·凡尔纳创作的长篇小说,是他写的三部曲之一。"); return book; } }对应的测试类WebTest.java @SpringBootTest(webEnvironment = SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.RANDOM_PORT) // 开启虚拟mvc调用 @AutoConfigureMockMvc public class WebTest { @Test public void testRandomPort() { } @Test public void testWeb(@Autowired MockMvc mvc) throws Exception { // 创建虚拟请求,当前访问 /books MockHttpServletRequestBuilder builder = MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/books/5"); mvc.perform(builder); } @Test public void testStatus(@Autowired MockMvc mvc) throws Exception { MockHttpServletRequestBuilder builder = MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/books1/6"); ResultActions action = mvc.perform(builder); // 设定预期值,与真实值进行比较,成功测试通过,失败测试不通过 // 定义本次调用的预期值 StatusResultMatchers srm = MockMvcResultMatchers.status(); // 预计本次调用成功的状态码:200 ResultMatcher ok = srm.isOk(); // 添加预计值到本次调用过程中进行匹配 action.andExpect(ok); } @Test public void testBody(@Autowired MockMvc mvc) throws Exception { MockHttpServletRequestBuilder builder = MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/books/6"); ResultActions action = mvc.perform(builder); // 设定预期值,与真实值进行比较,成功测试通过,失败测试不通过 // 定义本次调用的预期值 ContentResultMatchers crm = MockMvcResultMatchers.content(); // 预计本次调用成功的状态码:200 ResultMatcher rm = crm.string("getById..."); // 添加预计值到本次调用过程中进行匹配 action.andExpect(rm); } @Test public void testJson(@Autowired MockMvc mvc) throws Exception { MockHttpServletRequestBuilder builder = MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/books/7"); ResultActions action = mvc.perform(builder); // 设定预期值,与真实值进行比较,成功测试通过,失败测试不通过 // 定义本次调用的预期值 ContentResultMatchers jsonMatcher = MockMvcResultMatchers.content(); ResultMatcher rm = jsonMatcher.json("{\"id\":5,\"name\":\"神秘岛\",\"type\":\"科幻\",\"description\":\"《神秘岛》是法国科幻小说家儒勒·凡尔纳创作的长篇小说,是他写的三部曲之一。1\"}"); action.andExpect(rm); } @Test public void testContentType(@Autowired MockMvc mvc) throws Exception { MockHttpServletRequestBuilder builder = MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/books/7"); ResultActions action = mvc.perform(builder); // 设定预期值,与真实值进行比较,成功测试通过,失败测试不通过 // 定义本次调用的预期值 HeaderResultMatchers hrm = MockMvcResultMatchers.header(); ResultMatcher rm = hrm.string("Content-Type", "application/json"); action.andExpect(rm); } @Test // 完整测试 public void testGetById(@Autowired MockMvc mvc) throws Exception { MockHttpServletRequestBuilder builder = MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/books/8"); ResultActions action = mvc.perform(builder); // 1、比较状态码 StatusResultMatchers statusResultMatchers = MockMvcResultMatchers.status(); ResultMatcher statusResultMatcher = statusResultMatchers.isOk(); action.andExpect(statusResultMatcher); // 2、比较返回值类型 HeaderResultMatchers headerResultMatchers = MockMvcResultMatchers.header(); ResultMatcher headerResultMatcher = headerResultMatchers.string("Content-Type", "application/json"); action.andExpect(headerResultMatcher); /// 3、比较json返回值 ContentResultMatchers contentResultMatchers = MockMvcResultMatchers.content(); ResultMatcher jsonResultMatcher = contentResultMatchers.json("{\"id\":5,\"name\":\"神秘岛\",\"type\":\"科幻\",\"description\":\"《神秘岛》是法国科幻小说家儒勒·凡尔纳创作的长篇小说,是他写的三部曲之一。\"}"); action.andExpect(jsonResultMatcher); } }P87 实用开发篇-84-业务层测试事务回滚 测试过程中对数据库的增删改操作的影响是否回滚,由下面两个注解控制,需要在测试类上加: @Transactional,@Rollback(value=true):回滚,@Rollback(value=true)为默认值,也可以省略; @Transactional,@Rollback(value=false):不回滚,跟什么注解都不加的效果一样。 P88 实用开发篇-85-测试用例设置随机数据 可以把测试用例中的属性值都按照一定规则设置成随机值,可以让测试结果更具有普适性。并且可以把测试用例的属性的随机规则写在配置文件中,方便更改。 application.yml testcase: randomBook: id: ${random.int} id2: ${random.int(10)} # 生成10以内的整数 type: ${random.int(5, 10)} # 生成5-10之间的整数 name: 糖果墙${random.value} uuid: ${random.uuid} publicTime: ${random.long}BookCase.java @Data @Component @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "test-case.random-book") public class BookCase { private Integer id; private Integer id2; private String type; private String name; private String uuid; private Long publishTime; } 15. 数据层解决方案 springboot_15_01_datasourceP89 实用开发篇-86-内置数据源 在springboot项目中使用Druid数据源,需要先在pom.xml中加上Druid的依赖: com.alibaba druid-spring-boot-starter 1.2.8然后在application.yml中有两种配置方法,两种方法实现的效果一样 # 配法1: spring: datasource: druid: driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springboot_db?serverTimezone=UTC username: root password: 123 # 配法2: spring: datasource: driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springboot_db?serverTimezone=UTC username: root password: 123 type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource # 去掉type属性,Druid数据源依然会启用配法2去掉type属性后,再启动项目,发现Druid数据源依然启用了,这是由于引入了Druid数据源的依赖后,springboot会自动配置Druid。 如果不引入Druid数据源的依赖,springboot默认的数据源是Hikari数据源 # 默认为Hikari数据源 spring: datasource: driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springboot_db?serverTimezone=UTC username: root password: 123 # Hikari数据源详细配置,这里需要注意url需要和Hikari属性并列,而Hikari下的jdbc-url无效 spring: datasource: url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springboot_db?serverTimezone=UTC hikari: # jdbc-url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springboot_db?serverTimezone=UTC # 此项无效 driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver username: root password: 123 maximum-pool-size: 50 minimum-idle: 30 idle-timeout: 30000 springboot_15_02_jdbc_templateP90 实用开发篇-87-JdbcTemplate 使用JdbcTemplate 在pom.xml中加入相关依赖 application.yml中配置数据源,另外还可以对JdbcTemplate进行一些简单的配置 # 配置数据库和连接池 spring: datasource: url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springboot_db?serverTimezone=UTC hikari: driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver username: root password: TGQ@candywall123 maximum-pool-size: 50 minimum-idle: 30 # idle-timeout: 30000 # JdbcTemplate的一些配置 jdbc: template: query-timeout: 30s # 指定查询超时时间 max-rows: 500 # 最大查询条数 fetch-size: 500 # 数据条数比较多的时候,一次拿多少条数据测试类 @SpringBootTest class JdbcTemplateApplicationTests { @Autowired private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate; @Test void testJdbcTemplateSelect() { String sql = "select * from tbl_book"; // List maps = jdbcTemplate.queryForList(sql); // System.out.println(maps); RowMapper rm = new RowMapper() { @Override public Book mapRow(ResultSet rs, int rowNum) throws SQLException { Book book = new Book(); book.setId(rs.getInt("id")); book.setName(rs.getString("name")); book.setType(rs.getString("type")); book.setDescription(rs.getString("description")); return book; } }; List bookList = jdbcTemplate.query(sql, rm); bookList.forEach(System.out::println); } @Test void testJdbcTemplateInsert() { String sql = "insert into tbl_book values(null, ?, ?, ?)"; jdbcTemplate.update(sql, "springboot1", "springboot2", "springboot3"); } } springboot_15_03_h2P91 实用开发篇-88-H2数据库 使用H2数据库 在pom.xml中加入相关依赖 在application.yml中配置数据源并且启用H2数据库的控制台 server: port: 80 spring: # 配置数据库和连接池 datasource: url: jdbc:h2:~/test hikari: driver-class-name: org.h2.Driver username: sa password: 123456 # 启用H2的控制台 h2: console: enabled: true path: /h2在浏览器中输入访问H2控制台地址
