| 2 Greenplum目录结构、配置文件和环境变量 | 您所在的位置:网站首页 › greenplum集群详解 › 2 Greenplum目录结构、配置文件和环境变量 |
2 Greenplum目录结构、配置文件和环境变量
|
Greenplum目录结构、配置文件和环境变量
Greenplum目录结构、配置文件和环境变量1 日志1.1 集群初始化日志位置1.2 Greenplum日志配置方案1.3 数据库log文件1.3.1 pg_log1.3.2 pg_xlog1.3.3 pg_clog1.4 数据库的启动和关闭日志2 文件目录file layout2.1 master主机上目录结构2.1.1 软件安装目录结构2.1.2 用户HOME目录2.1.3 数据目录结构2.2 Segments主机上目录结构2.3 整体数据目录结果说明3 主要的配置文件3.1 环境文件greenplum_path.sh3.2 gp_segment ID 文件3.3 pg_hba.conf 客户端认证配置文件3.4 pg_ident.conf3.5 postgresql.conf3.6 gpinitsystem_config 1 日志 1.1 集群初始化日志位置 $HOME/gpAdminLogs 集群初始化撤销脚本:$HOME/gpAdminLogs/backout开头文件 1.2 Greenplum日志配置方案如下一共三个配置方案,可根据业务需求进行配置 参数说明logging_collector是否打印loglog_line_prefix日志格式log_directory日志保存目录log_statement打印sql 类型log_min_duration_statement*记录超时sql,超时多少秒记录**log日志方案(1)每天生成一个日志文件* log_filename = ‘postgresql-%Y-%m-%d_%H%M%S.log文件名log_truncate_on_rotation = off文件存在是否覆盖log_rotation_age = 1d间隔多长时间更换新文件log_rotation_size = 0超过大小则换一个文件log日志方案(2)每当日志写完一定大小,则换一个 log_filename = 'postgresql-%Y-%m-%d_%H%M%S.log log_truncate_on_rotation = off log_rotation_age = 0 log_rotation_size = 10M *log日志方案(3)只保留7天的日志,循环替换* log_filename = 'postgresql-%a.log星期log_truncate_on_rotation = on开启覆盖log_rotation_age = 1d log_rotation_size = 0
1.3 数据库log文件 1.3.1 pg_log 这个日志一般是记录服务器与DB的状态,比如各种Error信息,定位慢查询SQL,数据库的启动关闭信息,发生checkpoint过于频繁等的告警信息,诸如此类。linux自带的路径一般在/var/log/postgres下面。该日志有.csv格式和.log。个人建议用前一种,因为一般会按大小和时间自动切割,毕竟查看一个巨大的日志文件比查看不同时间段的多个日志要难得多。另外这种日志是可以被清理删除,压缩打包或者转移,同时并不影响DB的正常运行。当我们有遇到DB无法启动或者更改参数没有生效时,第一个想到的就是查看这个日志。 共有四类,FATAL-严重告警,ERROR-错误,WARNING-警告,LOG-操作日志。由于是文本文件所以查询检索很不方便,经过观察,发现这些文件是有固定格式的,可以采用外部表的方式进行查询,同时可以利用相关的工具进行过滤 1.3.2 pg_xlog这个日志是记录的Postgresql的WAL信息,也就是一些事务日志信息(transaction log),默认单个大小是16M,源码安装的时候可以更改其大小。这些信息通常名字是类似'000000010000000000000013'这样的文件,这些日志会在定时回滚恢复(PITR),流复制(Replication Stream)以及归档时能被用到,这些日志是非常重要的,记录着数据库发生的各种事务信息,不得随意删除或者移动这类日志文件,不然你的数据库会有无法恢复的风险 当你的归档或者流复制发生异常的时候,事务日志会不断地生成,有可能会造成你的磁盘空间被塞满,最终导致DB挂掉或者起不来。遇到这种情况不用慌,可以先关闭归档或者流复制功能,备份pg_xlog日志到其他地方,但请不要删除。然后删除较早时间的的pg_xlog,有一定空间后再试着启动Postgres。 日志分析可用通过如下手段(这块内容我会单独整理一个blog) 文件查看和检索 利用外部表方式进行查询 通过logstash工具进行定制分析 通过在安装了gpperfmon组件的情况下,通过log_alert_history 进行查询 查看系统视图 List of relationsSchema | Name | Type | Owner | Storage ------------+------------------------+------+----------+--------- gp_toolkit | gp_log_command_timings | view | digoal | none -- 统计 gp_toolkit | gp_log_database | view | digoal | none -- 这个包含当前数据库日志 gp_toolkit | gp_log_master_concise | view | digoal | none -- 统计 gp_toolkit | gp_log_system | view | digoal | none -- 这个包含所有日志 (4 rows) 通过gplogfilter工具来查找匹配指定标准的日志数据(包含segment gpssh) 1.3.3 pg_clog pg_clog这个文件也是事务日志文件,但与pg_xlog不同的是它记录的是事务的元数据(metadata),这个日志告诉我们哪些事务完成了,哪些没有完成。这个日志文件一般非常小,但是重要性也是相当高,不得随意删除或者对其更改信息。 总结: pg_log记录各种Error信息,以及服务器与DB的状态信息,可由用户随意更新删除 pg_xlog与pg_clog记录数据库的事务信息,不得随意删除更新,做物理备份时要记得备份着两个日志。 1.4 数据库的启动和关闭日志 程序日志文件:使用gpstart,gpstop 等相关命令的日志 缺省位于~/gpAdminLogs目录下 命令方式:_.log 日志记录的格式: ::::[INFO|WARN|FATAL]:
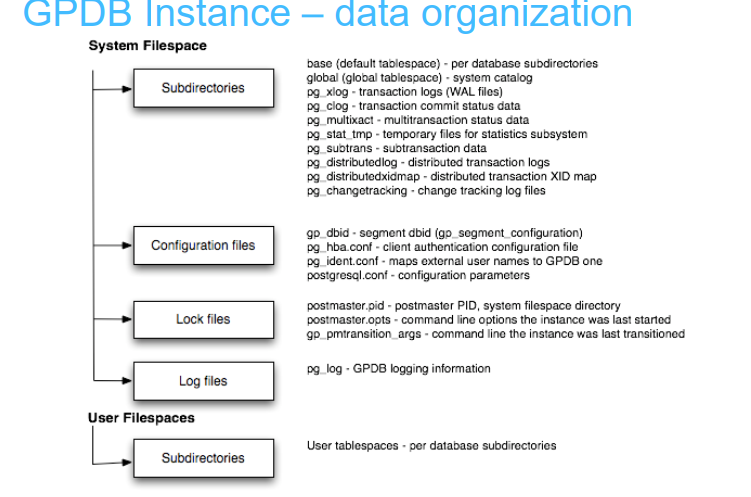
2 文件目录file layout 2.1 master主机上目录结构 2.1.1 软件安装目录结构 /usr/local/greenplum-db [gpadmin@mdw greenplum-db]$ ls -l total 40 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 279 Apr 19 00:57 ! drwxr-xr-x 7 gpadmin gpadmin 4096 Aug 10 2018 bin -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 451 Apr 19 00:27 checknetwork.out drwxr-xr-x 4 gpadmin gpadmin 37 Aug 10 2018 docs drwxr-xr-x 2 gpadmin gpadmin 98 Aug 10 2018 etc drwxr-xr-x 3 gpadmin gpadmin 20 Aug 10 2018 ext -rw-r--r-- 1 gpadmin gpadmin 737 Apr 18 23:52 greenplum_path.sh drwxr-xr-x 6 gpadmin gpadmin 4096 Aug 10 2018 include drwxr-xr-x 7 gpadmin gpadmin 8192 May 29 2018 lib drwxr-xr-x 8 gpadmin gpadmin 107 Jul 27 2018 pxf drwxr-xr-x 2 gpadmin gpadmin 4096 Aug 10 2018 sbin drwxr-xr-x 5 gpadmin gpadmin 57 Apr 19 00:58 share [gpadmin@mdw greenplum-db]$ pwd /usr/local/greenplum-db [gpadmin@mdw greenplum-d 目录说明bin包含所有的GP软件执行命令docs帮助文件etc配置文件include头文件目录.lib动态库目录,PG程序运行需要的动态库都在此目录下,如libpg.so.share此目录下存放有文档和配置模板文件,一些扩展包的sql文件,在此目录的子目录packages下.模板分为GP和PG两个方面greenplum_path.sh环境变量文件2.1.2 用户HOME目录 文件夹说明gpAdminLogs存放集群初始化,集群启动和关闭的日志 自定义的文件夹,用来存放主机列表文件,初始化配置参数文件
2.1.3 数据目录结构 export MASTER_DATA_DIRECTORY=/greenplum/gpdata/master/gpseg-1 [gpadmin@mdw gpseg-1]$ ls -l total 68 -rw------- 1 gpadmin gpadmin 208 Apr 21 00:30 backup_label.old drwx------ 6 gpadmin gpadmin 54 Apr 21 00:30 base drwx------ 2 gpadmin gpadmin 4096 Apr 21 00:37 global -r-------- 1 gpadmin gpadmin 127 Apr 21 00:40 gp_dbid drwxrwxr-x 3 gpadmin gpadmin 18 Apr 21 00:30 gpperfmon -rw-rw-r-- 1 gpadmin gpadmin 860 Apr 21 00:30 gpssh.conf drwx------ 2 gpadmin gpadmin 6 Apr 21 00:30 pg_changetracking drwx------ 2 gpadmin gpadmin 18 Apr 21 00:30 pg_clog drwx------ 2 gpadmin gpadmin 18 Apr 21 00:30 pg_distributedlog drwx------ 2 gpadmin gpadmin 6 Apr 21 00:30 pg_distributedxidmap -rw-rw-r-- 1 gpadmin gpadmin 4383 Apr 21 00:40 pg_hba.conf -rw------- 1 gpadmin gpadmin 1636 Apr 21 00:30 pg_ident.conf drwxrwxr-x 2 gpadmin gpadmin 161 Apr 23 00:00 pg_log drwx------ 4 gpadmin gpadmin 36 Apr 21 00:30 pg_multixact drwx------ 2 gpadmin gpadmin 25 Apr 21 00:37 pg_stat_tmp drwx------ 2 gpadmin gpadmin 18 Apr 21 00:30 pg_subtrans drwx------ 2 gpadmin gpadmin 6 Apr 21 00:30 pg_tblspc drwx------ 2 gpadmin gpadmin 6 Apr 21 00:30 pg_twophase drwx------ 2 gpadmin gpadmin 6 Apr 21 00:30 pg_utilitymodedtmredo -rw------- 1 gpadmin gpadmin 4 Apr 21 00:30 PG_VERSION drwx------ 2 gpadmin gpadmin 190 Apr 21 00:45 pg_xlog -rw------- 1 gpadmin gpadmin 21349 Apr 21 00:30 postgresql.conf -rw------- 1 gpadmin gpadmin 223 Apr 21 00:30 postmaster.opts -rw------- 1 gpadmin gpadmin 59 Apr 21 00:30 postmaster.pid -rw-rw-r-- 1 gpadmin gpadmin 126 Apr 21 00:30 recovery.done -rw------- 1 gpadmin gpadmin 0 Apr 21 00:33 wal_rcv.pid
base是数据目录,每个数据库在这个目录下,会有一个对应的文件夹 global是每一个数据库公用的数据目录 gpperfmon监控数据库性能时,存放监控数据的地方 pg_changetracking 是 segment 之间主备同步用到的一些原数据信息保存的地方 pg_clog 是记录数据库事务信息的地方,保存每一个事务id的状态,这个非常重要,不能丢失,一旦丢失,整个数据库就基本上不可用了 pg_log 是数据库的日志信息 pg_twophase 是二阶段提交的事务信息(二阶段提交参阅第7章) pg_xlog 是数据库重写日志保存的地方,其中每个文件固定大小为64MB,并不断重复使用 gp_dbid 记录这个数据库的dbid 以及它对应的 mirror节点的dbid pg_hba.conf 是访问权限控制文件 pg_ident.conf 是 Ident 映射文件 PG_VERSION 是 PostgreSQL 的版本号 postgresql.conf 是参数配置文件 postmaster.opts 是启动该数据库的 pg_ctl 命令 postmaster.pid 是该数据库的进程号和数据目录信息
其中base 下面的文件夹结构为: # ls 1 10890 10891 16992 285346 其中一个文件夹代表一个数据库,文件夹的名字就是数据库的oid,可以通过 pg_databse查询其对应关系
2.2 Segments主机上目录结构
2.2.1 数据目录结构(包含mirror目录) /data/primiary/gpseg#### is the segment numberbase/DataBase Primary instancepg_log/Segment DataBase Log Filedb_dumps/Local DataBase Backuperrlog/Bad rows rejected by loaderspostgres.conf & pg_hba.confConfiguration Files/data/mirror/gpseg#### is the segment numberDataBase Mirror Instance
2.3 整体数据目录结果说明
