| 从零搭建ELK日志监控分析平台(ElasticSearch+Logstash+Kibana) | 您所在的位置:网站首页 › Centos7搭建管理平台 › 从零搭建ELK日志监控分析平台(ElasticSearch+Logstash+Kibana) |
从零搭建ELK日志监控分析平台(ElasticSearch+Logstash+Kibana)
|
目录
前言ELK是什么(What)?ELK组件介绍ELK架构图
为什么要用ELK(Why)?ELK的使用场景(Where)?如何搭建ELK(How)?实战项目介绍实战项目分析从零搭建ELK完成实战项目搭建ElasticSearch搭建Logstash搭建Kibana
前言
学无止境,任何形式的学习,最终必须要有输出才有可能变成自己的知识体系和知识积累。这篇文章也是自己对ELK学习过程中的一次输出,我按照我一贯学习新技术的常用思维(3W1H)去总结归纳。 ELK是什么(What)?ELK 是ElasticSearch开源生态中提供的一套完整日志收集、分析以及展示的解决方案,是三个产品的首字母缩写,分别是ElasticSearch、Logstash 和 Kibana。除此之外,FileBeat也是目前使用较多的日志收集软件,相对于Logstash更加轻量级占用资源更少。本文学习还是以Logstash为例。 ELK组件介绍ElasticSearch ,它是一个近实时(NRT)的分布式搜索和分析引擎,它可以用于全文搜索,结构化搜索以及分析。它是一个建立在全文搜索引擎 Apache Lucene 基础上的搜索引擎,使用 Java 语言编写。 Logstash ,它是一个具有近实时(NRT)传输能力的数据收集、过滤、分析引擎,用来进行数据收集、解析、过滤,并最终将数据发送给ES。 Kibana ,它是一个为 ElasticSearch 提供分析和展示的可视化 Web 平台。它可以在 ElasticSearch 的索引中查找,交互数据,并生成各种维度表格、图形以及仪表盘。 ELK架构图
随着我们系统架构的不断升级,由单体转为分布式、微服务、网格系统等,用户访问产生的日志量也在不断增加,我们急需一个可以快速、准确查询和分析日志的平台。 一个完整的日志分析平台,需要包含以下几个主要特点: 收集-能够采集多种来源的日志数据(系统的错误日志+业务的访问日志)传输-能够稳定的把日志数据传输到日志平台存储-如何存储日志数据分析-可以支持 UI 分析警告-能够提供错误报告,监控机制而ELK的出现则为我们提供了一个完整的解决方案,并且都是开源软件,之间互相配合使用,完美衔接,高效的满足了很多场合的应用。是目前主流的一种日志系统。传统意义上,ELK也是作为替代Splunk(日志分析领域的领导者)的一个开源解决方案。 ELK的使用场景(Where)?ELK的核心使用场景,肯定是用于大型软硬件系统的日志采集、分析、展示。近年来随着互联网用户的急剧增加,各种场景也被进一步挖掘出来,刚好最近几年也是大数据比较火热的时候,大家都在使用各种大数据的产品,我们发现 Elasticsearch 就有处理海量数据的能力,几十百 TB 处理起来也很正常,并且比 Hadoop 更方便,速度更快。因此ELK也被用于其他场景,比如 SIEM 领域,有很多公司用来进行安全方面的数据分析,做企业防入侵检测、异常流量分析、用户行为分析等。 如何搭建ELK(How)?我们以一个实战项目为基础,从零开始搭建。 实战项目介绍对业务系统日志(系统日志+用户访问日志)进行实时搜索、分析和展示。 实战项目分析 目前业务系统日志存在oralce数据库的log表中。需要先通过Logstash采集oralce中的log表数据。将Logstash采集到的数据发送到ElasticSearch中。通过Kibana对ES中数据进行查询、分析和展示。 