输入默认密码:123456,然后点连接,会跳转到控制台主页
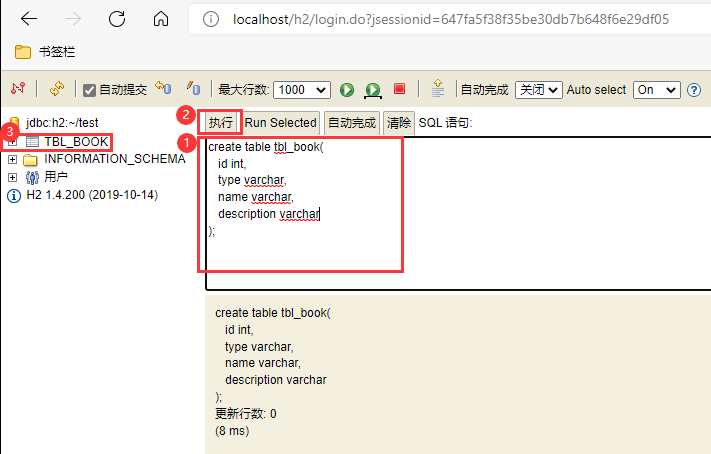
可以写sql语句建表,并插入几条数据 create table tbl_book( id int, type varchar, name varchar, description varchar ); insert into tbl_book values(1, 'springboot1', 'springboot2', 'springboot3'); insert into tbl_book values(2, 'springboot4', 'springboot5', 'springboot6'); insert into tbl_book values(3, 'springboot7', 'springboot8', 'springboot9'); insert into tbl_book values(4, 'springboot10', 'springboot11', 'springboot12');
查询tbl_book表中的数据 select * from tbl_book;
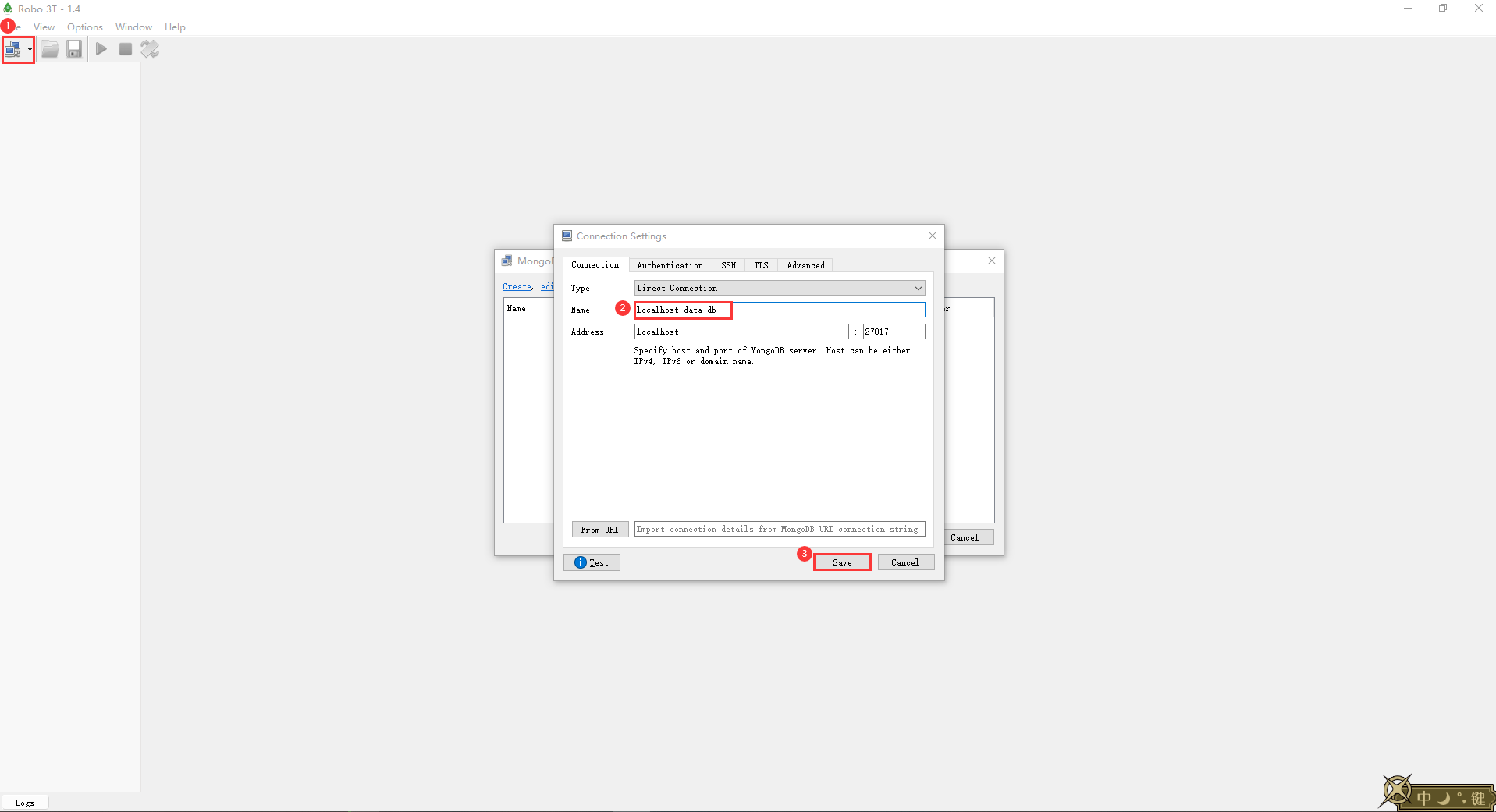
写代码连接H2数据库,需要注意启动测试类连接H2数据库的时候需要将之前的H2控制台的springboot程序先停止,否则会造成端口占用,测试类报错。 测试类: @SpringBootTest class H2ApplicationTests { @Autowired private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate; @Test public void testH2Select() { String sql = "select * from tbl_book"; RowMapper rm = new RowMapper() { @Override public Book mapRow(ResultSet rs, int rowNum) throws SQLException { Book book = new Book(); book.setId(rs.getInt("id")); book.setName(rs.getString("name")); book.setType(rs.getString("type")); book.setDescription(rs.getString("description")); return book; } }; List bookList = jdbcTemplate.query(sql, rm); bookList.forEach(System.out::println); } @Test public void testH2Save() { String sql = "insert into tbl_book values(?, ? ,? ,?)"; jdbcTemplate.update(sql, 5, "啊哈算法", "计算机", "数据结构和算法"); } }H2数据库线上运行时请务必关闭。 bind 0.0.0.0 protected-mode no port 6379 timeout 0 save 900 1 # 900s内至少一次写操作则执行bgsave进行RDB持久化 save 300 10 save 60 10000 rdbcompression yes dbfilename dump.rdb dir /data appendonly yes appendfsync everysec requirepass 12345678 springboot_15_04_redisP92 实用开发篇-89-redis下载安装与基本使用 windows版下载地址:https://github.com/tporadowski/redis/releases linux版下载地址:https://redis.io/ 在linux上安装redis除了最原始的方法外,推荐使用docker-compose一键启动redis,非常方便 redis.conf bind 0.0.0.0 protected-mode no port 6379 timeout 0 save 900 1 # 900s内至少一次写操作则执行bgsave进行RDB持久化 save 300 10 save 60 10000 rdbcompression yes dbfilename dump.rdb dir /data appendonly yes appendfsync everysec requirepass 123456docker-compose.yml version: '3' services: redis: image: redis:latest container_name: redis restart: always ports: - 6379:6379 volumes: - ./redis.conf:/etc/redis/redis.conf:rw - ./data:/data:rw command: ["redis-server","/etc/redis/redis.conf"]我的redis安装在虚拟机中的linux系统上,可以通过以下两种方式测试连通性: 通过windows版redis自带的redis-cli来远程连接linux上的redis服务,指令如下: redis-cli.exe -h 192.168.0.110 -p 6379 -a "123456" # 123456是密码 还可以使用AnotherRedisDesktopManager:这是一款非常稳定并且拥有美观的图形界面的redis客户端,操作起来也是相当简单,一看就会用,下载地址:https://github.com/qishibo/AnotherRedisDesktopManager/releasesP93 实用开发篇-90-SpringBoot整合Redis 在pom.xml中加入spring整合redis的依赖 org.springframework.boot spring-boot-starter-data-redisapplication.yml spring: # redis配置 redis: host: 192.168.0.110 port: 6379 password: 123456测试类 @SpringBootTest class RedisApplicationTests { @Autowired private StringRedisTemplate redisTemplate; @Test public void testSet() { ValueOperations valueOperations = redisTemplate.opsForValue(); valueOperations.set("age", "41"); } @Test public void testGet() { ValueOperations valueOperations = redisTemplate.opsForValue(); System.out.println("age = " + valueOperations.get("age")); System.out.println("username = " + valueOperations.get("username")); } }注:这里如果使用RedisTemplate而不使用StringRedisTemplate,去redis客户端里面查看会发现键值包含\xac\xed\x00\x05t\x00\特殊字符,这是由于RedisTemplate模板类在操作redis时默认使用JdkSerializationRedisSerializer来进行序列化。而存取序列化的方式从org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.JdkSerializationRedisSerializer 将序列化的方式改为 org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer 会自动去掉\xac\xed\x00\x05t\x00前缀,所以有两种解决方法: 直接使用StringRedisTemplate; 方案2 修改默认的序列化方式: private RedisTemplate redisTemplate; @Autowired(required = false) public void setRedisTemplate(RedisTemplate redisTemplate) { RedisSerializer stringSerializer = new StringRedisSerializer(); redisTemplate.setKeySerializer(stringSerializer); redisTemplate.setValueSerializer(stringSerializer); redisTemplate.setHashKeySerializer(stringSerializer); redisTemplate.setHashValueSerializer(stringSerializer); this.redisTemplate = redisTemplate; }P94 实用开发篇-91-SpringBoot读写Redis的客户端 P95 实用开发篇-92-SpringBoot操作Redis客户端实现技术切换(jedis) java操作redis底层有两种实现分别为lettuce和jedis,其中lettuce为springboot的RedisTemplate默认使用的技术。如果想要切换到jedis: 引入jedis的jar包 在application.yml中加入配置 spring: # redis配置 redis: host: 192.168.0.110 port: 6379 password: 123456 client-type: jedis # 默认为lettuce # 还可以进一步配置 jedis: pool: enabled: true max-active: 16 min-idle: 8 springboot_15_05_mongodbP96 实用开发篇-93-Mongodb简介 P97 实用开发篇-94-Mongodb下载与安装 解压mongodb安装包,然后在软件根目录下新建data\db,进入到bin目录下启动黑窗口,输入如下命令,启动mongodb数据库,并指定数据保存到data\db目录下。 .\mongod.exe --dbpath=..\data\db在bin目录下再开一个黑窗口,然后输入 .\mongo.exe会默认连接ip为localhost,port为27017的mongodb服务,连接成功会输出mongodb的版本等信息。 P98 实用开发篇-95-Mongodb基础操作 由于黑窗口操作较为繁琐,这里推荐使用带图形化界面的客户端robo3t,启动robo3t,创建一个连接
右击左侧连接名,在右键菜单中选择Create Database,新建一个数据库
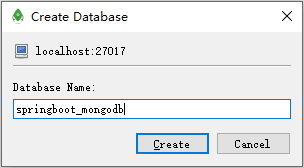
填写数据库名称
展开数据库名,右击Collections再新建一个Collection
填写collection名称
右击新建的Collection book,会弹出一个查询界面,可以在文本框中填写指令对Collection book进行操作
P99 实用开发篇-96-SpringBoot整合Mongodb 在pom.xml中加入springboot整合MongoDB的依赖 org.springframework.boot spring-boot-starter-data-mongodb在application.yml中进行MongoDB的配置 spring: data: mongodb: uri: mongodb://localhost/springboot_mongodb测试代码 @SpringBootTest class MongodbApplicationTests { @Autowired private MongoTemplate mongoTemplate; @Test void testSave() { Book book = new Book(); book.setId(2); book.setName("springboot2"); book.setType("springboot2"); book.setDescription("springboot2"); mongoTemplate.save(book); } @Test public void testFindAll() { List books = mongoTemplate.findAll(Book.class); books.forEach(System.out::println); } } springboot_15_06_elasticsearchP100 实用开发篇-97-ES简介 P101 实用开发篇-98-ES下载与安装 下载地址:https://www.elastic.co/cn/start 安装 解压es的安装包,然后去bin目录下双击elasticsearch.bat启动es服务器,然后就可以去浏览器输入http://localhost:9200/
如果有正常的json返回值,那么说明es启动正常 P102 实用开发篇-99-ES索引操作 安装IK分词器插件 我们希望es再新建索引的时候应用分词效果,所以需要先给es安装IK分词器插件 下载地址:https://github.com/medcl/elasticsearch-analysis-ik/releases 在es的plugin目录下新建一个ik文件夹(建文件夹是为了方便管理),然后把下载好的ik分词器压缩包中的内容解压到ik目录下
关闭当前es启动的黑窗口,去es的bin目录下,双击elasticsearch.bat,重新启动es 新建索引 打开postman,发送一个PUT请求,新建一个books索引 请求参数 { "mappings": { "properties": { "id": { "type": "keyword" }, "name": { "type": "text", "analyzer": "ik_max_word", "copy_to": "all" }, "type": { "type": "keyword" }, "description": { "type": "text", "analyzer": "ik_max_word", "copy_to": "all" }, "all": { "type": "text", "analyzer": "ik_max_word" } } } }