3 主要的配置文件 3.1 环境文件greenplum_path.sh [gpadmin@mdw greenplum-db]$ more greenplum_path.sh GPHOME=/usr/local/greenplum-db-5.10.2 # Replace with symlink path if it is present and correct if [ -h ${GPHOME}/../greenplum-db ]; then GPHOME_BY_SYMLINK=`(cd ${GPHOME}/../greenplum-db/ && pwd -P)` if [ x"${GPHOME_BY_SYMLINK}" = x"${GPHOME}" ]; then GPHOME=`(cd ${GPHOME}/../greenplum-db/ && pwd -L)`/. fi unset GPHOME_BY_SYMLINK fi #setup PYTHONHOME if [ -x $GPHOME/ext/python/bin/python ]; then PYTHONHOME="$GPHOME/ext/python" fi PYTHONPATH=$GPHOME/lib/python PATH=$GPHOME/bin:$PYTHONHOME/bin:$PATH LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$GPHOME/lib:$PYTHONHOME/lib:${LD_LIBRARY_PATH-} export LD_LIBRARY_PATH OPENSSL_CONF=$GPHOME/etc/openssl.cnf export GPHOME export PATH export PYTHONPATH export PYTHONHOME export OPENSSL_CONF 3.2 gp_segment ID 文件 [gpadmin@sdw3 gpseg4]$ more gp_dbid # Greenplum Database identifier for this master/segment. # Do not change the contents of this file. dbid = 6 3.3 pg_hba.conf 客户端认证配置文件 pg_hba.conf文件的一般格式是一组记录,每行一个。空行和任何注释字符#之后的文本会被忽略。第一个匹配行会被用来认证。在第一个匹配之后,后续的记录不会被考虑。如果客户端不能用第一个匹配记录中指定的方法认证,该连接会被拒绝。一个记录由多个被空格或者制表符分隔的域组成。如果域值被加上引号,域可以包含空格。记录不能跨越多行。每一个远程客户端访问记录具有如下的格式: host database role CIDR-address authentication-method每一个UNIX-域套接字记录具有如下的格式: local database role authentication-method下面的表格描述了每个域的含义。 域描述local匹配尝试使用UNIX-域套接字的连接。如果没有这种类型的记录,则UNIX-域套接字连接不被允许。host匹配尝试使用TCP/IP的连接。除非用合适的listen_addresses服务器配置参数值启动,就不能进行远程TCP/IP连接。hostssl匹配尝试使用TCP/IP建立的连接,但只有用SSL加密建立该连接时才允许。必须通过设置ssl配置参数在服务器启动时启用SSLhostnossl匹配在不使用SSL的TCP/IP上建立的连接尝试。database指定这一记录匹配的数据库名。值all指定它匹配所有数据库。可以提供多个数据库名,用逗号分隔它们。在文件名前面放一个@,可以指定一个含有数据库名的单独的文件。role指定这一记录匹配的数据库角色名。值all指定它匹配所有角色。如果指定的角色是一个组并且希望该组中的所有成员都被包括在内,在该角色名前面放一个+。可以提供多个角色名,用逗号分隔它们。在文件名前面放一个@,可以指定一个含有角色名的单独的文件。CIDR-address指定这一记录匹配的客户端机器的IP地址范围。它包含一个标准点分十进制表示的IP地址和一个CIDR掩码长度。IP地址只能用数字指定,不能写成域或者主机名。掩码长度指示客户端IP地址必须匹配的高位位数。给定IP地址中,在这些位的右边必须是零。IP地址、/和CIDR掩码长度之间不能有任何空格。典型的CIDR地址例子是:192.0.2.89/32是一个单一主机,192.0.2.0/24是一个小网络,10.6.0.0/16是一个大网络。要指定一个单一主机,对IPv4使用一个CIDR掩码32,对IPv6使用128。在一个网络地址中,不要省略拖尾的零。IP-addressIP-mask这些域可以被用作CIDR地址记号的一种替代。实际的掩码在一个单独的列中指定,而不是指定掩码长度。例如,255.255.255.255表示CIDR掩码长度32。这些域只适用于host、hostssl和hostnossl记录。authentication-method指定连接时使用的认证方法。Greenplum支持PostgreSQL 9.0支持的认证方法。重新装载pg_hba.conf配置文件来让更改生效: $ gpstop -u
host all gpadmin 10.102.254.27/32 trust host replication gpadmin 10.102.254.27/32 trust host all gpadmin 10.102.254.26/32 trust host replication gpadmin 10.102.254.26/32 trust local all gpadmin ident host all gpadmin 127.0.0.1/28 trust host all gpadmin 10.102.254.27/32 trust host all gpadmin ::1/128 trust host all gpadmin fe80::5b53:4d81:e39f:856c/128 trust local replication gpadmin ident host replication gpadmin samenet trust pg_hba.conf文件的一般格式是一组记录,每行一个。一个记录由多个被空格或者制表符分隔的域组成。如果域值被加上引号,域可以包含空格。记录不能跨越多行。 每一行的格式为: 连接方式 连接的数据库 连接的用户 连接的主机IP 认证方式 每一个远程客户端访问记录具有如下的格式: host database role CIDR-address authentication-method 每一个UNIX-域套接字记录具有如下的格式: local database role authentication-method 连接方式 连接方式有四种:local 、host、hostssl、hostnossl local 这条记录匹配通过 Unix 域套接字进行的联接企图, 没有这种类型的记录,就不允许 Unix 域套接字的联接。 host 这条记录匹配通过TCP/IP网络进行的联接尝试。他既匹配通过ssl方式的连接,也匹配通过非ssl方式的连接。 注意:要使用该选项你要在postgresql.conf文件里设置listen_address选项,不在listen_address里的IP地址是无法匹配到的。因为默认的行为是只在localhost上监听本地连接。 hostssl 这条记录匹配通过在TCP/IP上进行的SSL联接企图。 要使用该选项,服务器编译时必须使用–with-openssl选项,并且在服务器启动时ssl设置是打开的,具体内容可见这里。 hostnossl 这个和上面的hostssl相反,只匹配通过在TCP/IP上进行的非SSL联接企图。 数据库 指定这一记录匹配的数据库名。值all指定它匹配所有数据库。可以提供多个数据库名,用逗号分隔它们。在文件名前面放一个@,可以指定一个含有数据库名的单独的文件。 用户名 指定这一记录匹配的数据库角色名。值all指定它匹配所有角色。如果指定的角色是一个组并且希望该组中的所有成员都被包括在内,在该角色名前面放一个+。可以提供多个角色名,用逗号分隔它们。在文件名前面放一个@,可以指定一个含有角色名的单独的文件。 主机IP 指定这一记录匹配的客户端机器的IP地址范围。它包含一个标准点分十进制表示的IP地址和一个CIDR掩码长度。IP地址只能用数字指定,不能写成域或者主机名。掩码长度指示客户端IP地址必须匹配的高位位数。给定IP地址中,在这些位的右边必须是零。IP地址、/和CIDR掩码长度之间不能有任何空格。 典型的CIDR地址例子是:192.0.2.89/32是一个单一主机,192.0.2.0/24是一个小网络,10.6.0.0/16是一个大网络。要指定一个单一主机,对IPv4使用一个CIDR掩码32,对IPv6使用128。在一个网络地址中,不要省略拖尾的零。 ip地址(ip-address)、子网掩码(ip-mask) 这两个字段包含可以看成是标准点分十进制表示的 IP地址/掩码值的一个替代。 例如,使用255.255.255.0 代表一个24位的子网掩码。它们俩放在一起,声明了这条记录匹配的客户机的 IP 地址或者一个IP地址范围。本选项只能在连接方式是host,hostssl或者hostnossl的时候指定。 认证方法 常用的认证方法有: trust 无条件地允许联接,这个方法允许任何可以与PostgreSQL 数据库联接的用户以他们期望的任意 PostgreSQL 数据库用户身份进行联接,而不需要口令。 reject 联接无条件拒绝,常用于从一个组中"过滤"某些主机。 md5 要求客户端提供一个 MD5 加密的口令进行认证,这个方法是允许加密口令存储在pg_shadow里的唯一的一个方法。 password 和"md5"一样,但是口令是以明文形式在网络上传递的,我们不应该在不安全的网络上使用这个方式。 特别强调一点:在Greenplum数据库中,Master实例的pg_hba.conf文件控制对Greenplum数据库系统的客户端访问及认证。Greenplum数据库的Segment也有pg_hba.conf文件,它们被配置来只允许来自Master主机的客户端连接并且永不接受客户端连接。不要在Segment上更改pg_hba.conf文件。 ———————————————— 3.4 pg_ident.conf 对于身份识别,也可采用pg_ident.conf;这可以用于将数据库用户映射到本地用户。 假如用户“joe”是允许访问的PostgreSQL用户数据库“joe”和“电子商务”。pg_hba.conf文件包含如下:
而pg_ident.conf可能会包括:
这就允许系统用户“joe”作为“joe”或者“ecommerce.”来访问数据库。它也允许系统“postgres”用户以“joe”的身份连接到数据库。同时强化对于名字为“esite”识别方法的映射类型,如在pg_ident.conf中所定义的那样。这就意味着在本地类型(Unix域套接字)和本地TCP/IP地址(127.0.0.1)中,只有joe和postgres能够连接到数据库。没有其他的用户有权来访问它。 这种识别方法是一种很好的方式,用于控制哪一个本地用户可以连接到哪一个数据库。这种方法只对本地主机(TCP/IP 或者UNIX 域套接字)的连接起作用,而对于远程控制是无效的。
3.5 postgresql.conf 一、连接配置与安全认证 1、连接Connection Settings listen_addresses (string) 这个参数只有在启动数据库时,才能被设置。它指定数据库用来监听客户端连接的TCP/IP地址。默认是值是* ,表示数据库在启动以后将在运行数据的机器上的所有的IP地址上监听用户请求(如果机器只有一个网卡,只有一个IP地址,有多个网卡的机器有多个 IP地址)。可以写成机器的名字,也可以写成IP地址,不同的值用逗号分开,例如,’server01’, ’140.87.171.49, 140.87.171.21’。如果被设成localhost,表示数据库只能接受本地的客户端连接请求,不能接受远程的客户端连接请求。 port (integer) 这个参数只有在启动数据库时,才能被设置。它指定数据库监听户端连接的TCP端口。默认值是5432。 max_connections (integer) 这个参数只有在启动数据库时,才能被设置。它决定数据库可以同时建立的最大的客户端连接的数目。默认值是100。每个连接占用 400字节共享内存。Note: Increasing max_connections costs ~400 bytes of shared memory per connection slot, plus lock space (see max_locks_per_transaction). superuser_reserved_connections (integer) 这个参数只有在启动数据库时,才能被设置。它表示预留给超级用户的数据库连接数目。它的值必须小于max_connections。 普通用户可以在数据库中建立的最大的并发连接的数目是max_connections 默认值是3。 unix_socket_group (string) 这个参数只有在启动数据库时,才能被设置。设置Unix-domain socket所在的操作系统用户组。默认值是空串,用启动数据库的操作系统用户所在的组作为Unix-domain socket的用户组。 unix_socket_permissions (integer) 这个参数只有在启动数据库时,才能被设置。它设置Unix-domain socket的访问权限,格式与操作系统的文件访问权限是一样的。默认值是0770,表示任何操作系统用户都能访问Unix-domain socket。可以设为0770(所有Unix-domain socket文件的所有者所在的组包含的用户都能访问)和0700(只有Unix-domain socket文件的所有者才能访问)。对于Unix-domain socket,只有写权限才有意义,读和执行权限是没有意义的。 #unix_socket_directories = '/tmp' # comma-separated list of directories # (change requires restart) #bonjour = off # advertise server via Bonjour # (change requires restart) #bonjour_name = '' # defaults to the computer name # (change requires restart) 2、安全认证Security and Authentication authentication_timeout (integer) 这个参数只能在postgresql.conf文件中被设置,它指定一个时间长度,在这个时间长度内,必须完成客户端认证操作,否则客户端连接请求将被拒绝。它可以阻止某些客户端进行认证时长时间占用数据库连接。单位是秒,默认值是60。 ssl (boolean) 这个参数只有在启动数据库时,才能被设置。决定数据库是否接受SSL连接。默认值是off。 ssl_ciphers (string) 指定可以使用的SSL加密算法。查看操作系统关于openssl的用户手册可以得到完整的加密算法列表(执行命令openssl ciphers –v也可以得到)。 #ssl_prefer_server_ciphers = on # (change requires restart) #ssl_ecdh_curve = 'prime256v1' # (change requires restart) #ssl_renegotiation_limit = 0 # amount of data between renegotiations #ssl_cert_file = 'server.crt' # (change requires restart) #ssl_key_file = 'server.key' # (change requires restart) #ssl_ca_file = '' # (change requires restart) #ssl_crl_file = '' # (change requires restart) #password_encryption = on #db_user_namespace = off # GSSAPI using Kerberos #krb_server_keyfile = '' #krb_caseins_users = off # - TCP Keepalives - tcp_keepalives_idle (integer) 这个参数可以在任何时候被设置。默认值是0,意思是使用操作系统的默认值。它设置TCP套接字的TCP_KEEPIDLE属性。这个参数对于通过Unix-domain socket建立的数据库连接没有任何影响。即 间歇性发送TCP心跳包,房子连接被网络设备中断。 tcp_keepalives_interval (integer) 这个参数可以在任何时候被设置。默认值是0,意思是使用操作系统的默认值。它设置TCP套接字的TCP_KEEPINTVL属性。这个参数对于通过Unix-domain socket建立的数据库连接没有任何影响。 tcp_keepalives_count (integer) 这个参数可以在任何时候被设置。默认值是0,意思是使用操作系统的默认值。它设置TCP套接字的TCP_KEEPCNT属性。这个参数对于通过Unix-domain socket建立的数据库连接没有任何影响。 二、文件配置FILE LOCATIONS # The default values of these variables are driven from the -D command-line # option or PGDATA environment variable, represented here as ConfigDir. #data_directory = 'ConfigDir' # use data in another directory # (change requires restart) #hba_file = 'ConfigDir/pg_hba.conf' # host-based authentication file # (change requires restart) #ident_file = 'ConfigDir/pg_ident.conf' # ident configuration file # (change requires restart) # If external_pid_file is not explicitly set, no extra PID file is written. #external_pid_file = '' # write an extra PID file # (change requires restart) 三、内存 Memory shared_buffers (integer) 这个参数只有在启动数据库时,才能被设置。