从零搭建ELK完成实战项目 搭建ElasticSearch去官网下载ES,本文中以elasticsearch-6.4.3.tar.gz为例 解压缩 tar -zxvf elasticsearch-6.4.3.tar.gz配置ES的核心配置文件 cd /usr/local/elasticsearch-6.4.3/config vim elasticsearch.yml 配置如下: # ======================== Elasticsearch Configuration ========================= # # NOTE: Elasticsearch comes with reasonable defaults for most settings. # Before you set out to tweak and tune the configuration, make sure you # understand what are you trying to accomplish and the consequences. # # The primary way of configuring a node is via this file. This template lists # the most important settings you may want to configure for a production cluster. # # Please consult the documentation for further information on configuration options: # https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/index.html # # ---------------------------------- Cluster ----------------------------------- # # Use a descriptive name for your cluster: # cluster.name: zkc-elasticsearch # # ------------------------------------ Node ------------------------------------ # # Use a descriptive name for the node: # node.name: node-0 # # Add custom attributes to the node: # #node.attr.rack: r1 # # ----------------------------------- Paths ------------------------------------ # # Path to directory where to store the data (separate multiple locations by comma): # path.data: /usr/local/elasticsearch-6.4.3/data # # Path to log files: # path.logs: /usr/local/elasticsearch-6.4.3/logs # # ----------------------------------- Memory ----------------------------------- # # Lock the memory on startup: # #bootstrap.memory_lock: true # # Make sure that the heap size is set to about half the memory available # on the system and that the owner of the process is allowed to use this # limit. # # Elasticsearch performs poorly when the system is swapping the memory. # # ---------------------------------- Network ----------------------------------- # # Set the bind address to a specific IP (IPv4 or IPv6): # network.host: 0.0.0.0 # # Set a custom port for HTTP: # #http.port: 9200 http.cors.enabled : true http.cors.allow-origin : "*" # For more information, consult the network module