返回如下提示就表示新建索引成功
删除索引
P103 实用开发篇-100-ES文档操作 新建文档 有3种请求方式: 方式1:http://localhost:9200/books/_doc
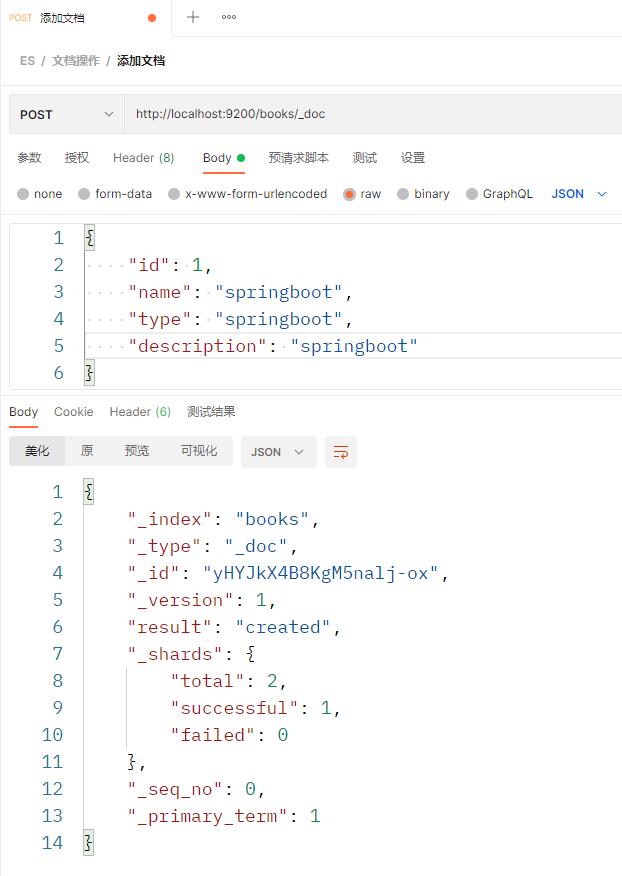
方式2:http://localhost:9200/books/_doc/221432414,其中221432414是文档中的_id属性,如果不指定,则随机生成
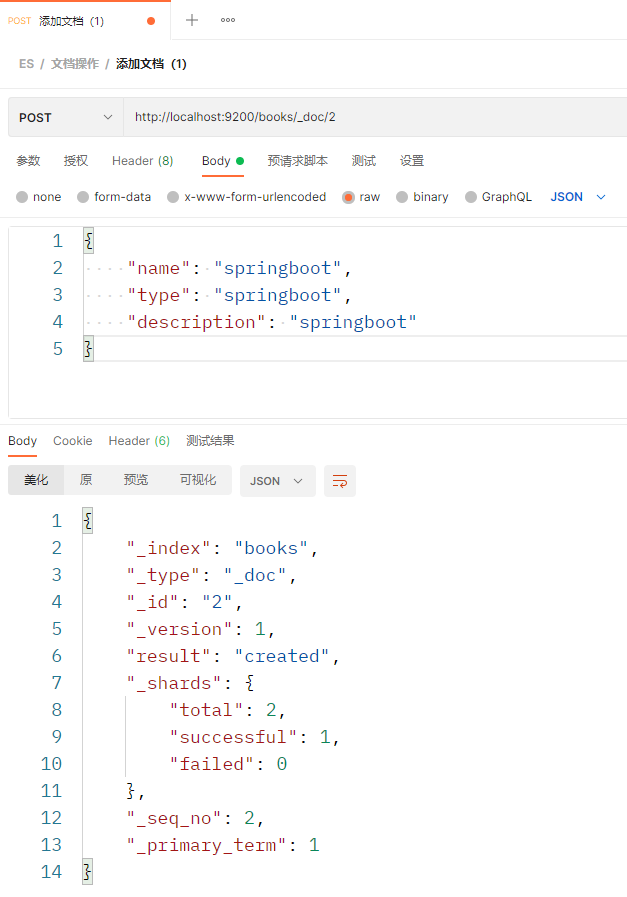
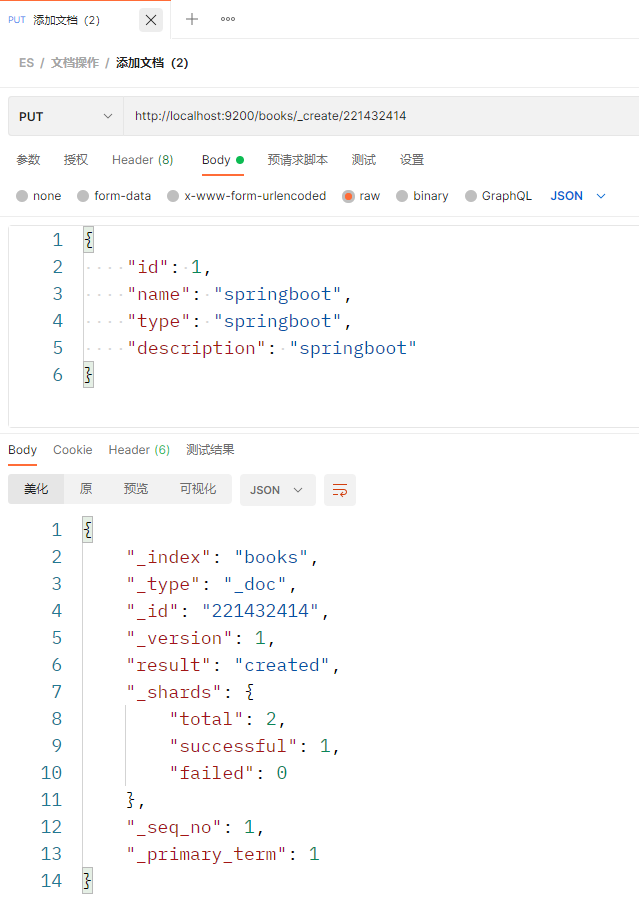
方式3:http://localhost:9200/books/_create/221432414,其中221432414是文档中的_id属性,这里不指定会报错 注:如果在新建的过程中出现[TOO_MANY_REQUESTS/12/disk usage exceeded flood-stage watermark, index has read-only-allow-delete block]的问题,可以发送下面的请求解决
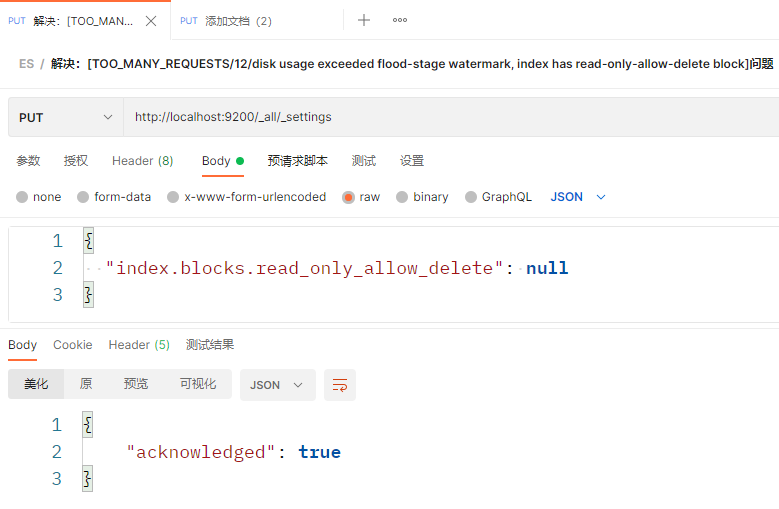
如果上面的方法也不能解决,检查一下自己的es安装目录所在磁盘的可用空间是否太小,默认必须大于5%才可以,比如磁盘空间500G, 需要至少25G的可用空间才可以。后来清了磁盘大于5%也不行,后来用这个方法解决了:Elasticsearch flood stage disk watermark exceeded 查询文档 查询全部文档
按条件查询
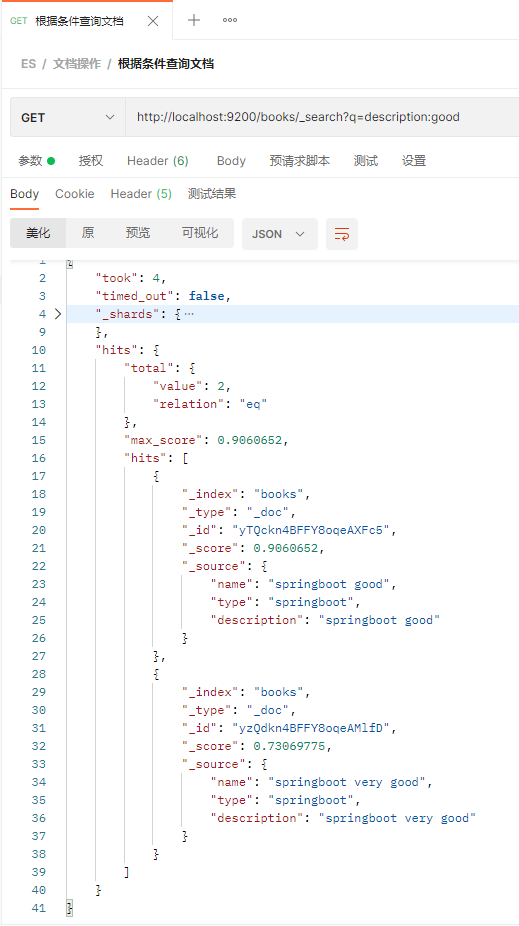
删除文档
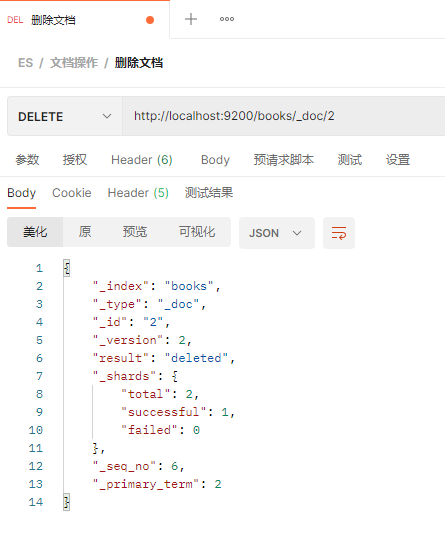
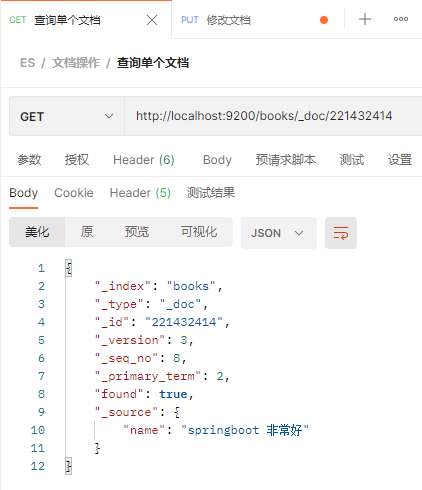
修改文档 将_id为221432414的文档的name修改的值修改为springboot 非常好 先查询一下
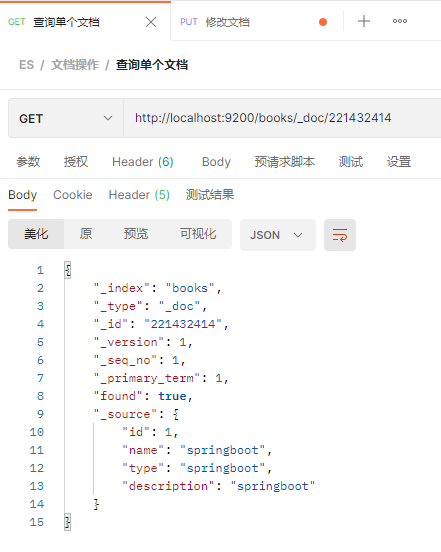
发起请求执行修改操作,这里请求体里面只填写要修改的属性
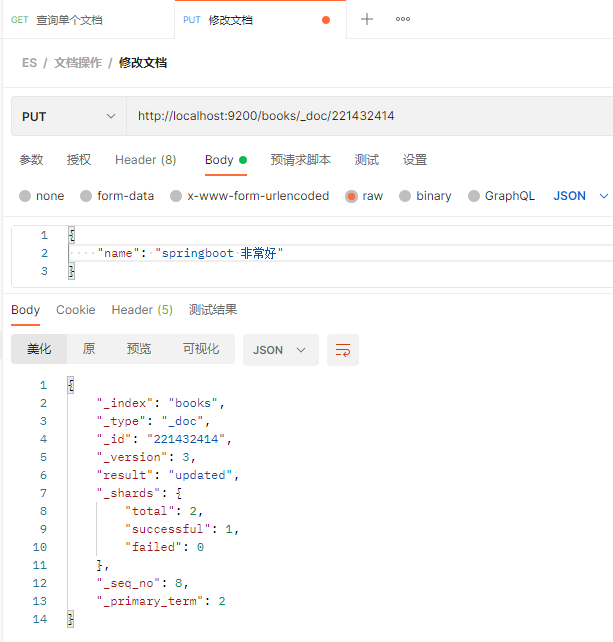
再查询一下
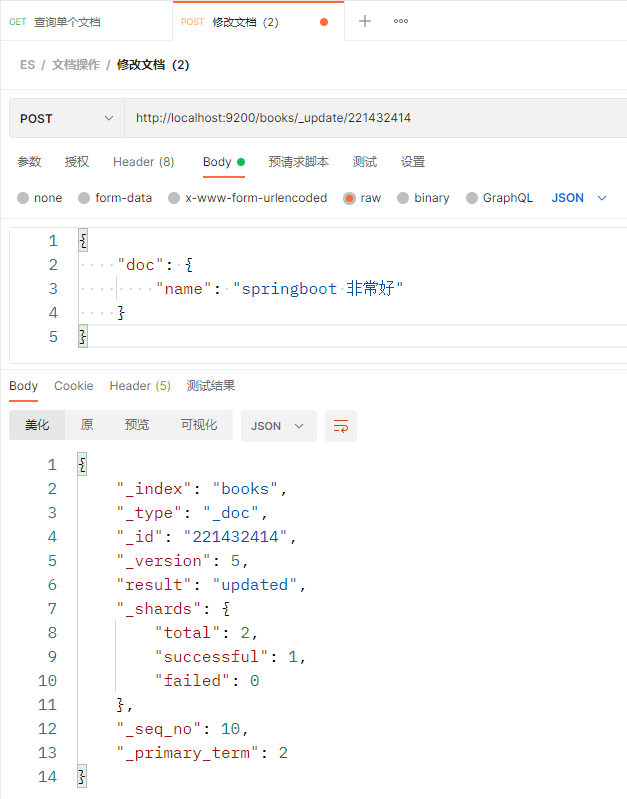
发现修改后的文档,另外两个没有修改的属性没有了,这不是期望的效果,这种请求的修改方式是全覆盖方式的修改。 如果要想只修改文档中name属性的值,需要使用新的请求方式(操作之前先将_id为221432414的文档数据恢复一下) 注意:这里发送的是POST请求,而上面的全量修改发送的是PUT请求
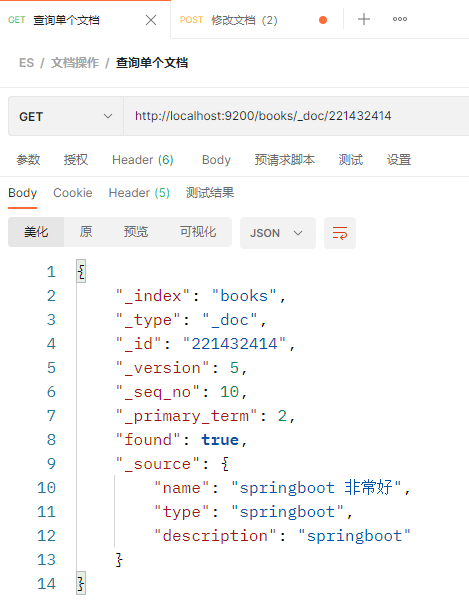
修改之后再查询一下
P104 实用开发篇-101-SpringBoot整合ES客户端操作 P105 实用开发篇-102-添加文档 P106 实用开发篇-103-查询文档 参考整合h2、redis、mongodb的方式,整合es的时候应该先在pom.xml中加入spring整合es的依赖,spring-boot-starter-data-elasticsearch,然后再去application.yml中编写es的配置,最后再去测试类里面注入es的template对象,进行相关操作。可是需要注意的是,springboot整合es有两套整合方案,一个是整合低级别的es客户端,另一个是整合高级别的es客户端。而开头所说的是springboot整合低级别的方式,这里不采用这种方式。直接整合高级别的es客户端,分为以下几个步骤: 在pom.xml中加入es的依赖,由于测试的过程中还要用到对象转json字符串,所以这里把json解析的依赖也一同加上 org.elasticsearch.client elasticsearch-rest-high-level-client com.fasterxml.jackson.core jackson-databind整合高级别的es客户端,意味着springboot没有提供默认的配置,所以就不能在application.yml中配置有关访问es客户端的url等参数了,这里直接编写测试类,采用硬编码的方式指定这些参数。 @SpringBootTest class ElasticsearchApplicationTests { // @Autowired // private ElasticsearchRestTemplate esTemplate; @Autowired private BookMapper bookMapper; private RestHighLevelClient client; // json转换工具 private static ObjectMapper objectMapper; @Test public void testConnect() throws IOException { HttpHost host = HttpHost.create("http://localhost:9200"); RestClientBuilder builder = RestClient.builder(host); client = new RestHighLevelClient(builder); client.close(); } @Test // 创建索引 public void testCreateIndex() throws IOException { CreateIndexRequest request = new CreateIndexRequest("books"); client.indices().create(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT); } @Test // 使用IK分词器创建索引 public void testCreateIndexByIK() throws IOException { CreateIndexRequest request = new CreateIndexRequest("books"); // 设置请求参数 String jsonParam = "{\n" + " \"mappings\": {\n" + " \"properties\": {\n" + " \"id\": {\n" + " \"type\": \"keyword\"\n" + " },\n" + " \"name\": {\n" + " \"type\": \"text\",\n" + " \"analyzer\": \"ik_max_word\",\n" + " \"copy_to\": \"all\"\n" + " },\n" + " \"type\": {\n" + " \"type\": \"keyword\"\n" + " },\n" + " \"description\": {\n" + " \"type\": \"text\",\n" + " \"analyzer\": \"ik_max_word\",\n" + " \"copy_to\": \"all\"\n" + " },\n" + " \"all\": {\n" + " \"type\": \"text\",\n" + " \"analyzer\": \"ik_max_word\"\n" + " }\n" + " }\n" + " }\n" + "}"; request.source(jsonParam, XContentType.JSON); client.indices().create(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT); } @Test public void testCreateDoc() throws Exception { Book book = bookMapper.selectById(1); IndexRequest request = new IndexRequest("books").id(book.getId() + ""); String jsonParams = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(book); request.source(jsonParams, XContentType.JSON); client.index(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT); } @Test // 将mysql数据库tbl_book表中的数据都存到es中 public void testCreateDocAllFromMySQL() throws Exception { List books = bookMapper.selectList(null); // 批处理请求,相当于一个request容器,可以把单个请求加进来 BulkRequest requests = new BulkRequest(); for (Book book : books) { IndexRequest request = new IndexRequest("books").id(book.getId() + ""); String jsonParams = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(book); request.source(jsonParams, XContentType.JSON); requests.add(request); } client.bulk(requests, RequestOptions.DEFAULT); } @Test // 按ID查询 public void testGet() throws IOException { GetRequest request = new GetRequest("books", "1"); GetResponse response = client.get(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT); System.out.println("book:" + response.getSourceAsString()); } @Test public void testSearch() throws IOException { SearchRequest request = new SearchRequest("books"); SearchSourceBuilder builder = new SearchSourceBuilder(); builder.query(QueryBuilders.termQuery("all", "spring")); request.source(builder); SearchResponse response = client.search(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT); SearchHits hits = response.getHits(); for (SearchHit hit : hits) { System.out.println(hit.getSourceAsString()); } } @BeforeEach void setUp() { objectMapper = new ObjectMapper(); HttpHost host = HttpHost.create("http://localhost:9200"); RestClientBuilder builder = RestClient.builder(host); client = new RestHighLevelClient(builder); } @AfterEach void tearDown() throws IOException { client.close(); } } 16. 整合第三方技术 16.1 缓存 springboot_16_01_01_cache_book_quickstartP107 实用开发篇-104-缓存的作用 P108 实用开发篇-105-Spring缓存使用方式 先自己用java的HashMap模拟一个缓存 BookController.java @GetMapping("{id}") // 模拟缓存 public R getById(@PathVariable Integer id) { return new R(true, bookService.getById(id)); }BookServiceImpl.java @Override // 模拟缓存 private HashMap cache = new HashMap(); public Book getById(Serializable id) { // 如果当前缓存中没有本次要查询的数据,则进行查询,否则直接从缓存中获取数据返回 Book book = cache.get(id); if (book == null) { book = super.getById(id); cache.put(id, book); } return book; } springboot_16_01_02_cache_book_simple使用spring中自带的缓存技术 在pom.xml中添加如下依赖 org.springframework.boot spring-boot-starter-cache在springboot启动类上加@EnableCaching注解 在业务层要使用缓存的方法上加上@Cacheable(value = "cacheSpace", key = "#id")注解,如下所示 @Cacheable(value = "cacheSpace", key = "#id") public Book getById(Serializable id) { System.out.println("id = " + id); return super.getById(id); }其中value表示缓存空间,key=“#id”,表示将方法参数id的值作为缓存中的一个key。 