它表示数据缓冲区中的数据块的个数,每个数据块的大小是8KB。数据缓冲区位于数据库的共享内存中,它越大越好,不能小于128KB。默认值是128MB。 temp_buffers (integer) 这个参数可以在任何时候被设置。默认值是8MB。它决定存放临时表的数据缓冲区中的数据块的个数,每个数据块的大小是8KB。临时表缓冲区存放在每个数据库进程的私有内存中,而不是存放在数据库的共享内存中。最小值800KB max_prepared_transactions (integer) 这个参数只有在启动数据库时,才能被设置。它决定能够同时处于prepared状态的事务的最大数目(参考PREPARE TRANSACTION命令)。如果它的值被设为0。则将数据库将关闭prepared事务的特性。它的值通常应该和max_connections的值一样大。每个事务消耗600字节(b)共享内存。 work_mem (integer) 这个参数可以在任何时候被设置。它决定数据库的排序操作和哈希表使用的内存缓冲区的大小。如果work_mem指定的内存被耗尽,数据库将使用磁盘文件进行完成操作,速度会慢很多。ORDER BY、DISTINCT和merge连接会使用排序操作。哈希表在Hash连接、hash聚集函数和用哈希表来处理IN谓词中的子查询中被使用。单位是KB,默认值是4MB。 maintenance_work_mem (integer) 这个参数可以在任何时候被设置。它决定数据库的维护操作使用的内存空间的大小。数据库的维护操作包括VACUUM、CREATE INDEX和ALTER TABLE ADD FOREIGN KEY等操作。 maintenance_work_mem的值如果比较大,通常可以缩短VACUUM数据库和从dump文件中恢复数据库需要的时间。maintenance_work_mem存放在每个数据库进程的私有内存中,而不是存放在数据库的共享内存中。单位是KB,默认值是64MB。 max_stack_depth (integer) 这个参数可以在任何时候被设置,但只有数据库超级用户才能修改它。它决定一个数据库进程在运行时的STACK所占的空间的最大值。数据库进程在运行时,会自动检查自己的STACK大小是否超过max_stack_depth,如果超过,会自动终止当前事务。这个值应该比操作系统设置的进程STACK的大小的上限小1MB。使用操作系统命令“ulimit –s“可以得到操作系统设置的进程STACK的最大值。单位是KB,默认值是2MB。 #huge_pages = try # on, off, or try (change requires restart) #尽量使用大页,需要操作系统的支持,配置vm.nr_hugepages*2MB大于 shared_buffers. dynamic_shared_memory_type = posix # the default is the first option # supported by the operating system: # posix # sysv # windows # mmap # use none to disable dynamic shared memory #autovacuum_work_mem = -1 # min 1MB, or -1 to use maintenance_work_mem 四、资源(空闲空间映射) Free Space Map 数据库的所有可用空间信息都存放在一个叫free space map (FSM)的结构中,它记载数据文件中每个数据块的可用空间的大小。FSM中没有记录的数据块,即使有可用空间,也不会系统使用。系统如果需要新的物理存储空间,会首先在FSM中查找,如果FSM中没有一个数据页有足够的可用空间,系统就会自动扩展数据文件。所以,FSM如果太小,会导致系统频繁地扩展数据文件,浪费物理存储空间。命令VACUUM VERBOSE在执行结束以后,会提示当前的FSM设置是否满足需要,如果FSM的参数值太小,它会提示增大参数。 FSM存放在数据库的共享内存中,由于物理内存的限制,FSM不可能跟踪数据库的所有的数据文件的所有数据块的可用空间信息,只能跟踪一部分数据块的可用空间信息。 max_fsm_relations (integer) 这个参数只有在启动数据库时,才能被设置。默认值是1000。它决定FSM跟踪的表和索引的个数的上限。每个表和索引在FSM中占7个字节的存储空间。 max_fsm_pages (integer) 这个参数只有在启动数据库时,才能被设置。它决定FSM中跟踪的数据块的个数的上限。initdb在创建数据库集群时会根据物理内存的大小决定它的值。每个数据块在fsm中占6个字节的存储空间。它的大小不能小于16 * max_fsm_relations。默认值是20000。 五、内核资源Kernel Resource Usage max_files_per_process (integer) 这个参数只有在启动数据库时,才能被设置。他设定每个数据库进程能够打开的文件的数目。默认值是1000。 shared_preload_libraries (string) 这个参数只有在启动数据库时,才能被设置。它设置数据库在启动时要加载的操作系统共享库文件。如果有多个库文件,名字用逗号分开。如果数据库在启动时未找到shared_preload_libraries指定的某个库文件,数据库将无法启动。默认值为空串。 六、垃圾资源回收Cost-Based Vacuum Delay 执行VACUUM 和ANALYZE命令时,因为它们会消耗大量的CPU与IO资源,而且执行一次要花很长时间,这样会干扰系统执行应用程序发出的SQL命令。为了解决这个问题,VACUUM 和ANALYZE命令执行一段时间后,系统会暂时终止它们的运行,过一段时间后再继续执行这两个命令。这个特性在默认的情况下是关闭的。将参数vacuum_cost_delay设为一个非零的正整数就可以打开这个特性。 用户通常只需要设置参数vacuum_cost_delay和vacuum_cost_limit,其它的参数使用默认值即可。VACUUM 和ANALYZE命令在执行过程中,系统会计算它们执行消耗的资源,资源的数量用一个正整数表示,如果资源的数量超过vacuum_cost_limit,则执行命令的进程会进入睡眠状态,睡眠的时间长度是是vacuum_cost_delay。vacuum_cost_limit的值越大,VACUUM 和ANALYZE命令在执行的过程中,睡眠的次数就越少,反之,vacuum_cost_limit的值越小,VACUUM 和ANALYZE命令在执行的过程中,睡眠的次数就越多。 vacuum_cost_delay (integer) 这个参数可以在任何时候被设置。默认值是0。它决定执行VACUUM 和ANALYZE命令的进程的睡眠时间。单位是毫秒。它的值最好是10的整数,如果不是10的整数,系统会自动将它设为比该值大的并且最接近该值的是10的倍数的整数。如果值是0,VACUUM 和ANALYZE命令在执行过程中不会主动进入睡眠状态,会一直执行下去直到结束。 vacuum_cost_page_hit (integer) 这个参数可以在任何时候被设置。默认值是1。锁住缓冲池,查找共享的散列表以及扫描页面的内容的开销(credits)。 vacuum_cost_page_miss (integer) 这个参数可以在任何时候被设置。默认值是10。表示锁住缓冲池,查找共享散列表,从磁盘读取需要的数据块以及扫描它的内容的开销。 vacuum_cost_page_dirty (integer) 这个参数可以在任何时候被设置。默认值是20。如果清理修改一个原先是干净的块的预计开销。它需要一个把脏的磁盘块再次冲刷到磁盘上的额外开销。 vacuum_cost_limit (integer) 这个参数可以在任何时候被设置。默认值是200。导致清理进程休眠的积累开销。 七、后台写数据库进程Background Writer 后台写数据库进程负责将数据缓冲区中的被修改的数据块(又叫脏数据块)写回到数据库物理文件中。 bgwriter_delay (integer) 这个参数只能在文件postgresql.conf中设置。它决定后台写数据库进程的睡眠时间。后台写数据库进程每次完成写数据到物理文件中的任务以后,就会睡眠bgwriter_delay指定的时间。 bgwriter_delay的值应该是10的倍数,如果用户设定的值不是10的倍数,数据库会自动将参数的值设为比用户指定的值大的最接近用户指定的值的同时是10的倍数的值。单位是毫秒,默认值是200。即 后端写进程每隔多少毫秒重复一次动作。 bgwriter_lru_maxpages (integer) 这个参数只能在文件postgresql.conf中设置。默认值是100。后台写数据库进程每次写脏数据块时,写到外部文件中的脏数据块的个数不能超过bgwriter_lru_maxpages指定的值。例如,如果它的值是500,则后台写数据库进程每次写到物理文件的数据页的个数不能超过500,若超过,进程将进入睡眠状态,等下次醒来再执行写物理文件的任务。如果它的值被设为0, 后台写数据库进程将不会写任何物理文件(但还会执行检查点操作)。 即 一个周期最多写多少脏页。 bgwriter_lru_multiplier (floating point) 这个参数只能在文件postgresql.conf中设置。默认值是2.0。它决定后台写数据库进程每次写物理文件时,写到外部文件中的脏数据块的个数(不能超过bgwriter_lru_maxpages指定的值)。一般使用默认值即可,不需要修改这个参数。这个参数的值越大,后台写数据库进程每次写的脏数据块的个数就越多 ----Asynchronous Behavior---- #effective_io_concurrency = 1 # 1-1000; 0 disables prefetching #max_worker_processes = 8 如果要使用 worker process,最多可以允许 fork多少个 worker进程 八、事务日志预写 full_page_writes (boolean) 这个参数只能在postgresql.conf文件中被设置。默认值是on。打开这个参数,可以提高数据库的可靠性,减少数据丢失的概率,但是会产生过多的事务日志,降低数据库的性能。 即 服务器在checkpoint之后在对页面的第一次写时将整个页面写到wal里面。 wal_buffers (integer) 这个参数只有在启动数据库时,才能被设置。默认值是8。它指定事务日志缓冲区中包含的数据块的个数,每个数据块的大小是8KB,所以默认的事务日志缓冲区的大小是8*8=64KB。事务日志缓冲区位于数据库的共享内存中。即 放在共享内存里用于wal 数据的磁盘页面缓冲区的数目,最小32kb,-1表示基于share buffer的设置。 wal_writer_delay (integer) 这个参数只能在postgresql.conf文件中被设置。它决定写事务日志进程的睡眠时间。WAL进程每次在完成写事务日志的任务后,就会睡眠wal_writer_delay指定的时间,然后醒来,继续将新产生的事务日志从缓冲区写到WAL文件中。单位是毫秒(millisecond),默认值是200。 即 每隔多长时间进行一次写操作。 commit_delay (integer) 这个参数可以在任何时候被设置。它设定事务在发出提交命令以后的睡眠时间,只有在睡眠了commit_delay指定的时间以后,事务产生的事务日志才会被写到事务日志文件中,事务才能真正地提交。增大这个参数会增加用户的等待时间,但是可以让多个事务被同时提交,提高系统的性能。如果数据库中的负载比较高,而且大部分事务都是更新类型的事务,可以考虑增大这个参数的值。下面的参数commit_siblings会影响commit_delay是否生效。默认值是0,单位是微秒(microsecond)。0表示无延迟。即 向WAL缓冲区写入记录和将缓冲区刷新到磁盘上之间的时间延迟。 commit_siblings (integer) 这个参数可以在任何时候被设置。这个参数的值决定参数commit_delay是否生效。假设commit_siblings的值是5,如果一个事务发出一个提交请求,此时,如果数据库中正在执行的事务的个数大于或等于5,那么该事务将睡眠commit_delay指定的时间。如果数据库中正在执行的事务的个数小于5,这个事务将直接提交。默认值是5。即 在commit_delay时间内,最少打开的并发事务数(1-1000); #wal_level = minimal 预写日志模式 # minimal, archive, hot_standby, or logical # (change requires restart) #fsync = on 设置同步方式 # turns forced synchronization on or off #synchronous_commit = on 如果磁盘的IOPS一般,建议使用异步提交来提高性能,但是数据库crash或操作系统crash时,最多可能丢失2*wal_writer_delay时间段产生的事务日志(在wal buffer中) # synchronization level; # off, local, remote_write, or on #wal_sync_method = fsync 用来向磁盘强制更新wal数据的方法。如果fsync 是关闭的,那这个设置就是无关无效的。 # the default is the first option # supported by the operating system: # open_datasync(用O_DSYNC选项的open()打开WAL文件) # fdatasync (default on Linux) 每次提交的时候都调用fdatasync() # fsync 每次提交的时候都调用fsync # fsync_writethrough每次提交的时候都调用fsync(),强制写出任何磁盘写缓冲区 # open_sync 用O_DSYNC选项的open()打开WAL文件 #wal_log_hints = off # also do full page writes of non-critical updates (change requires restart) 九、 十、检查点Checkpoints checkpoint_segments (integer) in logfile segments, min 1, 16MB each 这个参数只能在postgresql.conf文件中被设置。默认值是3。它影响系统何时启动一个检查点操作。如果上次检查点操作结束以后,系统产生的事务日志文件的个数超过checkpoint_segments的值,系统就会自动启动一个检查点操作。增大这个参数会增加数据库崩溃以后恢复操作需要的时间。即 最大多少大小的段发生一次checkpoint,等于shared_buffers除以单个wal segment的大小。 checkpoint_timeout (integer) range 30s-1h 这个参数只能在postgresql.conf文件中被设置。单位是秒,默认值是300。它影响系统何时启动一个检查点操作。如果现在的时间减去上次检查点操作结束的时间超过了checkpoint_timeout的值,系统就会自动启动一个检查点操作。增大这个参数会增加数据库崩溃以后恢复操作需要的时间。即 最大多长时间发生一次checkpoint checkpoint_completion_target (floating point) 这个参数控制检查点操作的执行时间。合法的取值在0到1之间,默认值是0.5。不要轻易地改变这个参数的值,使用默认值即可。 这个参数只能在postgresql.conf文件中被设置。 #checkpoint_warning = 30s 十一、磁盘 Disk #temp_file_limit = -1 # limits per-session temp file space # in kB, or -1 for no limit 每个会话的临时文件空间(kb),-1 表示无限制 十二、归档模式Archiving archive_mode (boolean) 这个参数只有在启动数据库时,才能被设置。默认值是off。它决定数据库是否打开归档模式。 