documentation. # # --------------------------------- Discovery ---------------------------------- # # Pass an initial list of hosts to perform discovery when new node is started: # The default list of hosts is ["127.0.0.1", "[::1]"] # #discovery.zen.ping.unicast.hosts: ["host1", "host2"] # # Prevent the "split brain" by configuring the majority of nodes (total number of master-eligible nodes / 2 + 1): # #discovery.zen.minimum_master_nodes: # #cluster.initial_master_nodes: ["node-0"] # For more information, consult the zen discovery module documentation. # # ---------------------------------- Gateway ----------------------------------- # # Block initial recovery after a full cluster restart until N nodes are started: # #gateway.recover_after_nodes: 3 # # For more information, consult the gateway module documentation. # # ---------------------------------- Various ----------------------------------- # # Require explicit names when deleting indices: # #action.destructive_requires_name: true 安装IK中文分析器,ES默认分析器无法对中文进行分析。去GitHub上下载IK分析器,本文中以elasticsearch-analysis-ik-6.4.3.zip为例解压缩IK unzip elasticsearch-analysis-ik-6.4.3.zip -d /usr/local/elasticsearch-6.4.3/plugins/ik/ES不能用root用户启动,所以需要创建普通用户并附权限 useradd esuser chown -R esuser /usr/local/elasticsearch-6.4.3/我在虚拟机测试,需要配置es的JVM参数,内存够的可以忽略 vim jvm.options 配置如下: -Xms128M -Xmx128M 配置es其他启动参数 vim /etc/security/limits.conf 配置如下: # /etc/security/limits.conf # #This file sets the resource limits for the users logged in via PAM. #It does not affect resource limits of the system services. # #Also note that configuration files in /etc/security/limits.d directory, #which are read in alphabetical order, override the settings in this #file in case the domain is the same or more specific. #That means for example that setting a limit for wildcard domain here #can be overriden with a wildcard setting in a config file in the #subdirectory, but a user specific setting here can