springboot_16_01_03_cache_smscode_simpleP109 实用开发篇-106-手机验证码案例-生成验证码 手机验证码案例基础代码准备 存储手机号和验证码的实体类SMSCode.java @Data public class SMSCode { private String phone; private String code; }生成验证码的工具类CodeUtils.java @Component public class CodeUtils { private final String padding = "000000"; // 生成验证码(位数少于6位左边填充0,填充方法1) public String generateCode(String phone) { int hash = phone.hashCode(); int encryption = 20228888; long result = hash ^ encryption; long nowTime = System.nanoTime(); result = (result ^ nowTime) % 1000000; String code = result + ""; // code = phone; // padding.substring(code.length()) code.length() // 6 // 0 5 // 00 4 // 000 3 // 000 3 // 0000 2 // 00000 1 // 000000 0 code = padding.substring(code.length()) + code; // System.out.println(code); return code; } private final String[] patch = {"000000", "00000", "0000", "000", "00", "0", ""}; // 生成验证码(位数少于6位左边填充0,填充方法2) public String generateCode1(String phone) { int hash = phone.hashCode(); int encryption = 20228888; long result = hash ^ encryption; long nowTime = System.nanoTime(); result = (result ^ nowTime) % 1000000; String code = result + ""; // code = phone; // patch[code.length] code.length() // 000000 0 // 00000 1 // 0000 2 // 000 3 // 00 4 // 0 5 // 6 code = patch[code.length()] + code; // System.out.println(code); return code; } // 根据手机号从缓存中获取验证码,缓存中有的话返回缓存中的值,没有的话就返回null @Cacheable(value = "smsCode", key = "#phone") public String getCodeByPhoneFromCache(String phone) { return null; } }业务层接口SMSCodeService.java public interface SMSCodeService { String sendCodeToSMS(String phone); boolean checkCode(SMSCode smsCode); }业务层接口实现类SMSCodeServiceImpl.java @Service public class SMSCodeServiceImpl implements SMSCodeService { @Autowired private CodeUtils codeUtils; @Override public String sendCodeToSMS(String phone) { return codeUtils.generateCode(phone); } @Override public boolean checkCode(SMSCode smsCode) { return false; } }加入spring默认的缓存功能 在pom.xml中添加缓存依赖 org.springframework.boot spring-boot-starter-cache在SMSCodeServiceImpl的sendCodeToSMS()方法上添加@CachePut(value = "smsCode", key = "#phone"),如下所示 @Override // @Cacheable(value = "smsCode", key = "#phone") // 这里@Cacheable注解不适用,因为@Cacheable注解的功能是:如果缓存中没有值就去执行一次方法,然后将值存到缓存中, // 如果有值就直接从缓存中取值并返回,并不会执行方法,因而缓存中值不会发生改变。 // 而用户点击界面发送一次验证码就调用了一次该方法,需要获取到新的验证码。 // 使用新的缓存注解@CachePut可以解决这个问题,每次调用都会执行方法,向缓存中存新的值并返回 @CachePut(value = "smsCode", key = "#phone") public String sendCodeToSMS(String phone) { return codeUtils.generateCode(phone); }编写checkCode()方法:校验验证码是否正确 错误的写法: @Override public boolean checkCode(SMSCode smsCode) { // 取出缓存中的验证码并与传递过来的验证码比对,如果相同,返回true,否则,返回false // 用户填写的验证码 String code = smsCode.getCode(); // 缓存中存的验证码 String cacheCode = getCodeByPhoneFromCache(smsCode.getPhone()); return cacheCode.equals(code); } // 根据手机号从缓存中获取验证码,缓存中有的话返回缓存中的值,没有的话就返回null @Cacheable(value = "cacheSpace", key = "#phone") public String getCodeByPhoneFromCache(String phone) { return null; }在getCodeByPhoneFromCache()方法上加了@Cacheable(value = "cacheSpace", key = "#phone"),然后在checkCode()方法中调用getCodeByPhoneFromCache()方法,这种方式看似是正确的,实际上@Cacheable注解不会生效,导致getCodeByPhoneFromCache()的返回值始终是null。这是由于被spring管理的类内的方法互调注解不会被解析。 由此可以想到解决办法,将getCodeByPhoneFromCache()放到另外一个类(这里为了方便起见,直接放到CodeUtils类中),并将这个类交由spring管理(在类上面加@Component注解),然后再用codeUtils.getCodeByPhoneFromCache(smsCode.getPhone())即可正常从缓存中拿到值。代码如下: @Override public boolean checkCode(SMSCode smsCode) { // 取出缓存中的验证码并与传递过来的验证码比对,如果相同,返回true,否则,返回false // 用户填写的验证码 String code = smsCode.getCode(); // 缓存中存的验证码 String cacheCode = codeUtils.getCodeByPhoneFromCache(smsCode.getPhone()); return cacheCode.equals(code); } springboot_16_01_04_cache_smscode_ehcacheP111 实用开发篇-108-变更缓存供应商Ehcache 基于验证码案例的代码和配置,使用ehcache替换spring默认的simple缓存 在pom.xml中加入ehcache的依赖 net.sf.ehcache ehcache在application.yml中加入如下配置 spring: cache: type: ehcache # 如果配置文件改名了,可以打开下面的配置指定配置文件路径 # ehcache: # config: ehcache-xxx.xml在resources目录下新建一个ehcache.xml配置文件,内容如下: 直接启动项目,并且验证码获取和验证的过程不报错,说明缓存替换成成功。 P112 补 知识加油站-04-数据淘汰策略 LRU: Least recently used, 淘汰最近最少被使用的数据LFU: Least frequently used,淘汰使用频率最低的数据 springboot_16_01_05_cache_smscode_redisP113 实用开发篇-109-变更缓存供应商Redis 基于验证码案例的代码和配置,使用redis替换spring默认的simple缓存 在pom.xml中加入redis的依赖 org.springframework.boot spring-boot-starter-data-redis在application.yml中加入如下配置 spring: cache: type: redis redis: # 是否使用缓存命名空间作为前缀,如:smsCode::18866668888,默认为true use-key-prefix: true cache-null-values: true # 是否缓存空值 key-prefix: aa # use-key-prefix为false的时候该项不生效 time-to-live: 10s # 缓存失效时间 redis: host: 192.168.0.110 port: 6379 password: 123456直接启动项目,并且验证码获取和验证的过程不报错,说明缓存替换成成功。 springboot_16_01_06_cache_smscode_memcachedP114 实用开发篇-110-memcached下载与安装 安装步骤以及下载地址:https://www.runoob.com/memcached/window-install-memcached.html P115 实用开发篇-111-变更缓存供应商memcached 基于验证码案例的代码和配置,使用memcached替换spring默认的simple缓存,memcached最新的客户端技术是xmemcached 在pom.xml中加入xmemcached的依赖 com.googlecode.xmemcached xmemcached 2.4.7由于springboot并未收录memcached,所以只能通过硬编码的方式完成相关配置 XMemcachedConfig.java @Component public class XMemcachedConfig { @Bean public MemcachedClient getMemcachedClient() throws IOException { MemcachedClientBuilder memcachedClientBuilder = new XMemcachedClientBuilder("192.168.0.102:11211"); MemcachedClient memcachedClient = memcachedClientBuilder.build(); return memcachedClient; } }SMSCodeServiceImpl.java @Service public class SMSCodeServiceImpl implements SMSCodeService { @Autowired private CodeUtils codeUtils; @Autowired private MemcachedClient memcachedClient; @Override public String sendCodeToSMS(String phone) { String code = codeUtils.generateCode(phone); try { memcachedClient.set(phone, 10, code); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return code; } @Override public boolean checkCode(SMSCode smsCode) { String code = null; try { code = memcachedClient.get(smsCode.getPhone()).toString(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return smsCode.getCode().equals(code); } }直接启动项目,并且验证码获取和验证的过程不报错,说明缓存替换成成功。 到这里整合memcached算是成功了,可是配置都写死在代码中了,不太方便,这里可以结合前面的Configuration属性绑定的内容将配置抽取到application.yml文件中。 先定义一个实体类XMemcachedProperties,保存XMemcached的配置属性,并加上@Component和@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "memcached")注解 @Component @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "memcached") @Data public class XMemcachedProperties { private String addressList; private int poolSize; private long opTimeout; }在application.yml中加入如下配置: memcached: address-list: 192.168.0.102:11211 poolSize: 10 opTimeout: 3000在XMemcachedConfig类中使用XMemcachedProperties类中封装的配置属性 @Component public class XMemcachedConfig { @Autowired private XMemcachedProperties xMemcachedProperties; @Bean public MemcachedClient getMemcachedClient() throws IOException { MemcachedClientBuilder memcachedClientBuilder = new XMemcachedClientBuilder(xMemcachedProperties.getAddressList()); memcachedClientBuilder.setConnectionPoolSize(xMemcachedProperties.getPoolSize()); memcachedClientBuilder.setOpTimeout(xMemcachedProperties.getOpTimeout()); MemcachedClient memcachedClient = memcachedClientBuilder.build(); return memcachedClient; } } springboot_16_01_07_cache_smscode_jetcacheP116 实用开发篇-112-jetcache远程缓存方案 基于验证码案例的代码和配置,使用redis替换spring默认的simple缓存 在pom.xml中加入redis的依赖 org.springframework.boot spring-boot-starter-data-redis在application.yml中加入如下配置 spring: cache: type: redis redis: # 是否使用缓存命名空间作为前缀,如:smsCode::18866668888,默认为true use-key-prefix: true cache-null-values: true # 是否缓存空值 key-prefix: aa # use-key-prefix为false的时候该项不生效 time-to-live: 10s # 缓存失效时间 redis: host: 192.168.0.110 port: 6379 password: 123456直接启动项目,并且验证码获取和验证的过程不报错,说明缓存替换成成功。 