archive_dir (string) 这个参数只有在启动数据库时,才能被设置。默认值是空串。它设定存放归档事务日志文件的目录。 archive_timeout (integer) 这个参数只能在postgresql.conf文件中被设置。默认值是0。单位是秒。如果archive_timeout的值不是0,而且当前时间减去数据库上次进行事务日志文件切换的时间大于archive_timeout的值,数据库将进行一次事务日志文件切换。一般情况下,数据库只有在一个事务日志文件写满以后,才会切换到下一个事务日志文件,设定这个参数可以让数据库在一个事务日志文件尚未写满的情况下切换到下一个事务日志文件。 十三、优化器参数QUERY TUNING 1、存取方法参数 Planner Method Configuration 下列参数控制查询优化器是否使用特定的存取方法。除非对优化器特别了解,一般情况下,使用它们默认值即可。 enable_bitmapscan (boolean) 打开或者关闭规划器对位图扫描规划类型的使用 。默认值是 on。 enable_hashagg (boolean) 打开或者关闭查询规划器对散列聚集规划类型的使用。默认值是 on。 enable_hashjoin (boolean) 打开或者关闭查询规划器对散列连接规划类型的使用。默认值是 on。 enable_indexscan (boolean) 打开或者关闭查询规划器对索引扫描规划类型的使用。默认值是 on。 enable_mergejoin (boolean) 打开或者关闭查询规划器对合并连接规划类型的使用。默认值是 on。 enable_nestloop (boolean) 打开或者关闭查询规划器对嵌套循环连接规划类型的使用。默认值是 on。 enable_seqscan (boolean) 打开或者关闭查询规划器对顺序扫描规划类型的使用。默认值是 on。 enable_sort (boolean) 打开或者关闭查询规划器使用明确的排序步骤。默认值是 on。 enable_tidscan (boolean) 打开或者关闭查询规划器对TID扫描规划类型的使用。默认值是 on。 2、 优化器成本常量 Planner Cost Constants 优化器用一个正的浮点数来表示不同的查询计划的执行成本,每个基本的数据库操作都会被赋给一个确定的成本常量,优化器根据每个基本操作的执行成本来计算每个查询计划的执行成本。不要轻易地改变下面的参数的值,使用它们的默认值即可。 seq_page_cost (floating point) 设置从数据文件上顺序读取一个数据块的执行成本。默认值是1.0。 random_page_cost (floating point) 设置从数据文件上随机读取一个数据块的执行成本。默认值是4.0。 cpu_tuple_cost (floating point) 设置处理每一个数据行的执行成本。默认值是0.01。 cpu_index_tuple_cost (floating point) 设置在扫描索引的过程中处理每一个索引项的执行成本。默认值是0.005。 cpu_operator_cost (floating point) 设置处理每一个运算符或函数的执行成本。默认值是0.0025。 effective_cache_size (integer) 设置单个查询可以使用的数据缓冲区的大小。默认值是128MB。 3、查询优化 Genetic Query Optimizer 下列参数控制优化器使用的遗传算法。除非对遗传算法特别了解,一般情况下,使用它们默认值即可。 geqo (boolean) 打开或者关闭遗传优化器。默认值是on。 geqo_threshold (integer) 确定使用遗传优化器的查询类型。默认值是12。如果FROM子句中引用的的表的数目超过geqo_threshold的值,就会使用遗传优化器。对于简单的查询使用穷举优化器。 geqo_effort (integer) 控制遗传优化器在生成查询计划需要的时间和查询计划的有效性之间做一个折中。有效的取值范围是1到 10。默认值是5。值越大,优化器花在选择查询计划的上的时间越长,同时找到一个最优的查询计划的可能性就越大。系统通常不直接使用geqo_effort的值,而是使用它的值来计算参数geqo_pool_size和geqo_generations的默认。 geqo_pool_size (integer) 控制遗传优化器的池(pool)大小。默认值是0。池大小是遗传群体中的个体数目。至少是2,典型的取值在10和1000之间。如果参数的值是0,系统会自动根据geqo_effort的值和查询中引用的表的个数选择一个默认值。 geqo_generations (integer) 控制遗传优化器的代(generation)的大小。默认值是0。代是遗传算法的迭代次数。至少是1,典型的取值范围与池的取值范围相同。如果参数的值是0,系统会自动根据geqo_pool_size的值和选择一个默认值。 geqo_selection_bias (floating point) 控制遗传优化器的代选择偏差(selection bias)的大小。默认值是2。取值范围在1.50到2.00之间。 4、其它优化器参数 Other Planner Options default_statistics_target (integer) 设置默认的收集优化器统计数据的目标值。它的值越大,ANALYZE操作的执行的时间越长,扫描的数据行的个数也就越多,得到的优化器统计数据就越准确。也可以使用命令ALTER TABLE ... ALTER COLUMN ... SET STATISTICS来为表的每个列设置一个单独的统计数据目标值,这个值的作用与参数default_statistics_target是一样,它只影响相关的列的统计数据收集过程。默认值是10。 constraint_exclusion (boolean) 如果该参数的值是on,查询优化器将使用表上的约束条件来优化查询。如果它的值是off,查询优化器不会使用表上的约束条件来优化查询。默认值是off。 #cursor_tuple_fraction = 0.1 # range 0.0-1.0 #from_collapse_limit = 8 #join_collapse_limit = 8 # 1 disables collapsing of explicit # JOIN clauses 十四、数据库运行日志配置参数 1、Where to Log log_destination = 'stderr' # Valid values are combinations of # stderr, csvlog, syslog, and eventlog, # depending on platform. csvlog # requires logging_collector to be on. # This is used when logging to stderr: logging_collector = on # Enable capturing of stderr and csvlog # into log files. Required to be on for # csvlogs. # (change requires restart) # These are only used if logging_collector is on: log_directory (string) 这个参数只能在postgresql.conf文件中被设置。它决定存放数据库运行日志文件的目录。默认值是pg_log。可以是绝对路径,也可是相对路径(相对于数据库文件所在的路径)。 log_filename (string) 它决定数据库运行日志文件的名称。默认值是postgresql-%Y-%m-%d_%H%M%S.log。它的值可以包含%Y、%m、%d、%H、%M和%S这样的字符串,分别表示年、月、日、小时、分和秒。 如果参数的值中没有指定时间信息(没有出现%Y、%m、%d、%H、%M和%S中的任何一个),系统会自动在log_filename值的末尾加上文件创建的时间作为文件名,例如,如果log_filename的值是 server_log,那么在Sun Aug 29 19:02:33 2004 MST被创建的日志文件的名称将是server_log.1093827753,1093827753是Sun Aug 29 19:02:33 2004 MST在数据库内部的表示形式。这个参数只能在postgresql.conf文件中被设置。 log_rotation_age (integer) 它决定何时创建一个新的数据库日志文件。单位是分钟。默认值是0。如果现在的时间减去上次创建一个数据库运行日志的时间超过了log_rotation_age的值,数据库将自动创建一个新的运行日志文件。如果它的值是0,该参数将不起任何作用。这个参数只能在postgresql.conf文件中被设置。 log_rotation_size (integer) 这个参数只能在postgresql.conf文件中被设置。它决定何时创建一个新的数据库日志文件。单位是KB。默认值是10240。如果一个日志文件写入的数据量超过log_rotation_size的值,数据库将创建一个新的日志文件。如果它的值被设为0,该参数将不起任何作用。 log_truncate_on_rotation (boolean) 系统在创建一个新的数据库运行日志文件时,如果发现存在一个同名的文件,当log_truncate_on_rotation的值是on时,系统覆盖这个同名文件。当log_truncate_on_rotation的值是off时,系统将重用这个同名文件,在它的末尾添加新的日志信息。另外要注意的是,只有在因为参数log_rotation_age起作用系统才创建新的日志文件的情况下,才会覆盖同名的日志文件。因为数据库重新启动或者因为参数log_rotation_size起作用而创建新的日志文件,不会覆盖同名的日志文件,而是在同名的日志文件末尾添加新的日志信息。这个参数只能在postgresql.conf文件中被设置。默认值是off。 例如,将这个参数设为on,将log_rotation_age设为60,将同时将log_filename设为postgresql-%H.log,系统中一共将只有24个日志文件,它们会被不断地重用,任何时刻,系统中最多只有最近24小时的日志信息。 # These are relevant when logging to syslog: #syslog_facility = 'LOCAL0' #syslog_ident = 'postgres' # This is only relevant when logging to eventlog (win32): #event_source = 'PostgreSQL 2、When to Log client_min_messages (string) 控制发送给客户端的消息级别。合法的取值是DEBUG5、DEBUG4、DEBUG3、DEBUG2、DEBUG1、LOG、NOTICE、WARNING、ERROR、FATAL和PANIC,每个级别都包含排在它后面的所有级别中的信息。级别越低,发送给客户端的消息就越少。 默认值是NOTICE。这个参数可以在任何时候被设置。 log_min_messages (string) 控制写到数据库日志文件中的消息的级别。合法的取值是DEBUG5、DEBUG4、DEBUG3、DEBUG2、DEBUG1、INFO、NOTICE、WARNING、ERROR、 LOG、FATAL和PANIC,每个级别都包含排在它后面的所有级别中的信息。级别越低,数据库运行日志中记录的消息就越少。默认值是NOTICE。只有超级用户才能修改这个参数。只有超级用户才能设置这个参数。 log_error_verbosity (string) 控制每条日志信息的详细程度。合法的取值是TERSE、DEFAULT和VERBOSE(每个取值都比它前面的取值提供更详细的信息)。只有超级用户才能修改这个参数。默认值是DEFAULT。 log_min_error_statement (string) 控制日志中是否记录导致数据库出现错误的SQL语句。合法的取值是DEBUG5、DEBUG4、DEBUG3、DEBUG2、DEBUG1、INFO、NOTICE、WARNING、ERROR、 LOG、FATAL和PANIC,每个级别都包含排在它后面的所有级别。默认值是ERROR。只有超级用户才能修改这个参数。 消息严重级别 严重级别 用法 DEBUG1..DEBUG5 报告详细的调试信息。 INFO 报告用户可能需要的信息。 NOTICE 报告对用户有用的信息。 WARNING 报告警告信息。 ERROR 报告错误信息。 LOG 报告对数据库管理员有用的信息, 例如,检查点操作统计信息。 FATAL 报告导致当前会话被终止的错误信息。 PANIC 报告导致整个数据库被关闭的错误信息。 3、What to Log debug_print_parse (boolean) debug_print_rewritten (boolean) debug_print_plan (boolean) debug_pretty_print (boolean) 这些参数控制数据库是否输出运行时的调试信息。这些参数的默认值是off。这些参数可以被任何用户设置。 log_checkpoints (boolean) 控制是否及记录检查点操作信息。默认值是off。这个参数只能在postgresql.conf文件中被设置。必须重启数据库才能生效。 log_connections (boolean) 控制是否及记录客户端连接请求信息。默认值是off。这个参数只能在postgresql.conf文件中被设置。必须重启数据库才能生效。 log_disconnections (boolean) 控制是否记录客户端结束连接信息。默认值是off。这个参数只能在postgresql.conf文件中被设置。 log_duration (boolean) 控制是否记录每个完成的SQL语句的执行时间。只有超级用户才能修改这个参数。默认值是off。对于使用扩展协议与数据库通信的客户端,会记载Parse、Bind和Execute的执行时间。 log_hostname (boolean) 控制是否及记录客户端的主机名。默认值是off。如果设为on,可能会影响数据库的性能,因为解析主机名可能需要一定的时间。这个参数只能在postgresql.conf文件中被设置。这个参数只能在postgresql.conf文件中被设置。 log_line_prefix (string) 控制每条日志信息的前缀格式。默认值是空串。它的格式类似c语言中printf函数的format字符串。这个参数只能在postgresql.conf文件中被设置。 log_line_prefix = '< %m >' # special values: 转义序列 # %a = application name # %u = user name 用户名 # %d = database name 数据库名 # %r = remote host and port 客户端机器名或IP地址,还有客户端端口 # %h = remote host 客户端机器名或IP地址 # %p = process ID 进程ID # %t = timestamp without milliseconds 带微秒的时间 # %m = timestamp with milliseconds 不带微秒的时间 # %i = command tag 命令标签: 会话当前执行的命令类型 # %e = SQL state # %c = session ID 会话ID # %l = session line number 每个会话的日志编号,从1开始 # %s = session start timestamp 进程启动时间 # %v = virtual transaction ID 虚拟事务ID (backendID/localXID) # %x = transaction ID (0 if none) 事务ID (0表示没有分配事务ID) # %q = stop here in non-session 不产生任何输出。如果当前进程是backend进程,忽略这个转义序列,继续处理后面的转义序列。如果当前进程不是backend进程,忽略这个转义序列和它后面的所有转义序列。 # processes # %% '%' 字符% log_lock_waits (boolean) 如果一个会话等待某个类型的锁的时间超过deadlock_timeout的值,该参数决定是否在数据库日志中记录这个信息。默认值是off。只有超级用户才能修改这个参数。 log_statement (string) 控制记录哪种SQL语句的执行信息。有效的取值是none、ddl、mod和all。默认值是none。ddl包括所有数据定义语句,如CREATE、ALTER和DROP语句。