be overriden only #with a user specific setting in the subdirectory. # #Each line describes a limit for a user in the form: # # # #Where: # can be: # - a user name # - a group name, with @group syntax # - the wildcard *, for default entry # - the wildcard %, can be also used with %group syntax, # for maxlogin limit # # can have the two values: # - "soft" for enforcing the soft limits # - "hard" for enforcing hard limits # # can be one of the following: # - core - limits the core file size (KB) # - data - max data size (KB) # - fsize - maximum filesize (KB) # - memlock - max locked-in-memory address space (KB) # - nofile - max number of open file descriptors # - rss - max resident set size (KB) # - stack - max stack size (KB) # - cpu - max CPU time (MIN) # - nproc - max number of processes # - as - address space limit (KB) # - maxlogins - max number of logins for this user # - maxsyslogins - max number of logins on the system # - priority - the priority to run user process with # - locks - max number of file locks the user can hold # - sigpending - max number of pending signals # - msgqueue - max memory used by POSIX message queues (bytes) # - nice - max nice priority allowed to raise to values: [-20, 19] # - rtprio - max realtime priority # # # #* soft core 0 #* hard rss 10000 #@student hard nproc 20 #@faculty soft nproc 20 #@faculty hard nproc 50 #ftp hard nproc 0 #@student - maxlogins 4 * soft nofile 65536 * hard nofile 131072 * soft nproc 2048 * hard nproc 4096 # End of filevim /etc/sysctl.conf 配置如下: # sysctl settings are defined through files in # /usr/lib/sysctl.d/, /run/sysctl.d/, and /etc/sysctl.d/. # # Vendors settings live in /usr/lib/sysctl.d/. # To override a whole file, create a new file with the same in # /etc/sysctl.d/ and put new settings there. To override # only specific settings, add a file with a lexically later # name in /etc/sysctl.d/ and put new settings there. # # For more information, see sysctl.conf(5) and sysctl.d(5). # vm.max_map_count=262145配置生效 sysctl -p 8. 