P117 实用开发篇-113-jetcache本地缓存方案 jetcache是阿里巴巴公司的缓存技术,可以同时支持本地和远程两种缓存,所谓本地就是使用HashMap类似的技术做的缓存,远程就是可以连接到redis。 基于验证码案例的代码和配置,使用jetcache替换spring默认的simple缓存 springboot整合jetcache的时候使用2.6.3版本会报循环依赖的错误,我在网上搜索了一个解决循环依赖的方法,链接地址:https://blog.csdn.net/chengxuyuanjava123/article/details/122459521较复杂,仅供参考。教程的弹幕中有个小伙伴讲springboot 2.5.4版本和jetcache整合不会出现这个问题,我就尝试了一下,居然真的可以,所以我就暂时使用了这个简单的方法。使用了springboot 2.5.4,有更好的办法解决这个问题的小伙伴,可以评论区告知,谢谢。 首先用jetcache的远程方案,也就是底层用redis作为真正的缓存工具。 在pom.xml中加入jetcache的依赖 com.alicp.jetcache jetcache-starter-redis 2.6.2在application.yml中加入如下配置 # 配置jetcache jetcache: areaInCacheName: false # 是否把area加入的缓存的key中,默认为true # 远程方案 remote: default: type: redis host: 192.168.0.110 port: 6379 password: 123456 # keyConvertor: fastjson # valueEncoder: java # valueDecoder: java poolConfig: # minIdle: 5 # maxIdle: 20 maxTotal: 50 # 如果自定义命名空间,需要在@CreateCache注解中添加area=“sms”,不写默认为default # sms: # type: redis # host: localhost # port: 6379 # password: 123456 # poolConfig: # maxTotal: 50在springboot启动类上加@EnableCreateCacheAnnotation注解 在业务层类SMSCodeServiceImpl中使用缓存 @Service public class SMSCodeServiceImpl implements SMSCodeService { @Autowired private CodeUtils codeUtils; // 1、定义一个缓存 @CreateCache(name = "jetCache_", expire = 10, timeUnit = TimeUnit.SECONDS) private Cache jetCache; @Override public String sendCodeToSMS(String phone) { String code = codeUtils.generateCode(phone); // 2、向缓存中存值 jetCache.put(phone, code); return code; } @Override public boolean checkCode(SMSCode smsCode) { if (smsCode == null) { return false; } // 取出缓存中的验证码并与传递过来的验证码比对,如果相同,返回true,否则,返回false // 用户填写的验证码 String code = smsCode.getCode(); // 3、获取缓存中存的验证码 String cacheCode = jetCache.get(smsCode.getPhone()); return code.equals(cacheCode); } }直接启动项目,并且验证码获取和验证的过程不报错,说明缓存替换成成功。 再使用jetcache的本地方案 修改application.yml中jetcache的配置 # 配置jetcache jetcache: areaInCacheName: false # 是否把area加入的缓存的key中,默认为true # 本地方案 local: default: type: linkedhashmap keyConvertor: fastjson # 将对象转换成key使用的技术,这里转成json # limit: 100 # 远程方案 remote: default: type: redis host: 192.168.0.110 port: 6379 password: 123456 # keyConvertor: fastjson # valueEncoder: java # valueDecoder: java poolConfig: # minIdle: 5 # maxIdle: 20 maxTotal: 50 # 如果自定义命名空间,需要在@CreateCache注解中添加area=“sms”,不写默认为default # sms: # type: redis # host: localhost # port: 6379 # password: 123456 # poolConfig: # maxTotal: 50将SMSCodeServiceImpl.java中的@CreateCache注解中指定cacheType = CacheType.LOCAL @Service public class SMSCodeServiceImpl implements SMSCodeService { @Autowired private CodeUtils codeUtils; // 1、定义一个缓存 // remote方案 // @CreateCache(area="sms", name = "jetCache_", expire = 10, timeUnit = TimeUnit.SECONDS) // 本地方案(查看源码知晓,如果不指定cacheType = CacheType.LOCAL,默认为远程。) @CreateCache(name = "jetCache_", expire = 10, timeUnit = TimeUnit.SECONDS, cacheType = CacheType.LOCAL) // 还可以指定远程和本地两种缓存方案共存 // @CreateCache(name = "jetCache_", expire = 10, timeUnit = TimeUnit.SECONDS, cacheType = CacheType.BOTH) private Cache jetCache; @Override public String sendCodeToSMS(String phone) { String code = codeUtils.generateCode(phone); // 2、向缓存中存值 jetCache.put(phone, code); return code; } @Override public boolean checkCode(SMSCode smsCode) { if (smsCode == null) { return false; } // 取出缓存中的验证码并与传递过来的验证码比对,如果相同,返回true,否则,返回false // 用户填写的验证码 String code = smsCode.getCode(); // 3、获取缓存中存的验证码 String cacheCode = jetCache.get(smsCode.getPhone()); return code.equals(cacheCode); } }如果远程和本地两种方案都启用,只需要将SMSCodeServiceImpl.java中的@CreateCache注解中指定cacheType = CacheType.BOTH即可。 另附:jetcache详细配置属性
P118 实用开发篇-114-jetcache方法缓存 jetcache也可以和spring默认的simple-cache一样在方法上加上缓存注解。这里为了体现对缓存的增删改查更多的操作,基于springboot_16_01_02_cache_Book_simple案例的代码进行修改。 在pom.xml中加入jetcache的依赖 com.alicp.jetcache jetcache-starter-redis 2.6.2在application.yml中加入如下配置 # 配置jetcache jetcache: statIntervalMinutes: 1 # 按照统计间隔打印输出缓存命中率,0表示不统计,默认为0 areaInCacheName: false # 是否把area加入的缓存的key中,默认为true # 远程方案 remote: default: type: redis host: 192.168.0.110 port: 6379 password: 123456 keyConvertor: fastjson valueEncoder: java valueDecoder: java poolConfig: # minIdle: 5 # maxIdle: 20 maxTotal: 50 # 如果自定义命名空间,需要在@CreateCache注解中添加area=“sms”,不写默认为default # sms: # type: redis # host: localhost # port: 6379 # password: 123456 # poolConfig: # maxTotal: 50在springboot的启动类上加@EnableMethodCache(basePackages = "top.jacktgq"),其中basePackages=“top.jacktgq"中的包名需要覆盖到用到缓存的业务类,另外@EnableMethodCache注解需要依赖@EnableCreateCacheAnnotation注解。如下所示。 @SpringBootApplication // jetcache启用缓存的主开关 @EnableCreateCacheAnnotation // 开启方法缓存注解, @EnableMethodCache(basePackages = "top.jacktgq") public class CacheApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(CacheApplication.class, args); } }在BookServiceImpl类中添加方法缓存注解 这里需要参考springboot_16_01_03_cache_smscode,在CodeUtils.java的getCodeByPhoneFromCache()方法上添加@Cached(name = "smsCode", key = "#", expire = 10),其中name和之前的spring自带缓存的@Cacheable注解中的value一样都表示缓存的命名空间,key和@Cacheable中的key一样,expire表示缓存失效时间,默认单位为秒,不指定就是永不失效。如下所示。 如果在修改操作后想更新缓存,可以在修改方法上加上@CacheUpdate(name = "book_", key = "#book.id", value = "#book")注解; 如果想在删除操作后删除对应缓存,可以在删除方法上加上@CacheInvalidate(name = "book_", key = "#id")注解。 如果数据库由多个业务系统共用,一个系统对数据库的修改不能同步到另一个系统的缓存,这时就需要使用的到@CacheRefresh(refresh = 5),其中refresh=5,表示每隔5秒钟刷新一次缓存。 具体代码如下: @Override @Cached(name = "book_", key="#id", expire = 3600) @CacheRefresh(refresh = 5) public Book getById(Serializable id) { return super.getById(id); } @Override @CacheUpdate(name = "book_", key = "#book.id", value = "#book") public boolean updateById(Book book) { return super.updateById(book); } @Override @CacheInvalidate(name = "book_", key = "#id") public boolean removeById(Serializable id) { return super.removeById(id); } @Override public IPage getPage(int currentPage, int pageSize) { IPage page = new Page(currentPage, pageSize); bookMapper.selectPage(page, null); return page; }注:如果这里被@Cache注解修饰的方法的返回值为普通的实体类,那么这个实体类需要实现Serializable接口,并且在application.yml配置文件的jetcache下配置 keyConvertor: fastjson, valueEncoder: java, valueDecoder: java,否则会报错。 