mod包括所有ddl语句和更新数据的语句,例如INSERT、UPDATE、DELETE、TRUNCATE、 COPY FROM、PREPARE和 EXECUTE。All包括所有的语句。只有超级用户才能修改这个参数。 log_temp_files (integer) 控制是否记录临时文件的删除信息。单位是KB。0表示记录所有临时文件的删除信息。正整数表示只记录大小比log_temp_files的值大的临时文件的删除信息。-1表示不记录任何临时文件删除信息。默认值是-1。这个参数可以在任何时候被设置。 log_timezone (string) 设置数据库日志文件在写日志文件时使用的时区。默认值是unknown,意识是使用操作系统的时区。这个参数只能在postgresql.conf文件中被设置 十五、数据库运行统计相关参数RUNTIME STATISTICS 下面的参数控制是否搜集特定的数据库运行统计数据: ---Query/Index Statistics Collector---- track_activities (boolean) 是否收集每个会话的当前正在执行的命令的统计数据,包括命令开始执行的时间。默认值是on。只有超级用户才能修改这个参数。 track_counts (boolean) 是否收集数据库活动的统计数据。默认值是on。只有超级用户才能修改这个参数。 #track_io_timing = off #track_functions = none # none, pl, all #track_activity_query_size = 1024 # (change requires restart) #update_process_title = on #stats_temp_directory = 'pg_stat_tmp' ---统计监测Statistics Monitoring-- log_statement_stats (boolean) log_parser_stats (boolean) log_planner_stats (boolean) log_executor_stats (boolean) 这些参数决定是否在数据库的运行日志里记载每个SQL语句执行的统计数据。如果log_statement_stats的值是on,其它的三个参数的值必须是off。所有的这些参数的默认值都是off。log_statement_stats报告整个语句的统计数据,log_parser_stats记载数据库解析器的统计数据,log_planner_stats报告数据库查询优化器的统计数据,log_executor_stats报告数据库执行器的统计数据。只有超级用户才能修改这些参数。 十六、自动垃圾收集相关参数AUTOVACUUM PARAMETERS 下面的参数控制自动垃圾收集的行为: autovacuum (boolean) 控制是够打开数据库的自动垃圾收集功能。默认值是on。如果autovacuum被设为on,参数track_counts(参考本章10.9)也要被设为on,自动垃圾收集才能正常工作。注意,即使这个参数被设为off,如果事务ID回绕即将发生,数据库会自动启动一个垃圾收集操作。这个参数只能在文件postgresql.conf中被设置。 log_autovacuum_min_duration (integer) 单位是毫秒。如果它的值为0,所有的垃圾搜集操作都会被记录在数据库运行日志中,如果它的值是-1,所有的垃圾收集操作都不会被记录在数据库运行日志中。如果把它的值设为250毫秒,只要自动垃圾搜集发出的VACUUM和ANALYZE命令的执行时间超过250毫秒,VACUUM和ANALYZE命令的相关信息就会被记录在数据库运行日志中。默认值是-1。这个参数只能在 postgresql.conf中被设置。 autovacuum_max_workers (integer) 设置能同时运行的最大的自动垃圾收集工作进程的数目。默认值是3。这个参数只能在文件postgresql.conf中被设置。 autovacuum_naptime (integer) 设置自动垃圾收集控制进程的睡眠时间。单位是秒,默认值是60。这个参数只能在文件postgresql.conf中被设置。 autovacuum_vacuum_threshold (integer) 设置触发垃圾收集操作的阈值。默认值是50。这个参数只能在文件postgresql.conf中被设置。只有一个表上被删除或更新的记录的数目超过了autovacuum_vacuum_threshold的值,才会对这个表执行垃圾收集操作。 autovacuum_analyze_threshold (integer) 设置触发ANALYZE操作的阈值。默认值是50。这个参数只能在文件postgresql.conf中被设置。只有一个表上被删除、插入或更新的记录的数目超过了autovacuum_analyze_threshold的值,才会对这个表执行ANALYZE操作。 autovacuum_vacuum_scale_factor (floating point) 这个参数与何时对一个表进行垃圾收集操作相关。默认值是0.2。这个参数只能在文件postgresql.conf中被设置。 autovacuum_analyze_scale_factor (floating point) 这个参数与何时对一个表进行ANALYZE操作相关。默认值是0.1。这个参数只能在文件postgresql.conf中被设置。 autovacuum_freeze_max_age = 200000000 # maximum XID age before forced vacuum # (change requires restart) 指定表上事务的最大年龄,默认2亿,达到这个阀值将触发 autovacuum进程,从而避免 wraparound. 表上的事务年龄可通过 pg_class.relfrozenxid查询 autovacuum_multixact_freeze_max_age = 400000000 # maximum multixact age # before forced vacuum # (change requires restart) autovacuum_vacuum_cost_delay = 20ms # default vacuum cost delay for # autovacuum, in milliseconds; # -1 means use vacuum_cost_delay 当 autovacuum进程即将执行时,对vacuum执行cost进行评估,如果超过 autovacuum_vacuum_cost_limit的值时,则延迟,这个延迟的时间值即为改成的值. autovacuum_vacuum_cost_limit = -1 # default vacuum cost limit for # autovacuum, -1 means use # vacuum_cost_limit 这个值 为 autovacuum进程的评估阀值,默认值为-1,表使用 vacuum_cost_limit值,如果在执行 autovacuum进程期间评估的 cost 超过 autovacuum_vacuum_cost_limit,则 autovacuum进程则会休眠 十七、锁管理LOCK MANAGEMENT deadlock_timeout(integer) 设置死锁超时检测时间。单位是微秒,默认值是1000。死锁检测是一个消耗许多 CPU资源的操作。这个参数的值不能太小。在数据库负载比较大的情况下,应当增大这个参数的值。 max_locks_per_transaction(integer) 这个参数控制每个事务能够得到的平均的对象锁的个数。默认值是64。数据库在启动以后创建的共享锁表的最大可以保存max_locks_per_transaction * (max_connections + max_prepared_transactions)个对象锁。单个事务可以同时获得的对象锁的数目可以超过max_locks_per_transaction的值,只要共享锁表中还有剩余空间。每个锁占用270个字节的共享内存 # lock table slots. #max_pred_locks_per_transaction = 64 # min 10 # (change requires restart) 十八、客户端连接管理CLIENT CONNECTION DEFAULTS # - Statement Behavior - #search_path = '"$user",public' # schema names #default_tablespace = '' # a tablespace name, '' uses the default #temp_tablespaces = '' # a list of tablespace names, '' uses # only default tablespace #check_function_bodies = on #default_transaction_isolation = 'read committed' #default_transaction_read_only = off #default_transaction_deferrable = off #session_replication_role = 'origin' #statement_timeout = 0 # in milliseconds, 0 is disabled #lock_timeout = 0 # in milliseconds, 0 is disabled #vacuum_freeze_min_age = 50000000 #vacuum_freeze_table_age = 150000000 #vacuum_multixact_freeze_min_age = 5000000 #vacuum_multixact_freeze_table_age = 150000000 #bytea_output = 'hex' # hex, escape #xmlbinary = 'base64' #xmloption = 'content' #gin_fuzzy_search_limit = 0 # - Locale and Formatting - datestyle = 'iso, mdy' #intervalstyle = 'postgres' timezone = 'PRC' #timezone_abbreviations = 'Default' # Select the set of available time zone # abbreviations. Currently, there are # Default # Australia (historical usage) # India # You can create your own file in # share/timezonesets/. #extra_float_digits = 0 # min -15, max 3 #client_encoding = sql_ascii # actually, defaults to database # encoding # These settings are initialized by initdb, but they can be changed. lc_messages = 'en_US.UTF-8' # locale for system error message # strings lc_monetary = 'en_US.UTF-8' # locale for monetary formatting lc_numeric = 'en_US.UTF-8' # locale for number formatting lc_time = 'en_US.UTF-8' # locale for time formatting # default configuration for text search default_text_search_config = 'pg_catalog.english' # - Other Defaults - #dynamic_library_path = '$libdir' #local_preload_libraries = '' #session_preload_libraries = '' 十九、错误处理ERROR HANDLING #exit_on_error = off # terminate session on any error? #restart_after_crash = on # reinitialize after backend crash? 二十、配置文件包括 CONFIG FILE INCLUDES 一个配置文件也可以包含其他配置文件,使用include 指令能够达到这个目的。 比如 在postgresql.conf文件中 有如下一行: include 'my.confg' 这样的话 my.confg文件中的配置信息也会被数据库读入。 include 指令指定的配置文件也可以用include指令再包含其他配置文件。如果include指令中指定的文件名不是绝对路径,数据库会在postgresql.conf文件所在的目录下查找这个文件。 #include_dir = 'conf.d' # include files ending in '.conf' from # directory 'conf.d' #include_if_exists = 'exists.conf' # include file only if it exists #include = 'special.conf' # include file 二十一、版本\平台兼容VERSION/PLATFORM COMPATIBILITY # - Previous PostgreSQL Versions - #array_nulls = on #backslash_quote = safe_encoding # on, off, or safe_encoding #default_with_oids = off #escape_string_warning = on #lo_compat_privileges = off #quote_all_identifiers = off #sql_inheritance = on #standard_conforming_strings = on #synchronize_seqscans = on # - Other Platforms and Clients - #transform_null_equals = off 二十二、复制REPLICATION # - Sending Server(s) - # Set these on the master and on any standby that will send replication data. #max_wal_senders = 0 # max number of walsender processes # (change requires restart) #wal_keep_segments = 0 # in logfile segments, 16MB each; 0 disables #wal_sender_timeout = 60s # in milliseconds; 0 disables #max_replication_slots = 0 # max number of replication slots # (change requires restart) # - Master Server - # These settings are ignored on a standby server. #synchronous_standby_names = '' # standby servers that provide sync rep # comma-separated list of application_name # from standby(s); '*' = all #vacuum_defer_cleanup_age = 0 # number of xacts by which cleanup is delayed # - Standby Servers - # These settings are ignored on a master server. #hot_standby = off # "on" allows queries during recovery # (change requires restart) #max_standby_archive_delay = 30s # max delay before canceling queries # when reading WAL from archive; # -1 allows indefinite