切换用户并启动ES su esuser cd /usr/local/elasticsearch-6.4.3/bin/ ./elasticsearch 9. 启动后查看控制台,并访问ES http://192.168.184.145:9200 去官网下载压缩包,本文以logstash-6.4.3.tar.gz为例 解压缩 tar -zxvf logstash-6.4.3.tar.gz mv logstash-6.4.3 /usr/local/创建同步文件夹,后面会存入同步相关jar包和配置文件 mkdir sync创建并编辑同步配置文件 cd sync vim logstash-db-sync.conf 配置如下: input{ jdbc{ # 设置 MySql/MariaDB 数据库url以及数据库名称 jdbc_connection_string => "jdbc:oracle:thin:@172.16.4.29:1521:urpdb" # 用户名和密码 jdbc_user => "USR_JWJC_DEV" jdbc_password => "JWJCDEV1234" # 数据库驱动所在位置,可以是绝对路径或者相对路径 jdbc_driver_library => "/usr/local/logstash-6.4.3/sync/ojdbc8-12.2.0.1.jar" # 驱动类名 jdbc_driver_class => "Java::oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver" # 开启分页 jdbc_paging_enabled => "true" # 分页数量 jdbc_page_size => "1000" # 执行的sql文件路径 statement_filepath => "/usr/local/logstash-6.4.3/sync/jwf_log.sql" # 设置任务间隔 含义:分 时 天 月 年 全部*默认每分钟跑一次 schedule => "* * * * *" # 索引类型 type => "_doc" # 是否开启记录上次追踪的结果 use_column_value => true # 记录上次追踪的结果值 last_run_metadata_path => "/usr/local/logstash-6.4.3/sync/track_time" # 追踪字段名称 tracking_column => "ID" # 追踪字段类型 tracking_column_type => "numeric" # 是否清除追踪记录 clean_run => false # 数据库字段名称大写转小写 lowercase_column_names => false } } output{ # es配置 elasticsearch{ # es地址 hosts => ["192.168.184.145:9200"] # 索引库名称 index => "jwf-logs" # 设置索引ID document_id => "%{ID}" } # 日志输出 stdout{ codec => json_lines } } 拷贝配置中涉及的数据库驱动jar包,根据实际数据库来 编辑用于同步的sql vim jwf_log.sql
SELECT * from T_SYSTEM_REQUEST_LOG WHERE ID > :sql_last_value
启动logstash并观察es索引和数据是否正确 cd bin/ ./logstash -f /usr/local/logstash-6.4.3/sync/logstash-db-sync.conf通过es-head观察或者直接es的rest api查询是否存在索引jwf-logs 编辑用于同步的sql vim jwf_log.sql
SELECT * from T_SYSTEM_REQUEST_LOG WHERE ID > :sql_last_value