Book实体类要实现Serializable接口 @Component @Data public class Book implements Serializable { private Integer id; private String name; private String type; private String description; }在application.yml配置文件的jetcache下配置valueEncoder: java, valueDecoder: java # 配置jetcache jetcache: statIntervalMinutes: 1 # 按照统计间隔打印输出缓存命中率,0表示不统计,默认为0 areaInCacheName: false # 是否把area加入的缓存的key中,默认为true # 本地方案 local: default: type: linkedhashmap keyConvertor: fastjson # 将对象转换成key使用的技术,这里转成json # limit: 100 # 远程方案 remote: default: type: redis host: 192.168.0.110 port: 6379 password: 123456 keyConvertor: fastjson valueEncoder: java valueDecoder: java poolConfig: # minIdle: 5 # maxIdle: 20 maxTotal: 50 springboot_16_01_09_cache_smscode_j2cache_ehcache_redisP119 实用开发篇-115-j2cache基本操作 j2cache是一个缓存整合框架,可以提供缓存的整合方案,使个各种缓存搭配使用,自身不提供缓存功能。 这里基于验证码案例的代码和配置,使用j2cache整合ehcache和redis替换spring原有的simple缓存。 在pom.xml中加入j2cache的相关依赖 net.oschina.j2cache j2cache-core 2.8.4-release net.oschina.j2cache j2cache-spring-boot2-starter 2.8.0-release net.sf.ehcache ehcache在resources目录下创建配置文件 ehcache.xml j2cache.properties # 一级缓存 j2cache.L1.provider_class = ehcache ehcache.configXml = ehcache.xml # 二级缓存 j2cache.L2.provider_class = net.oschina.j2cache.cache.support.redis.SpringRedisProvider j2cache.L2.config_section = redis redis.hosts = 192.168.0.110:6379 redis.timeout = 2000 redis.password = 123456 # 指定模式,可以消除一行警告信息 redis.mode = single # 一级缓存中的数据如何到达二级缓存 j2cache.broadcast = net.oschina.j2cache.cache.support.redis.SpringRedisPubSubPolicy更详细的配置内容可以去j2cache的jar包路径下寻得
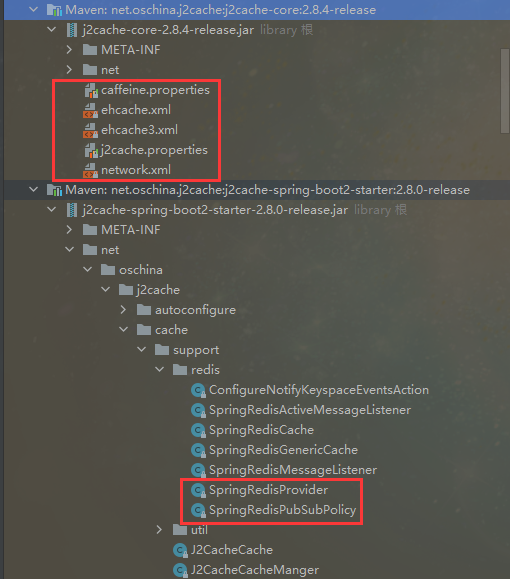
在SMSCodeServiceImpl类中编写j2cache相关代码 @Service public class SMSCodeServiceImpl implements SMSCodeService { @Autowired private CodeUtils codeUtils; @Autowired private CacheChannel cacheChannel; @Override public String sendCodeToSMS(String phone) { String code = codeUtils.generateCode(phone); cacheChannel.set("sms", phone, code); return code; } @Override public boolean checkCode(SMSCode smsCode) { if (smsCode == null) { return false; } // 取出缓存中的验证码并与传递过来的验证码比对,如果相同,返回true,否则,返回false // 用户填写的验证码 String code = smsCode.getCode(); // 缓存中存的验证码 String cacheCode = cacheChannel.get("sms", smsCode.getPhone()).asString(); return code.equals(cacheCode); } }注:如果运行工过程中报如下错误: Caused by: net.sf.ehcache.CacheException: Another unnamedCacheManager already exists in the same VM. Please provide uniquenames for each CacheManagerxxxxxxxxxx1 1Caused by: net.sf.ehcache.CacheException: Another unnamed CacheManager alreadyCaused by: net.sf.ehcache.CacheException: Another unnamedCacheManager already exists in the same VM. Please provide uniquenames for each CacheManager检查一下springboot启动类上面有没有多余的缓存注解,如@EnableCaching,这会跟j2cache发生冲突,j2cache不需要在springboot启动类上面加注解,复制项目的时候需要小心。 消除一些警告日志 到此项目是可以正常启动的,功能也正常,但是控制台报了一些警告信息 日志冲突异常 SLF4J: Class path contains multiple SLF4J bindings. SLF4J: Found binding in [jar:file:/D:/repository/ch/qos/logback/logback-classic/1.2.10/logback-classic-1.2.10.jar!/org/slf4j/impl/StaticLoggerBinder.class] SLF4J: Found binding in [jar:file:/D:/repository/org/slf4j/slf4j-simple/1.7.33/slf4j-simple-1.7.33.jar!/org/slf4j/impl/StaticLoggerBinder.class] SLF4J: See http://www.slf4j.org/codes.html#multiple_bindings for an explanation. SLF4J: Actual binding is of type [ch.qos.logback.classic.util.ContextSelectorStaticBinder]冲突的意思是slf4j-simple和logback-classic发生了冲突,这里选择保留springboot默认的logback日志,排除slf4j-simple。打开maven面板,选中项目,然后点击显示依赖项按钮,
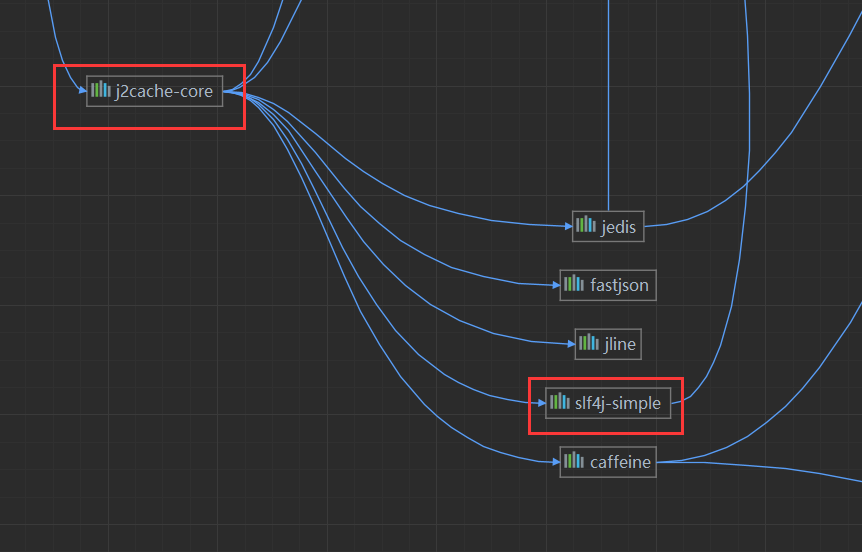
会弹出一个依赖项拓扑图,在拓扑图中寻找到slf4j-simple的上层包为j2cache-core
去pom.xml中的j2cache-core的依赖中排除slf4j-simple即可 net.oschina.j2cache j2cache-core 2.8.4-release org.slf4j slf4j-simple再启动项目,就不会再报这个警告了。 P120 实用开发篇-116-j2cache相关配置 在application.yml中对j2cache的其他配置 # 指定命名空间,可以作为key的公共前缀 redis.namespace = j2cache # 设置是否启用二级缓存,默认为true j2cache.l2-cache-open = false 16.2 任务 springboot_16_02_01_task_quartzP121 实用开发篇-117-springboot整合quartz springboot整合quartz分为以下几个步骤: 在pom.xml中加入Springboot整合quartz的依赖 org.springframework.boot spring-boot-starter-quartz在springboot程序启动类上加@EnableScheduling注解,开启定时任务功能 //开启定时任务功能 @EnableScheduling编写一个类MyQuartz继承QuartzJobBean,作为Quartz要执行的工作(任务) public class MyQuartz extends QuartzJobBean { @Override protected void executeInternal(JobExecutionContext context) throws JobExecutionException { System.out.println("Quartz task run..."); } }编写一个QuartzConfig类,配置Quartz具体的执行过程,并加上@Configuration注解 @Configuration public class QuartzConfig { @Bean public JobDetail printJobDetail() { //绑定具体的工作 return JobBuilder.newJob(MyQuartz.class).storeDurably().build(); } @Bean public Trigger printJobTrigger() { CronScheduleBuilder scheduleBuilder = CronScheduleBuilder.cronSchedule("0/5 * * * * ?"); // 绑定具体的工作明细 return TriggerBuilder.newTrigger().forJob(printJobDetail()).withSchedule(scheduleBuilder).build(); } }直接启动springboot程序,任务便会自动执行 springboot_16_02_02_task_springP122 实用开发篇-118-springboot整合task 使用springboot自带的定时任务 在springboot程序启动类上加@EnableScheduling注解,开启定时任务功能 //开启定时任务功能 @EnableScheduling编写一个任务类,加上@Component注解,要定时执行的方法上加上@Scheduled(cron = "0/3 * * * * ?"),用cron表达式指定执行的周期 @Component public class MyTask { @Scheduled(cron = "0/3 * * * * ?") public void print() { System.out.println("spring task run..."); } }直接启动springboot程序,任务便会自动执行 Spring Task还可以在application.yml文件中进行更细致的配置 spring: task: scheduling: # 任务调度的线程池的大小 pool: size: 1 # 调度线程名称前缀 默认 scheduling-,方便调试时使用 thread-name-prefix: spring_task_ shutdown: # 线程池关闭时等待所有任务完成 await-termination: false # 调度线程关闭前最大等待时间,确保最后一定关闭 await-termination-period: 10s 16.3 邮件 springboot_16_03_mailP123 实用开发篇-119-发送简单邮件 完成代码发邮件案例之前先准备好两个邮箱,这里采用一个QQ邮箱和一个163邮箱,后面用这两个邮箱互相发送消息。 代码发邮件采用的是SMTP协议,收邮件采用的是POP3或者IMAP协议,使用代码发邮件需要在配置文件中填写账号和授权码,授权码需要去邮箱管理后台界面进行设置。 QQ邮箱开启POP3/SMTP服务,获取授权码 进入QQ邮箱主页,找到设置,然后点击账户选项
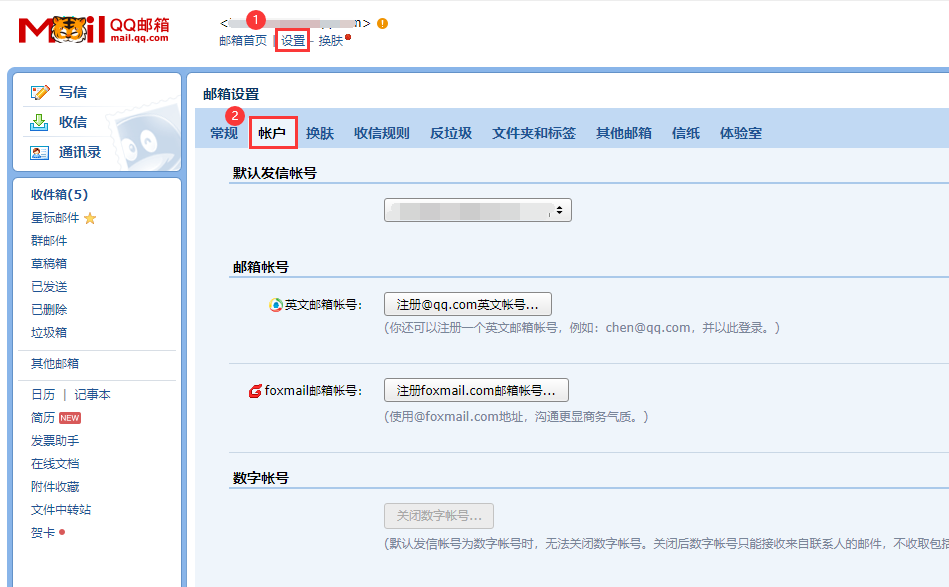
鼠标滚轮往下滑,找到POP3/SMTP服务开启的地方
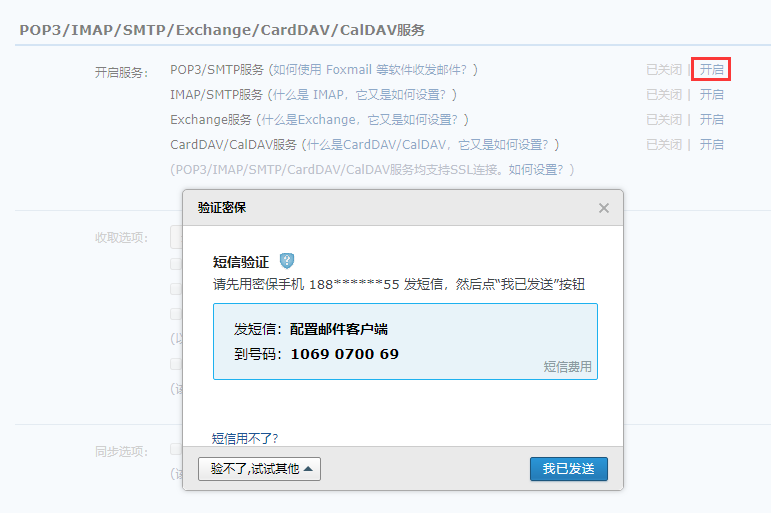
163邮箱开启POP3/SMTP服务,获取授权码 进入163邮箱主页,点击设置,选择POP3/SMTP/IMAP
点击开启IMAP/SMTP服务
发送短信获取授权码
spring整合mail 在pom.xml中加入spring整合mail的依赖 org.springframework.boot spring-boot-starter-mail在application.yml中添加邮箱的相关配置 spring: mail: host: smtp.qq.com # 邮件服务供应商 username: [email protected] # 邮箱账号 password: xxxxxxxxxxxx # 授权码业务层接口 public interface MailService { // 发送简单消息 void sendMail(); }业务层实现类,实现sendMail()方法,使用JavaMailSender类对象进行邮件的发送,这里先发送一个简单的邮件,仅包含发送人、接收人、主题、正文四项,消息需要设置到SimpleMailMessage类对象中。 @Service public class MailServiceImpl implements MailService { @Autowired private JavaMailSender javaMailSender; // 发送人 private String from = "[email protected]"; // 接收人 private String to = "[email protected]"; // 主题 private String subject = "测试发邮件"; // 正文 private String context = "测试邮件的正文内容"; @Override public void sendMail() { SimpleMailMessage msg = new SimpleMailMessage(); msg.setFrom(from); msg.setTo(to); msg.setSubject(subject); msg.setText(context); javaMailSender.send(msg); } }测试类 @SpringBootTest class MailApplicationTests { @Autowired private MailService mailService; @Test void contextLoads() { mailService.sendMail(); } }运行测试类,去收件邮箱中查看消息接收到了