delay #max_standby_streaming_delay = 30s # max delay before canceling queries # when reading streaming WAL; # -1 allows indefinite delay #wal_receiver_status_interval = 10s # send replies at least this often # 0 disables #hot_standby_feedback = off # send info from standby to prevent # query conflicts #wal_receiver_timeout = 60s # time that receiver waits for # communication from master # in milliseconds; 0 disables # FILE LOCATIONS #------------------------------------------------------------------------------ # The default values of these variables are driven from the -D command-line # option or PGDATA environment variable, represented here as ConfigDir. #data_directory = 'ConfigDir' # use data in another directory # (change requires restart) #hba_file = 'ConfigDir/pg_hba.conf' # host-based authentication file # (change requires restart) #ident_file = 'ConfigDir/pg_ident.conf' # ident configuration file # (change requires restart) # If external_pid_file is not explicitly set, no extra PID file is written. #external_pid_file = '(none)' # write an extra PID file # (change requires restart) #------------------------------------------------------------------------------ # CONNECTIONS AND AUTHENTICATION #------------------------------------------------------------------------------ # - Connection Settings - #listen_addresses = '*' # what IP address(es) to listen on; # comma-separated list of addresses; # defaults to '*', '*' = all # (change requires restart) port=5432 ##port = 5432 # sets the database listener port for # a Greenplum instance. The master and # each segment has its own port number. # note: Port numbers for the Greenplum system must also be changed in the # gp_configuration catalog. See the Greenplum Database Administrator Guide # for instructions! # # WARNING: YOU MUST SHUT DOWN YOUR GREENPLUM SYSTEM BEFORE CHANGING # THE PORT NUMBER IN THIS FILE. max_connections = 250 # inserted by initdb #max_connections = 200 # (change requires restart) # Note: Increasing max_connections costs ~400 bytes of shared memory per # connection slot, plus lock space (see max_locks_per_transaction). You might # also need to raise shared_buffers to support more connections. #superuser_reserved_connections = 3 # (change requires restart) #unix_socket_directory = '' # (change requires restart) #unix_socket_group = '' # (change requires restart) #unix_socket_permissions = 0777 # begin with 0 to use octal notation # (change requires restart) #bonjour_name = '' # defaults to the computer name # (change requires restart) # - Security and Authentication - #authentication_timeout = 1min # 1s-600s #ssl = off # (change requires restart) #ssl_ciphers = 'ALL:!ADH:!LOW:!EXP:!MD5:@STRENGTH' # allowed SSL ciphers # (change requires restart) #ssl_renegotiation_limit = 512MB # amount of data between renegotiations #password_encryption = on #db_user_namespace = off # Kerberos and GSSAPI #krb_server_keyfile = '' # (change requires restart) #krb_srvname = 'postgres' # (change requires restart, Kerberos only) #krb_caseins_users = off # (change requires restart) # - TCP Keepalives - # see "man 7 tcp" for details #tcp_keepalives_idle = 0 # TCP_KEEPIDLE, in seconds; # 0 selects the system default #tcp_keepalives_interval = 0 # TCP_KEEPINTVL, in seconds; # 0 selects the system default #tcp_keepalives_count = 0 # TCP_KEEPCNT; # 0 selects the system default #------------------------------------------------------------------------------ # RESOURCE USAGE (except WAL) #------------------------------------------------------------------------------ # - Memory - shared_buffers = 125MB # inserted by initdb #shared_buffers = 128MB # min 128kB or max_connections*16kB # (change requires restart) #temp_buffers = 8MB # min 800kB max_prepared_transactions = 250 # can be 0 or more # (change requires restart) # Note: Increasing max_prepared_transactions costs ~600 bytes of shared memory # per transaction slot, plus lock space (see max_locks_per_transaction). #work_mem = 32MB # min 64kB #maintenance_work_mem = 64MB # min 1MB #max_stack_depth = 2MB # min 100kB # - Free Space Map - max_fsm_pages = 200000 # inserted by initdb #max_fsm_pages = 204800 # min max_fsm_relations*16, 6 bytes each # (change requires restart) #max_fsm_relations = 1000 # min 100, ~70 bytes each # (change requires restart) # - Kernel Resource Usage - #max_files_per_process = 1000 # min 25 # (change requires restart) #shared_preload_libraries = '' # (change requires restart) # - Cost-Based Vacuum Delay - #vacuum_cost_delay = 0ms # 0-100 milliseconds #vacuum_cost_page_hit = 1 # 0-10000 credits #vacuum_cost_page_miss = 10 # 0-10000 credits #vacuum_cost_page_dirty = 20 # 0-10000 credits #vacuum_cost_limit = 200 # 1-10000 credits #------------------------------------------------------------------------------ # QUERY TUNING #------------------------------------------------------------------------------ # - Planner Method Configuration - #enable_bitmapscan = on #enable_indexscan = on #enable_seqscan = on #enable_tidscan = on #enable_hashjoin = on #enable_mergejoin = off #enable_nestloop = off #gp_enable_adaptive_nestloop = on #gp_enable_multiphase_agg = on #gp_enable_preunique = on #gp_enable_agg_distinct = on #gp_enable_agg_distinct_pruning = on #enable_groupagg = on #enable_hashagg = on #gp_selectivity_damping_for_scans = on #gp_selectivity_damping_for_joins = off #gp_enable_sequential_window_plans = off #enable_sort = on #gp_enable_sort_limit = on #gp_enable_sort_distinct = on # - Planner Cost Constants - #seq_page_cost = 1.0 # measured on an arbitrary scale #random_page_cost = 100 # same scale as above #cpu_tuple_cost = 0.01 # same scale as above #cpu_index_tuple_cost = 0.005 # same scale as above #cpu_operator_cost = 0.0025 # same scale as above #gp_motion_cost_per_row = 0.0 # (same) (if 0, 2*cpu_tuple_cost is used) #effective_cache_size = 4MB # - Other Planner Options - #from_collapse_limit = 20 #join_collapse_limit = 20 # 1 disables collapsing of explicit # JOIN clauses #gp_segments_for_planner = 0 # if 0, actual number of segments is used #gp_enable_direct_dispatch = on optimizer_analyze_root_partition = on # stats collection on root partitions #------------------------------------------------------------------------------ # ERROR REPORTING AND LOGGING #------------------------------------------------------------------------------ # - Set gp_reraise_signal to on to generate core files on SIGSEGV #gp_reraise_signal = off # - Where to Log - #log_truncate_on_rotation = off # If on, an existing log file of the # same name as the new log file will be # truncated rather than appended to. # But such truncation only occurs on # time-driven rotation, not on restarts # or size-driven rotation. Default is # off, meaning append to existing files # in all cases. #log_rotation_age = 1d # Automatic rotation of logfiles will # happen after that time. 0 to disable. #log_rotation_size = 10MB # Automatic rotation of logfiles will # happen after that much log output. # 0 to disable. # - When to Log - #client_min_messages = notice # values in order of decreasing detail: # debug5 # debug4 # debug3 # debug2 # debug1 # log # notice # warning # error #log_min_messages = warning # Values in order of decreasing detail: # debug5 # debug4 # debug3 # debug2 # debug1 # info # notice # warning # error # log # fatal # panic #log_error_verbosity = default # terse, default, or verbose messages #log_min_error_statement = error # values in order of decreasing detail: # debug5 # debug4 # debug3 # debug2 # debug1 # info # notice # warning # error # log # fatal # panic (effectively off) #log_min_duration_statement = -1 # -1 is disabled, 0 logs all statements # and their durations, > 0 logs only # statements running at least this time. # - What to Log - #debug_print_parse = off #debug_print_rewritten = off #debug_print_prelim_plan = off #debug_print_slice_table = off #debug_print_plan = off #debug_pretty_print = off #log_checkpoints = off #log_connections = off #log_disconnections = off #log_duration = off #log_hostname = off #log_statement = 'none' # none, mod, ddl, all #log_temp_files = -1 # Log temporary files equal or larger # than the specified number of kilobytes. # -1 disables; 0 logs all temp files #log_timezone = unknown # actually, defaults to TZ environment # setting #------------------------------------------------------------------------------ # PL/JAVA #------------------------------------------------------------------------------ #pljava_classpath = '' # ':' separated list of installed jar files #pljava_vmoptions = '' # Options sent to the JVM on startup #pljava_statement_cache_size = 0 # Size of the prepared statement MRU cache #pljava_release_lingering_savepoints = off # on/off to release/abort lingering savepoints #------------------------------------------------------------------------------ # PERFORMANCE MONITOR #------------------------------------------------------------------------------ #gp_enable_gpperfmon=on # Enable the performance monitor #gpperfmon_port=8888 # Port used by the performance monitor daemons gp_enable_query_metrics = on #------------------------------------------------------------------------------ # EMAIL ALERTS #------------------------------------------------------------------------------ # Configure the DNS name of the SMTP server you want to use, # the port it runs on (which will be either 25 or 587), and # the SASL authentication information used to connect to it. #gp_email_smtp_server = 'localhost:25' # SMTP server hostname and port (don't forget the port!) #gp_email_smtp_userid = '' # Userid used to authenticate with SMTP server, if needed #gp_email_smtp_password = '' # Password/Passphrase used to authenticate with SMTP server, if needed # Here you need to specify e-mail addresses. The email_from address doesn't actually need # to be a valid e-mail address, but it is much better if it is, because delivery failure notifications # go to that address. The email_to is a list of recipients who will get the alerts. # # The e-mail addresses need to be in the form of [email protected], not just userid. # If email_to list is empty, it disables e-mail alerts. # # e-mail addresses can be just the actual e-mail address, [email protected], or can be a # human readable name with attached e-mail address in the form 'Joe Smith ". # If using the latter format, the e-mail address must be between ''. The first part of # the string can be any text, and if used for the gp_email_from address, can help differentiate the e-mails # from different servers (for example: 'my test GPDB system "). #gp_email_from = '' # Who do we say the e-mails are from? and who is the return-path? #gp_email_to = '' # Semicolon separated list of recipients that will get e-mail alerts. # empty means disable e-mail alerts. #------------------------------------------------------------------------------ # SNMP INFORM/TRAP ALERTS #------------------------------------------------------------------------------ # Configure the gp_snmp_monitor_address to be the system your SNMP monitor runs on, or a proxy # that will relay the message to the SNMP monitor. You can specify transport, DNS name, and port: # [:][:port] # # where can be 'udp', 'tcp', 'udpv6', 'tcpv6', or 'unix' for unix domain sockets (optional). # For udp or tcp, the port is typically 162. # For a SNMP monitor running locally, you might use 'localhost:162', but more typically # the SNMP monitor is running on some other machine. # You can send to multiple network monitors by using a comma separated list of addresses. # # if gp_snmp_peername is empty, snmp alerts are disabled. #gp_snmp_monitor_address = '' # name or IP address(es) (and optionally the port) of the SNMP monitor(s) that will receive the alerts. #gp_snmp_community = 'public' # Change to whatever community string you use in your monitor #gp_snmp_use_inform_or_trap = 'trap' # Set to 'inform' or 'trap', we will send SNMP v2c inform, or SNMP v2c trap. #------------------------------------------------------------------------------ # RUNTIME STATISTICS #------------------------------------------------------------------------------ # - ANALYZE Statistics on Database Contents - #default_statistics_target = 100 # range 1 - 10000 (target # of # histogram bins) #gp_analyze_relative_error = 0.25 # range 0.0 - 1.0 (target relative # error fraction) # - Query/Index Statistics Collector - #track_activities = on #track_counts = off #update_process_title = on #stats_queue_level = off # - Statistics Monitoring - #log_parser_stats = off #log_planner_stats = off #log_executor_stats = off #log_statement_stats = off gp_autostats_mode=on_no_stats # none, on_no_stats, on_change. see documentation for semantics. gp_autostats_on_change_threshold=2147483647 # [0..INT_MAX]. see documentation for semantics. log_autostats=off # print additional autostats information #------------------------------------------------------------------------------ # AUTOVACUUM PARAMETERS #------------------------------------------------------------------------------ #autovacuum = on # Enable autovacuum subprocess? 'on' # requires track_counts to also be on. #log_autovacuum_min_duration = -1 # -1 disables, 0 logs all actions and # their durations, > 0 logs only # actions running at least that time. #autovacuum_max_workers = 3 # max number of autovacuum subprocesses #autovacuum_naptime = 1min # time between autovacuum runs #autovacuum_vacuum_threshold = 50 # min number of row updates before # vacuum #autovacuum_analyze_threshold = 50 # min number of row updates before # analyze #autovacuum_vacuum_scale_factor = 0.2 # fraction of table size before vacuum #autovacuum_analyze_scale_factor = 0.1 # fraction of table size before analyze #autovacuum_freeze_max_age = 200000000 # maximum XID age before forced vacuum # (change requires restart) #autovacuum_vacuum_cost_delay = 20 # default vacuum cost delay for # autovacuum, -1 means use # vacuum_cost_delay #autovacuum_vacuum_cost_limit = -1 # default vacuum cost limit for # autovacuum, -1 means use # vacuum_cost_limit #------------------------------------------------------------------------------ # CLIENT CONNECTION DEFAULTS #------------------------------------------------------------------------------ # - Statement Behavior - #search_path = '"$user",public' # schema names #default_tablespace = '' # a tablespace name, '' uses the default #check_function_bodies = on #default_transaction_isolation = 'read committed' #default_transaction_read_only = off #session_replication_role = 'origin' #statement_timeout = 0 # 0 is disabled #idle_session_gang_timeout = 18s # in milliseconds, 0 is disabled #vacuum_freeze_min_age = 100000000 #bytea_output='escape' # - Locale and Formatting - datestyle = 'iso, mdy' # inserted by initdb #datestyle = 'iso, mdy' #timezone = unknown # actually, defaults to TZ environment # setting #timezone_abbreviations = 'Default' # Select the set of available time zone # abbreviations. Currently, there are # Default # Australia # India # You can create your own file in # share/timezonesets/. #extra_float_digits = 0 # min -15, max 2 #client_encoding = sql_ascii # actually, defaults to database # encoding # These settings are initialized by initdb, but they can be changed. lc_messages = 'en_US.utf8' # inserted by initdb #lc_messages = 'C' # locale for system error message # strings lc_monetary = 'en_US.utf8' # inserted by initdb #lc_monetary = 'C' # locale for monetary formatting lc_numeric = 'en_US.utf8' # inserted by initdb #lc_numeric = 'C' # locale for number formatting lc_time = 'en_US.utf8' # inserted by initdb #lc_time = 'C' # locale for time formatting # default configuration for text search default_text_search_config = 'pg_catalog.english' # - Other Defaults - #dynamic_library_path = '$libdir' #explain_pretty_print = on #local_preload_libraries = '' #------------------------------------------------------------------------------ # LOCK MANAGEMENT #------------------------------------------------------------------------------ #deadlock_timeout = 1s #max_locks_per_transaction = 128 # min 10 # (change requires restart) # Note: Each lock table slot uses ~270 bytes of shared memory, and there are # max_locks_per_transaction * (max_connections + max_prepared_transactions) # lock table slots. #--------------------------------------------------------------------------- # RESOURCE SCHEDULING #--------------------------------------------------------------------------- #max_resource_queues = 9 # no. of resource queues to create. #max_resource_portals_per_transaction = 64 # no. of portals per backend. #resource_select_only = on # resource lock SELECT queries only. #resource_cleanup_gangs_on_wait = on # Cleanup idle reader gangs before # resource lockwait. gp_resqueue_memory_policy = 'eager_free' # memory request based queueing. # eager_free, auto or none #--------------------------------------------------------------------------- # EXTERNAL TABLES #--------------------------------------------------------------------------- #gp_external_enable_exec = on # enable external tables with EXECUTE. #--------------------------------------------------------------------------- # APPEND ONLY TABLES #--------------------------------------------------------------------------- #gp_safefswritesize = 0 # minimum size for safe AO writes in a non-mature fs max_appendonly_tables = 10000 # Maximum number of append only tables that can # participate in writing data concurrently. #------------------------------------------------------------------------------ # VERSION/PLATFORM COMPATIBILITY #------------------------------------------------------------------------------ # - Previous PostgreSQL Versions - #add_missing_from = off #array_nulls = on #backslash_quote = safe_encoding # on, off, or safe_encoding #escape_string_warning = on #regex_flavor = advanced # advanced, extended, or basic #standard_conforming_strings = on #synchronize_seqscans = on # - Other Platforms and Clients - #transform_null_equals = off #--------------------------------------------------------------------------- # GREENPLUM ARRAY CONFIGURATION #--------------------------------------------------------------------------- #--------------------------------------------------------------------------- # GREENPLUM ARRAY TUNING #--------------------------------------------------------------------------- # - Interconnect - #gp_max_packet_size = 8192 gp_interconnect_type=udpifc # - Worker Process Creation - gp_connections_per_thread = 0 gp_segment_connect_timeout = 600s # - Resource limits - gp_vmem_protect_limit = 8192 #Virtual memory limit (in MB). #gp_vmem_idle_resource_timeout = 18000 # idle-time before gang-release, in milliseconds (zero disables release). #------------------------------------------------------------------------------ # CUSTOMIZED OPTIONS #------------------------------------------------------------------------------ #custom_variable_classes = '' # list of custom variable class names gp_backup_directIO = off # enable\disable dump with direct IO gp_backup_directIO_read_chunk_mb = 20 # Size of read Chunk buffer in directIO dump (in MB) shared_preload_libraries = '$libdir/metrics_collector,$libdir/gp_wlm' #Greenplum specific configuration parameters for Master instance database #------------------------------------------------------------------------ log_statement=all checkpoint_segments=8 3.6 gpinitsystem_config 此文件是初始化安装的配置文件,用来初始化整个greenplum集群数据库 [gpadmin@mdw gpconfig]$ more gpinitsystem_config # FILE NAME: gpinitsystem_config # Configuration file needed by the gpinitsystem ################################################ #### REQUIRED PARAMETERS ################################################ #### Name of this Greenplum system enclosed in quotes. ARRAY_NAME="Greenplum Data Platform" #### Naming convention for utility-generated data directories. SEG_PREFIX=gpseg #### Base number by which primary segment port numbers #### are calculated. PORT_BASE=40000 #### File system location(s) where primary segment data directories #### will be created. The number of locations in the list dictate #### the number of primary segments that will get created per #### physical host (if multiple addresses for a host are listed in #### the hostfile, the number of segments will be spread evenly across #### the specified interface addresses). declare -a DATA_DIRECTORY=(/greenplum/gpdata/primary1 /greenplum/gpdata/primary2) #### OS-configured hostname or IP address of the master host. MASTER_HOSTNAME=mdw #### File system location where the master data directory #### will be created. MASTER_DIRECTORY=/greenplum/gpdata/master #### Port number for the master instance. MASTER_PORT=5432 #### Shell utility used to connect to remote hosts. TRUSTED_SHELL=ssh #### Maximum log file segments between automatic WAL checkpoints. CHECK_POINT_SEGMENTS=8 #### Default server-side character set encoding. ENCODING=UNICODE ################################################ #### OPTIONAL MIRROR PARAMETERS ################################################ #### Base number by which mirror segment port numbers #### are calculated. MIRROR_PORT_BASE=50000 #### Base number by which primary file replication port #### numbers are calculated. REPLICATION_PORT_BASE=41000 #### Base number by which mirror file replication port #### numbers are calculated. MIRROR_REPLICATION_PORT_BASE=51000 #### File system location(s) where mirror segment data directories #### will be created. The number of mirror locations must equal the #### number of primary locations as specified in the #### DATA_DIRECTORY parameter. declare -a MIRROR_DATA_DIRECTORY=(/greenplum/gpdata/mirror1 /greenplum/gpdata/mirror2) ################################################ #### OTHER OPTIONAL PARAMETERS ################################################ #### Create a database of this name after initialization. #DATABASE_NAME=name_of_database #### Specify the location of the host address file here instead of #### with the the -h option of gpinitsystem. #MACHINE_LIST_FILE=/home/gpadmin/gpconfigs/hostfile_gpinitsystem
|
【本文地址】
 转存失败重新上传取消
转存失败重新上传取消