启动logstash并观察es索引和数据是否正确 cd bin/ ./logstash -f /usr/local/logstash-6.4.3/sync/logstash-db-sync.conf通过es-head观察或者直接es的rest api查询是否存在索引jwf-logs 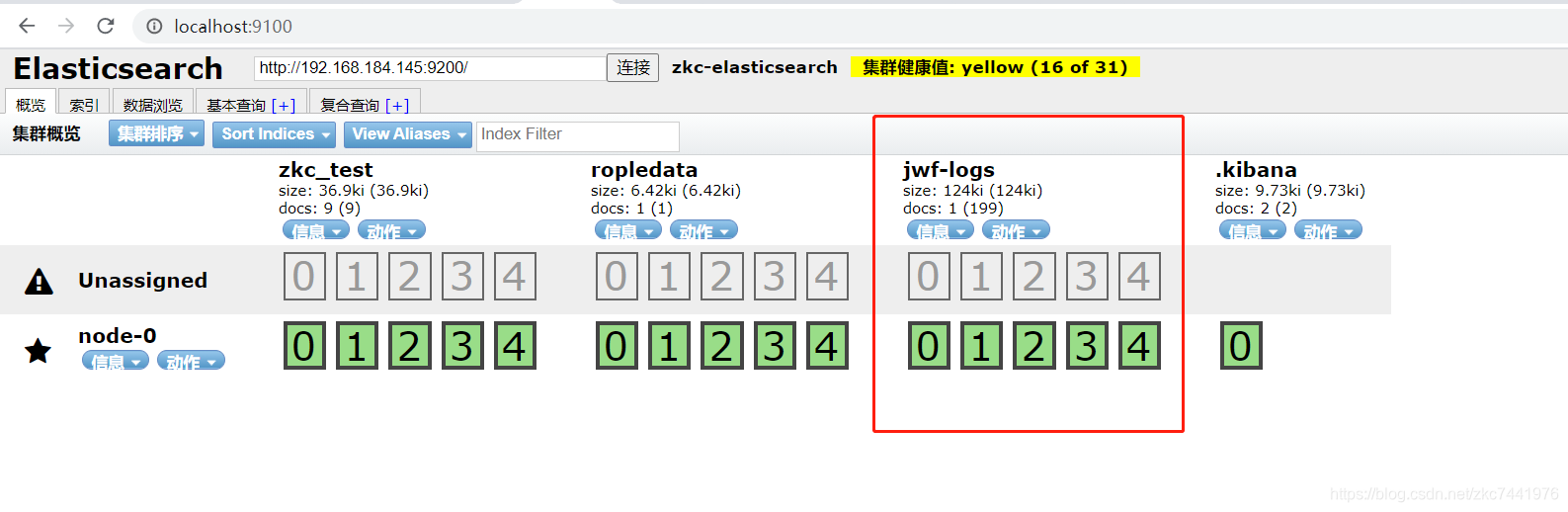 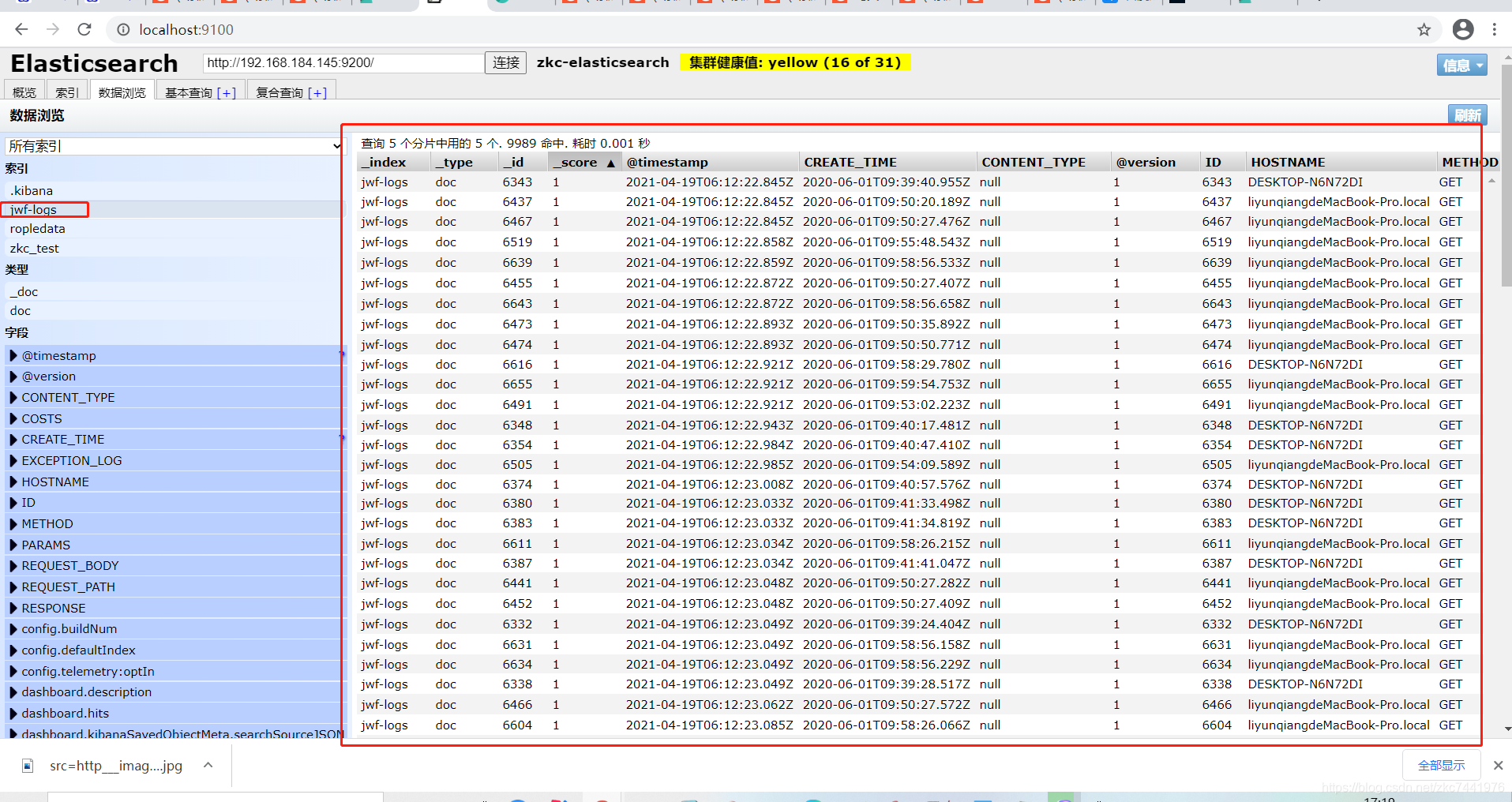 搭建Kibana
搭建Kibana
去官网下载压缩包,本案例中以kibana-6.4.3-linux-x86_64.tar.gz为例。 解压缩 tar -zxvf kibana-6.4.3-linux-x86_64.tar.gz配置kibana配置文件 cd /usr/local/kibana-6.4.3-linux-x86_64/config/ vim kibana.yml 配置如下: 默认kibana只能连接本机的ES # Kibana is served by a back end server. This setting specifies the port to use. #server.port: 5601 # Specifies the address to which the Kibana server will bind. IP addresses and host names are both valid values. # The default is 'localhost', which usually means remote machines will not be able to connect. # To allow connections from remote users, set this parameter to a non-loopback address. server.host: "192.168.184.145" # Enables you to specify a path to mount Kibana at if you are running behind a proxy. # Use the `server.rewriteBasePath` setting to tell Kibana if it should remove the basePath # from requests it receives, and to prevent a deprecation warning at startup. # This setting cannot end in a slash. #server.basePath: "" # Specifies whether Kibana should rewrite requests that are prefixed with # `server.basePath` or require that they are rewritten by your reverse proxy. # This setting was effectively always `false` before Kibana 6.3 and will # default to `true` starting in Kibana 7.0. #server.rewriteBasePath: false # The maximum payload size in bytes for incoming server requests. #server.maxPayloadBytes: 1048576 # The Kibana server's name. This is used for display purposes. #server.name: "your-hostname" # The URL of the Elasticsearch instance to use for all your queries. elasticsearch.url: "http://192.168.184.145:9200" # When this setting's value is true Kibana uses the hostname specified in the server.host # setting. When the value of this setting is false, Kibana uses the hostname of the host # that connects to this