如果msg.setFrom(from + "(章北海)"),那么会将收件人的邮箱前加上这个备注名称
P124 实用开发篇-120-发送多部件邮件 要想在发送邮件的时候可以带上图片或者文件等附件,需要使用MimeMessage类对象封装消息 要想正文以html格式解析,需要指定第二个参数为true 要想发送附件,需要指定第二个参数为true 具体代码如下: @Override // 发送带链接和附件的消息 public void sendMailWithLinkAttachment() throws MessagingException { MimeMessage msg = javaMailSender.createMimeMessage(); // 要想发送附件,需要指定第二个参数为true MimeMessageHelper msgHelper = new MimeMessageHelper(msg, true); msgHelper.setFrom(from + "(章北海)"); msgHelper.setTo(to); // 主题 String subject = "测试发送带链接和附件的消息"; // 正文 String context = "百度一下 ";
msgHelper.setSubject(subject);
// 要想正文以html格式解析,需要指定第二个参数为true
msgHelper.setText(context, true);
// 添加附件
File file1 = new File("D:\\ideacode\\spring-boot-study\\springboot_16_03_mail\\src\\main\\resources\\test.jpg");
File file2 = new File("D:\\ideacode\\spring-boot-study\\springboot_16_03_mail\\target\\springboot_16_03_mail-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar");
msgHelper.addAttachment(file1.getName(), file1);
msgHelper.addAttachment(file2.getName(), file2);
javaMailSender.send(msg);
} ";
msgHelper.setSubject(subject);
// 要想正文以html格式解析,需要指定第二个参数为true
msgHelper.setText(context, true);
// 添加附件
File file1 = new File("D:\\ideacode\\spring-boot-study\\springboot_16_03_mail\\src\\main\\resources\\test.jpg");
File file2 = new File("D:\\ideacode\\spring-boot-study\\springboot_16_03_mail\\target\\springboot_16_03_mail-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar");
msgHelper.addAttachment(file1.getName(), file1);
msgHelper.addAttachment(file2.getName(), file2);
javaMailSender.send(msg);
}
去邮箱中查看消息,图片和文件都顺利接收到了
P125 实用开发篇-121-消息简介
P126 实用开发篇-122-购物订单案例-发送短信 购物订单案例-发送短信基础代码准备 发送短信的业务层接口MessageService.java public interface MessageService { void sendMessage(String orderId); String doMessage(); }发送短信的业务层实现类MessageServiceImpl.java @Service public class MessageServiceImpl implements MessageService { private ArrayList msgList = new ArrayList(); @Override public void sendMessage(String orderId) { System.out.println("待发送短信的订单已纳入处理队列,id:" + orderId); msgList.add(orderId); } @Override public String doMessage() { String orderId = msgList.remove(0); System.out.println("已发送短信发送业务,id:" + orderId); return orderId; } }发送短信的表现层控制类MessageController.java @RestController @RequestMapping("/msgs") public class MessageController { @Autowired private MessageService messageService; @GetMapping public String doMessage() { String id = messageService.doMessage(); return id; } }处理订单的业务层接口OrderService.java public interface OrderService { void order(String id); }处理订单的业务层实现类OrderServiceImpl.java @Service public class OrderServiceImpl implements OrderService { @Autowired private MessageService messageService; @Override public void order(String orderId) { // 一系列的操作,包含各种服务调用,处理各种业务 System.out.println("订单开始处理"); // 短信消息处理 messageService.sendMessage(orderId); System.out.println("订单处理结束"); System.out.println(); } }处理订单的表现层控制类OrderController.java @RestController @RequestMapping("/orders") public class OrderController { @Autowired private OrderService orderService; @PostMapping("{id}") public void order(@PathVariable String orderId) { orderService.order(orderId); } }到此案例基础代码准备完成 P127 实用开发篇-123-ActiveMQ安装 下载地址:https://activemq.apache.org/components/classic/download/ 这里以windows平台为例,下载好安装包以后解压缩,去软件目录的bin\win64下面双击activemq.bat即可启动。 运行过程中报错了,发现了我电脑上的1883端口被占用
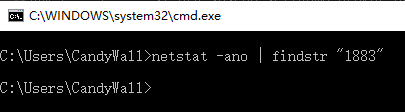
启动一个命令行,输入netstat -ano | findstr "1883"
结果居然什么也没查出来,这就奇怪了。没办法先去配置文件里面改个端口吧,编辑软件目录的conf\activemq.xml文件,然后找到标签下面的mqtt的那一项,将uri里面的端口改成8888,
改完后再启动一下ActiveMQ,没有报错
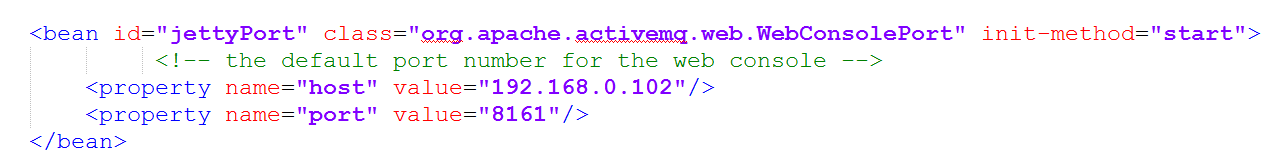
去浏览器输入http://localhost:8161,账号密码都是admin,可以登录到主界面,表示ActiveMQ启动正常 注:如果ActiveMQ不是安装在本地,比如阿里云或者局域网,需要修改软件目录的conf\jetty.xml的jettyPort属性,将默认的localhost改成实际IP地址即可。
P128 实用开发篇-124-springboot整合ActiveMQ 基于购物订单案例-发送短信案例的代码,整合ActiveMQ 在pom.xml中加入springboot整合ActiveMQ的依赖 org.springframework.boot spring-boot-starter-activemq在application.yml中加入activemq的配置 spring: activemq: broker-url: tcp://192.168.0.102:61616 jms: template: # 指定消息队列的名字 default-destination: jacktgq编写业务层接口MessageService的实现类MessageServiceActivemqImpl,注意需要将上个案例中的MessageServiceImpl类上的@Service注解去掉,要不然自动注入的时候会发生冲突。 @Service public class MessageServiceActivemqImpl implements MessageService { @Autowired private JmsMessagingTemplate messagingTemplate; @Override public void sendMessage(String orderId) { System.out.println("待发送短信的订单已纳入处理队列,id:" + orderId); // 将消息存到消息队列的时候如果不指定destination,也就是队列名,就会存到默认的队列中, 如果application.yml中没有配置默认的队列名, 就会报错 // messagingTemplate.convertAndSend(orderId); // 也可以手动指定队列名 messagingTemplate.convertAndSend("order.queue.id", orderId); } @Override public String doMessage() { // 从默认队列中获取消息 // String orderId = messagingTemplate.receiveAndConvert(String.class); // 从指定队列中获取消息 String orderId = messagingTemplate.receiveAndConvert("order.queue.id", String.class); System.out.println("已发送短信发送业务,id:" + orderId); return orderId; } }启动项目,访问下面的地址,往MQ中存取一些消息 http://localhost:8080/orders/1 http://localhost:8080/orders/2 http://localhost:8080/orders/3 http://localhost:8080/orders/4 http://localhost:8080/msgs/去MQ的后台管理页面查看一下数据储存情况
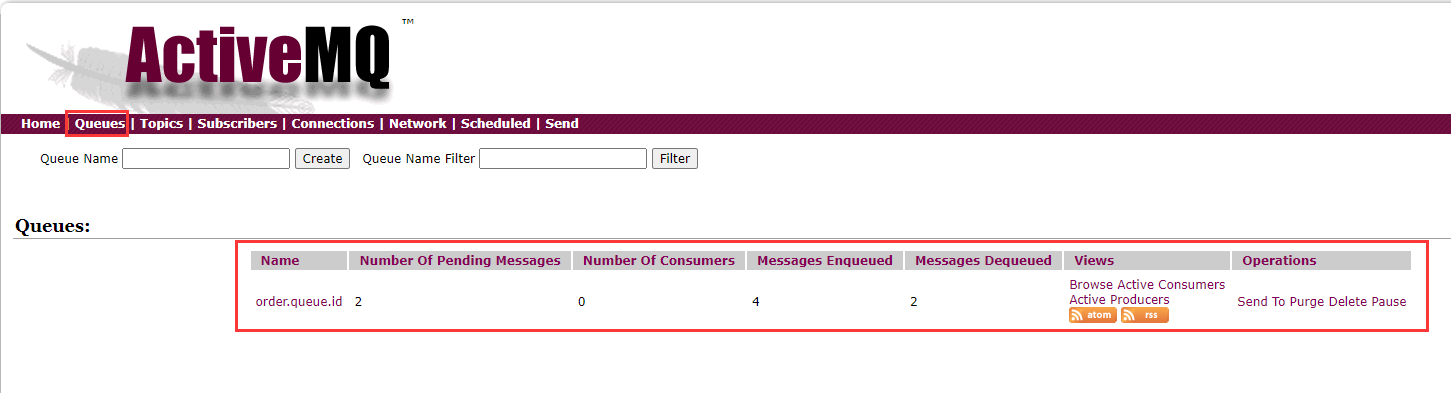
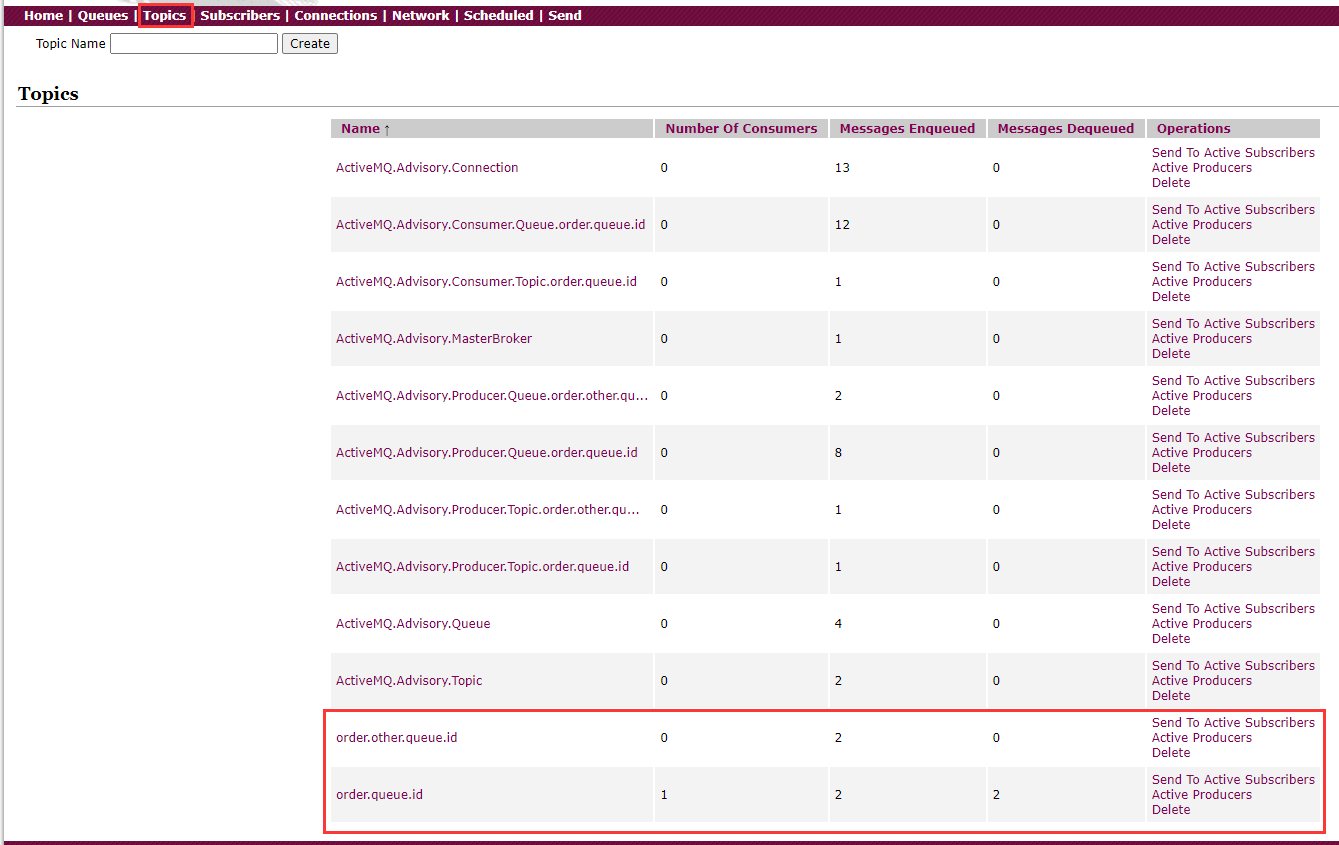
消息存取正常。 要想消息存到MQ中以后自动去消费,就要用到JMS的消息监听器技术,只要被监听的队列中接收到新的数据就会去取出来执行。 定义一个MessageListener类,在类头上加上@Component注解,将这个类交给spring管理定义一个方法receive(String orderId), 在方法上加上@JmsListener(destination = "order.queue.id"),需要指定队列名称。还可以在方法上加@SendTo("order.other.queue.id")注解将当前方法的返回值再发送到其他队列然后启动项目即可。 @Component public class MessageListener { @JmsListener(destination = "order.queue.id") // 还可以将当前方法的返回值再发送到其他队列 @SendTo("order.other.queue.id") public String receive(String orderId) { System.out.println("已完成短信发送业务,id:" + orderId); return "done::id::" + orderId; } }在application.yml文件中使用pub-sub-domain属性设置消息模型 spring: activemq: broker-url: tcp://192.168.0.102:61616 jms: # 是否使用发布订阅模型,默认为false,点对点模型 pub-sub-domain: true template: # 指定消息队列的名字 default-destination: jacktgq如果使用了发布订阅模型,那么在ActiveMQ的管理界面中查看消息,需要在Topics选项下面查找(不会发到Queues选项下面)。
P129 实用开发篇-125-RabbitMQ安装 RabbitMQ基于Erlang语言编写,需要先安装Erlang环境,类似执行java程序需要先安装jdk(jre)。 Erlang安装 下载地址:https://www.erlang.org/downloads 安装:一键傻瓜式安装,安装完毕需要重启,需要依赖windows组件 配置环境变量:ERLANG_HOME、PATH
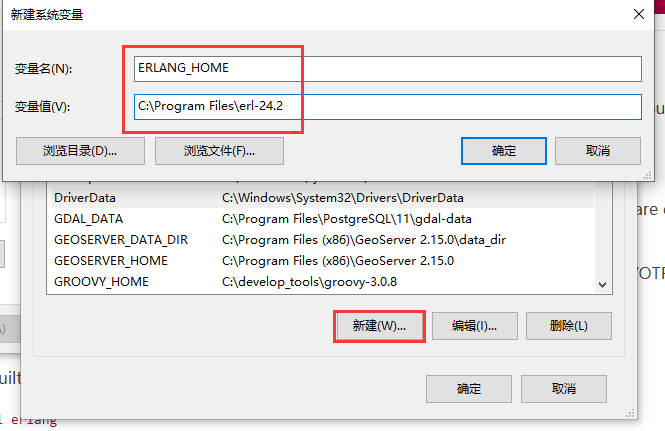
安装RabbitMQ 下载地址:https://www.rabbitmq.com/install-windows.html 找到Direct Downloads的地方,点击直接下载exe文件
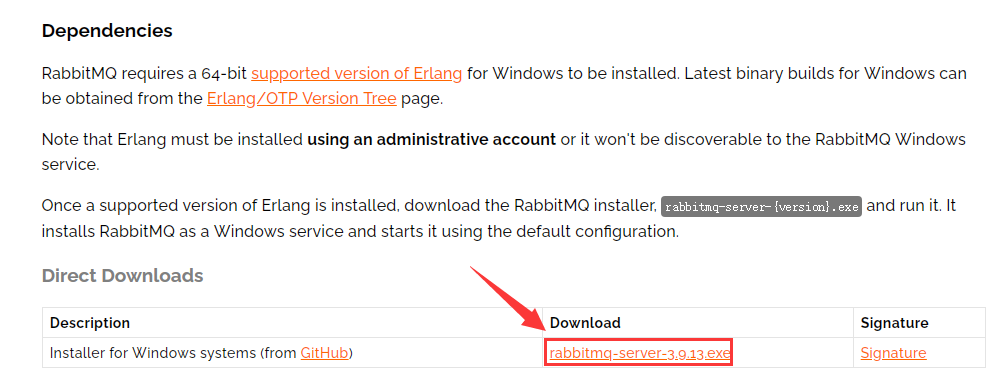
安装:一键傻瓜式安装 启动:先以管理员权限启动一个黑窗口,cd到软件安装目录的rabbitmq_server-3.9.13\sbin下,输入rabbitmq-service.bat start,提示服务已经启动即可。  在任务管理器的服务选项下面也可以找到RabbitMQ服务,以后启动和停止就可以在这里操作了
开启图形化管理页面插件 继续在刚才上面的黑窗口中输入rabbitmq-plugins.bat list,会以列表的形式枚举自带的所有插件,找到rabbitmq_management就是我们需要开启的插件。