Kibana instance. #elasticsearch.preserveHost: true # Kibana uses an index in Elasticsearch to store saved searches, visualizations and # dashboards. Kibana creates a new index if the index doesn't already exist. #kibana.index: ".kibana" # The default application to load. #kibana.defaultAppId: "home" # If your Elasticsearch is protected with basic authentication, these settings provide # the username and password that the Kibana server uses to perform maintenance on the Kibana # index at startup. Your Kibana users still need to authenticate with Elasticsearch, which # is proxied through the Kibana server. #elasticsearch.username: "user" #elasticsearch.password: "pass" # Enables SSL and paths to the PEM-format SSL certificate and SSL key files, respectively. # These settings enable SSL for outgoing requests from the Kibana server to the browser. #server.ssl.enabled: false #server.ssl.certificate: /path/to/your/server.crt #server.ssl.key: /path/to/your/server.key # Optional settings that provide the paths to the PEM-format SSL certificate and key files. # These files validate that your Elasticsearch backend uses the same key files. #elasticsearch.ssl.certificate: /path/to/your/client.crt #elasticsearch.ssl.key: /path/to/your/client.key # Optional setting that enables you to specify a path to the PEM file for the certificate # authority for your Elasticsearch instance. #elasticsearch.ssl.certificateAuthorities: [ "/path/to/your/CA.pem" ] # To disregard the validity of SSL certificates, change this setting's value to 'none'. #elasticsearch.ssl.verificationMode: full # Time in milliseconds to wait for Elasticsearch to respond to pings. Defaults to the value of # the elasticsearch.requestTimeout setting. #elasticsearch.pingTimeout: 1500 # Time in milliseconds to wait for responses from the back end or Elasticsearch. This value # must be a positive integer. #elasticsearch.requestTimeout: 