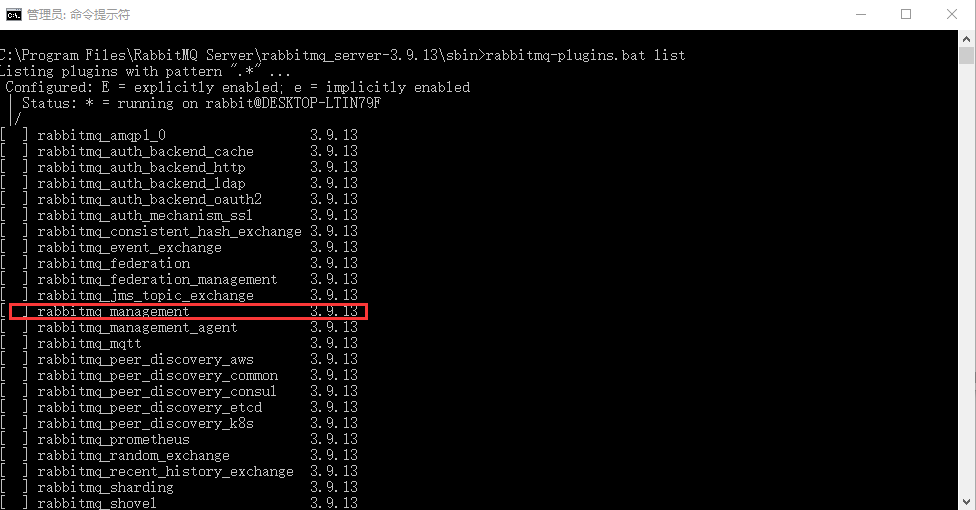
继续输入命令rabbitmq-plugins.bat enable rabbitmq_management,然后回车,会显示开启了三个关联的插件。
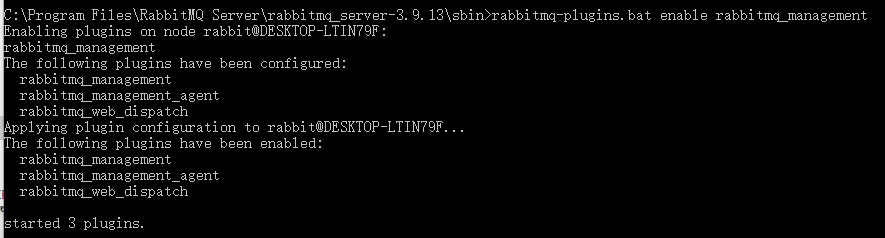
再次输入rabbitmq-plugins.bat list,这次列表中显示rabbitmq_management前面多了E*,表示这个插件处于启用状态。 去浏览器中输入http://localhost:15672/,会显示登录界面
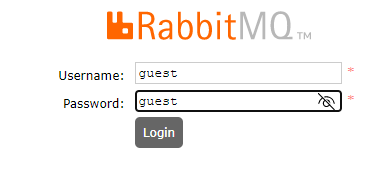
输入账号密码(都是guest),会跳转到RabbitMQ管理页面
P130 实用开发篇-126-springboot整合RabbitMQ(direct模式) 在pom.xml中加入springboot整合RabbitMQ的依赖 org.springframework.boot spring-boot-starter-amqp在application.yml中加入RabbitMQ的配置 spring: rabbitmq: host: localhost port: 5672编写RabbitDirectConfig类,配置直连模式的交换机和队列 @Configuration public class RabbitDirectConfig { @Bean // Direct模式的队列 public Queue directQueue() { // durable:是否持久化,默认false // exclusive:是否当前连接专用,默认False,连接关闭后队列即被删除 // autoDelete:是否自动删除,当生产者或消费者不再使用此队列,自动删除 // 一个参数的构造方法内部默认调用了4个参数的构造方法,后三个参数依次为true,false,false return new Queue("direct_queue"); } @Bean // Direct模式的交换机 public DirectExchange directExchange() { return new DirectExchange("directExchange"); } @Bean public Binding bindingDirect() { return BindingBuilder.bind(directQueue()).to(directExchange()).with("direct"); } }编写业务层接口MessageService的实现类MessageServiceRabbitmqDirectImpl,注意需要将上个案例中的MessageServiceImpl类上的@Service注解去掉,要不然自动注入的时候会发生冲突。 @Service public class MessageServiceRabbitmqDirectImpl implements MessageService { private AmqpTemplate amqpTemplate; @Override public void sendMessage(String orderId) { System.out.println("待发送短信的订单已纳入处理队列,id:" + orderId); // 指定RabbitDirectConfig中的内容 amqpTemplate.convertAndSend("directExchange", "direct", orderId); } @Override public String doMessage() { String orderId = (String) amqpTemplate.receiveAndConvert("directExchange"); System.out.println("已发送短信发送业务,id:" + orderId); return orderId; } }要想消息存到MQ中以后自动去消费,就要用到JMS的消息监听器技术,只要被监听的队列中接收到新的数据就会去取出来执行。 定义一个MessageListener类,在类头上加上@Component注解,将这个类交给spring管理定义一个方法receive(String orderId), 在方法上加上@RabbitListener(queues = "direct_queue"),需要指定队列名称。然后启动项目即可。 @Component public class MessageListener { @RabbitListener(queues = "direct_queue") public void receive(String orderId) { System.out.println("已完成短信发送业务(RabbitMQ Direct one),id:" + orderId); } }注: 如果这里receive()方法带了返回值,则会报错如下错误: Caused by: org.springframework.amqp.AmqpException: Cannot determine ReplyTo message网上查找相关资料后得知,出错的原因是:@RabbitListener注解修饰监听的方法添加了返回值。此方法返回的消息没有设置目的地,解决:只要把监听的方法的返回值改为void即可。 将MessageListener.java复制出来一份,然后把仅修改receive方法中的输出语句,代码如下所示: @Component public class MessageListener2 { @RabbitListener(queues = "direct_queue") public void receive(String orderId) { System.out.println("已完成短信发送业务(RabbitMQ Direct two),id:" + orderId); } }启动项目以后向消息队列中存值,查看控制台的输出语句,可以知道两个监听器轮询交替被调用。
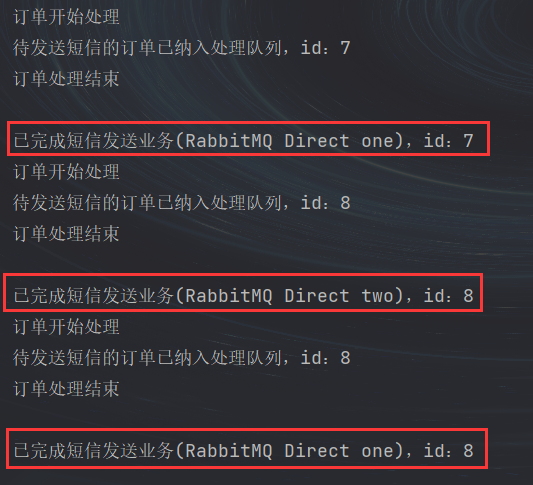
P131 实用开发篇-127-springboot整合RabbitMQ(topic模式) Topic模式的代码和Direct模式的代码很相似,所以,只需要根据Direct模式的代码复制一份修改即可。 编写RabbitTopicConfig类,配置Topic模式的交换机和队列,这里为了看效果,配置两个队列topic_queue1和topic_queue2 @Configuration public class RabbitTopicConfig { @Bean // Topic模式的队列 public Queue topicQueue1() { // durable:是否持久化,默认false // exclusive:是否当前连接专用,默认False,连接关闭后队列即被删除 // autoDelete:是否自动删除,当生产者或消费者不再使用此队列,自动删除 // 一个参数的构造方法内部默认调用了4个参数的构造方法,后三个参数依次为true,false,false return new Queue("topic_queue1"); } @Bean // Topic模式的队列 public Queue topicQueue2() { // durable:是否持久化,默认false // exclusive:是否当前连接专用,默认False,连接关闭后队列即被删除 // autoDelete:是否自动删除,当生产者或消费者不再使用此队列,自动删除 // 一个参数的构造方法内部默认调用了4个参数的构造方法,后三个参数依次为true,false,false return new Queue("topic_queue2"); } @Bean // Topic模式的交换机 public TopicExchange topicExchange() { return new TopicExchange("topicExchange"); } @Bean public Binding bindingTopic1() { return BindingBuilder.bind(topicQueue1()).to(topicExchange()).with("topic.order.id"); } @Bean public Binding bindingTopic2() { return BindingBuilder.bind(topicQueue2()).to(topicExchange()).with("id"); } }编写业务层接口MessageService的实现类MessageServiceRabbitmqTopicImpl @Service public class MessageServiceRabbitmqTopicImpl implements MessageService { @Autowired private AmqpTemplate amqpTemplate; @Override public void sendMessage(String orderId) { System.out.println("待发送短信的订单已纳入处理队列,id:" + orderId); // 指定RabbitDirectConfig中的内容 amqpTemplate.convertAndSend("topicExchange", "top.order.id", orderId); } @Override public String doMessage() { String orderId = (String) amqpTemplate.receiveAndConvert("topicExchange"); System.out.println("已发送短信发送业务,id:" + orderId); return orderId; } }要想消息存到MQ中以后自动去消费,就要用到JMS的消息监听器技术,只要被监听的队列中接收到新的数据就会去取出来执行。 定义一个MessageListener类,在类头上加上@Component注解,将这个类交给spring管理上面定义了两个队列,所以这里定义2个方法receive1(String orderId)和receive2(String orderId), 分别在方法上加上@RabbitListener(queues = "topic_queue1")和@RabbitListener(queues = "topic_queue2")监听两个队列然后启动项目即可。 @Component public class MessageListener { @RabbitListener(queues = "topic_queue1") public void receive1(String orderId) { System.out.println("已完成短信发送业务(RabbitMQ topic_queue111111),id:" + orderId); } @RabbitListener(queues = "topic_queue2") public void receive2(String orderId) { System.out.println("已完成短信发送业务(RabbitMQ topic_queue222222),id:" + orderId); } }与Direct模式不同的是,Topic模式在定义队列的时候,routingKey支持模糊匹配,比如可以在RabbitTopicConfig类中的bindingTopic1()和bindingTopic2()方法,两个方法里面的routingKey参数的指定都是绝对匹配的,发送消息的时候必须指定成一样routingKey的值才能将消息存到对应的队列中。 @Bean public Binding bindingTopic1() { return BindingBuilder.bind(topicQueue1()).to(topicExchange()).with("topic.order.id"); } @Bean public Binding bindingTopic2() { return BindingBuilder.bind(topicQueue2()).to(topicExchange()).with("id"); }如果对于with里面填的routingKey,bindingTopic1()方法中的配置为topic.*.id,bindingTopic2()方法中的配置为topic.order.*,其中*可以匹配任意单词,具体代码如下: @Bean public Binding bindingTopic1() { return BindingBuilder.bind(topicQueue1()).to(topicExchange()).with("topic.*.id"); } @Bean public Binding bindingTopic2() { return BindingBuilder.bind(topicQueue2()).to(topicExchange()).with("topic.order.*"); }这样修改后,MessageServiceRabbitmqTopicImpl类中的消息发送到消息队列的时候,amqpTemplate.convertAndSend()方法的第二个参数routingKey的值, 如果指定为topic.order.ids,那么top.order.*能匹配上,而topic.*.id不能匹配上,消息会存到名字为topic_queue2的消息队列中; 如果routingKey的值指定为top.orders.id,那么只有topic.*.id能匹配上,消息会存到名字为topic_queue1; 如果routingKey的值指定为top.orders.id,那么top.order.*和topic.*.id都能匹配上,消息就会同时存到两个队列中。 @Service public class MessageServiceRabbitmqTopicImpl implements MessageService { @Autowired private AmqpTemplate amqpTemplate; @Override public void sendMessage(String orderId) { System.out.println("待发送短信的订单已纳入处理队列,id:" + orderId); // 指定routingKey的值为topic.order.id,消息会同时存到两个消息队列中 amqpTemplate.convertAndSend("topicExchange", "topic.order.id", orderId); } @Override public String doMessage() { String orderId = (String) amqpTemplate.receiveAndConvert("topicExchange"); System.out.println("已发送短信发送业务,id:" + orderId); return orderId; } }令
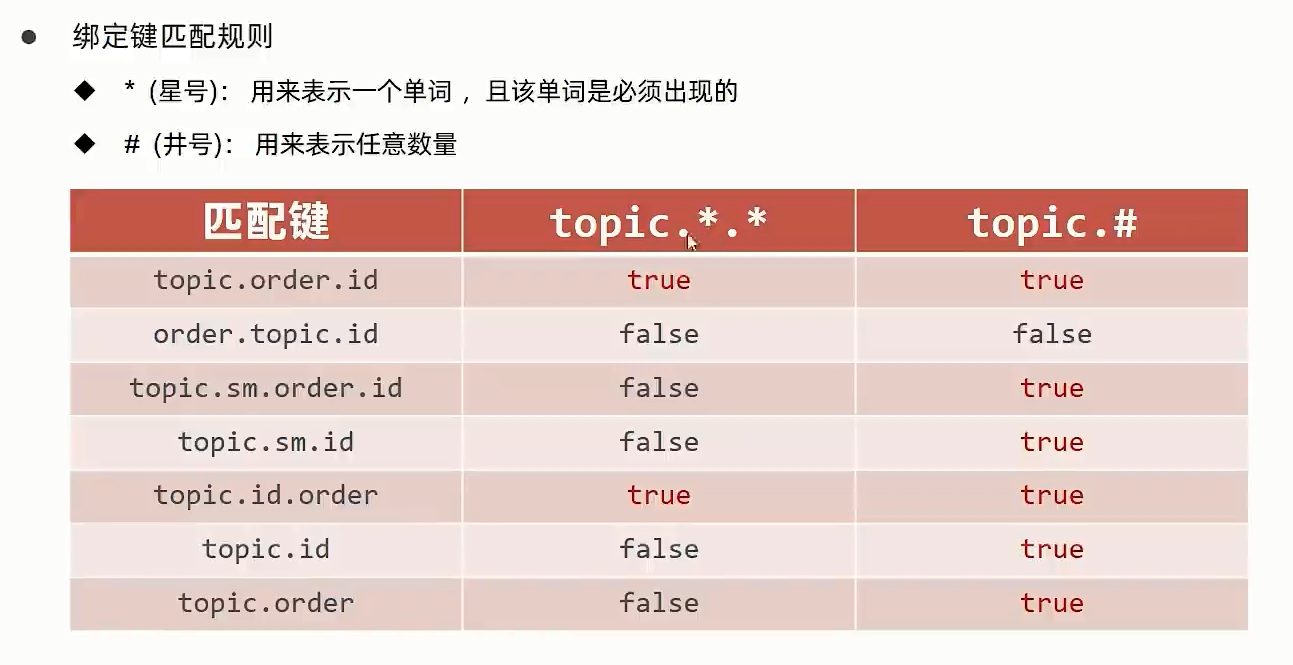
|
【本文地址】


 打开这个连接
打开这个连接