30000 # List of Kibana client-side headers to send to Elasticsearch. To send *no* client-side # headers, set this value to [] (an empty list). #elasticsearch.requestHeadersWhitelist: [ authorization ] # Header names and values that are sent to Elasticsearch. Any custom headers cannot be overwritten # by client-side headers, regardless of the elasticsearch.requestHeadersWhitelist configuration. #elasticsearch.customHeaders: {} # Time in milliseconds for Elasticsearch to wait for responses from shards. Set to 0 to disable. #elasticsearch.shardTimeout: 30000 # Time in milliseconds to wait for Elasticsearch at Kibana startup before retrying. #elasticsearch.startupTimeout: 5000 # Logs queries sent to Elasticsearch. Requires logging.verbose set to true. #elasticsearch.logQueries: false # Specifies the path where Kibana creates the process ID file. #pid.file: /var/run/kibana.pid # Enables you specify a file where Kibana stores log output. #logging.dest: stdout # Set the value of this setting to true to suppress all logging output. #logging.silent: false # Set the value of this setting to true to suppress all logging output other than error messages. #logging.quiet: false # Set the value of this setting to true to log all events, including system usage information # and all requests. #logging.verbose: false # Set the interval in milliseconds to sample system and process performance # metrics. Minimum is 100ms. Defaults to 5000. #ops.interval: 5000 # The default locale. This locale can be used in certain circumstances to substitute any missing # translations. #i18n.defaultLocale: "en" 启动Kibana cd bin/ ./kibana进入Kibana主页并配置查询的index索引规则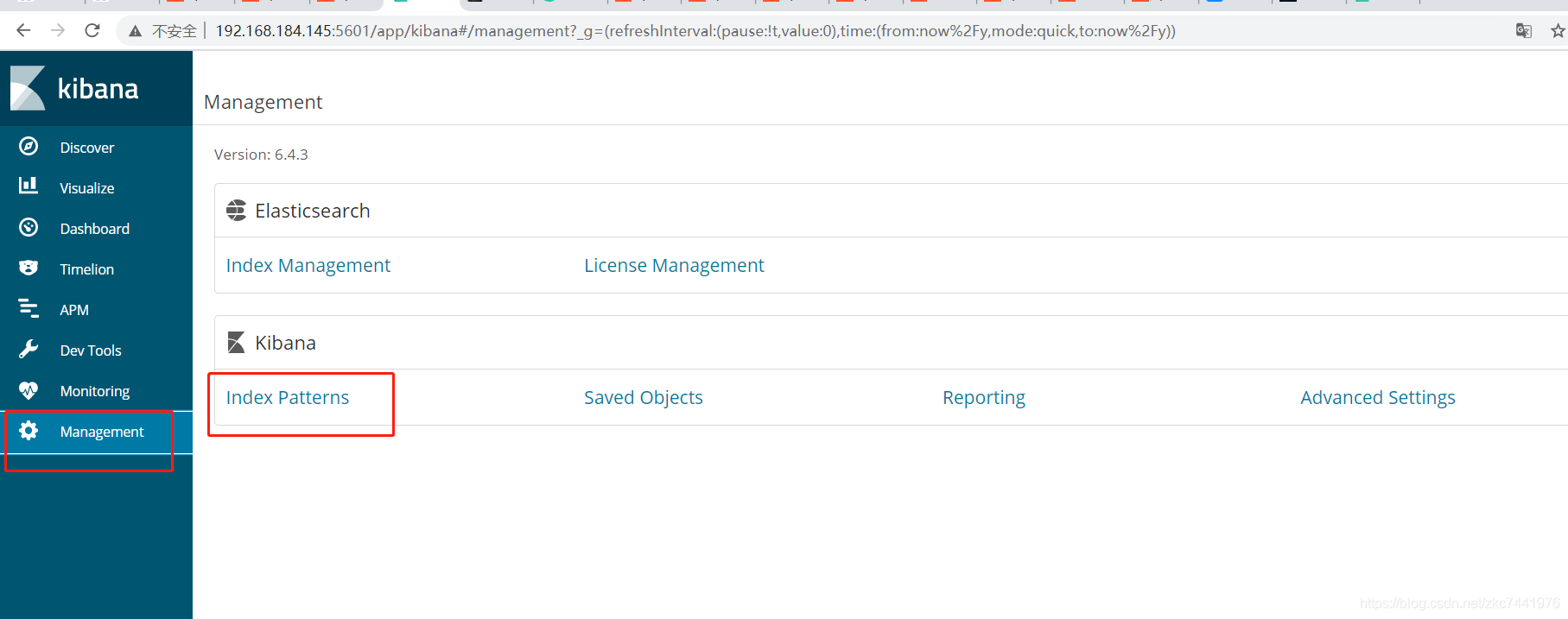 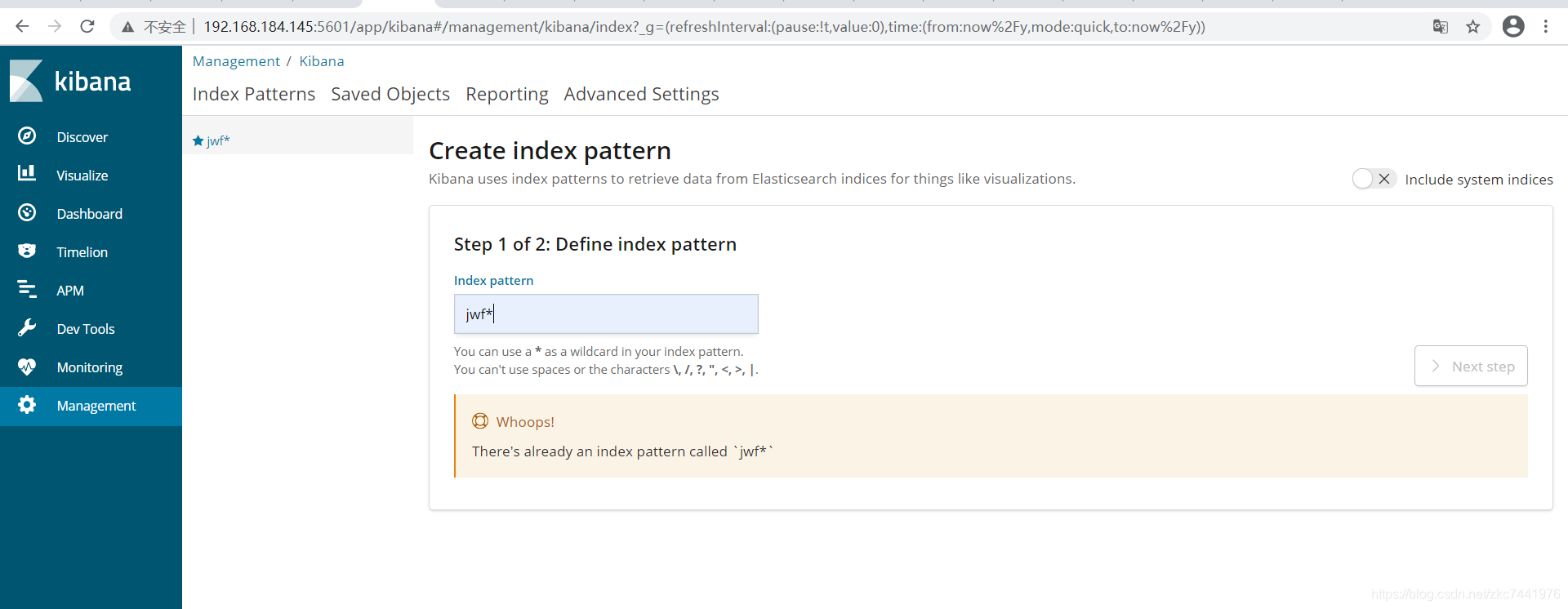 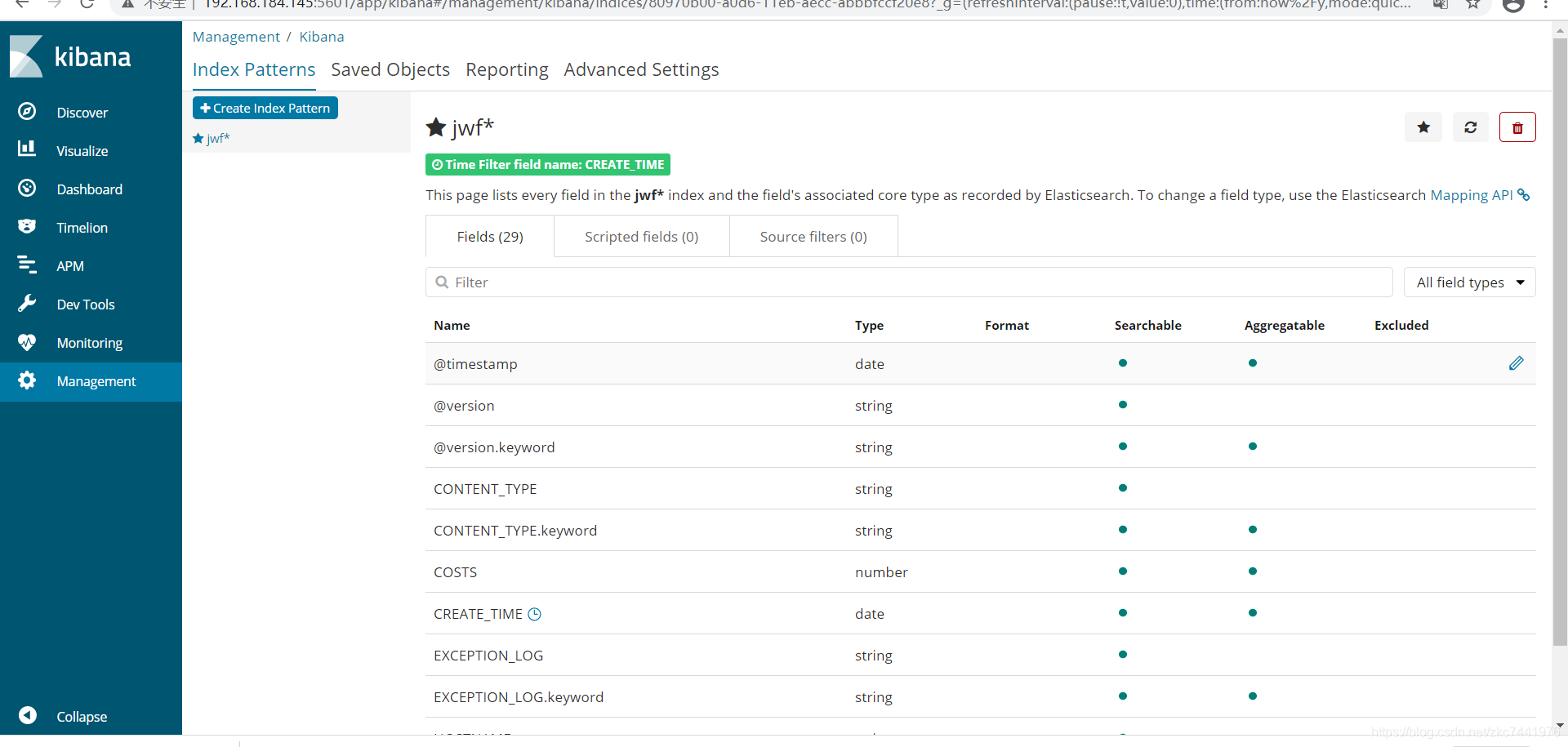 索引规则创建后,进入Discover即可查询到被规则命中的索引记录,基于Lucene语法 索引规则创建后,进入Discover即可查询到被规则命中的索引记录,基于Lucene语法 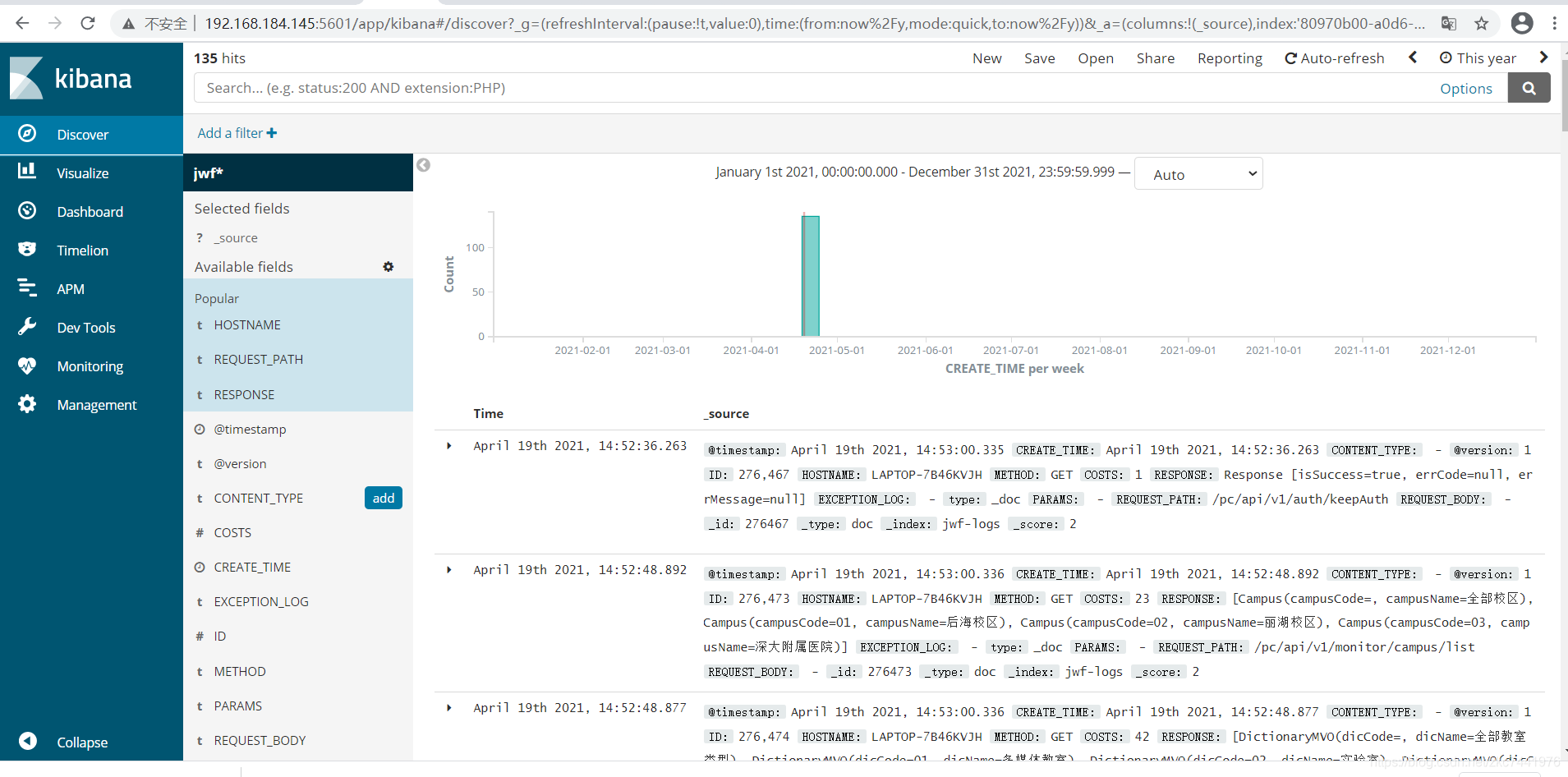 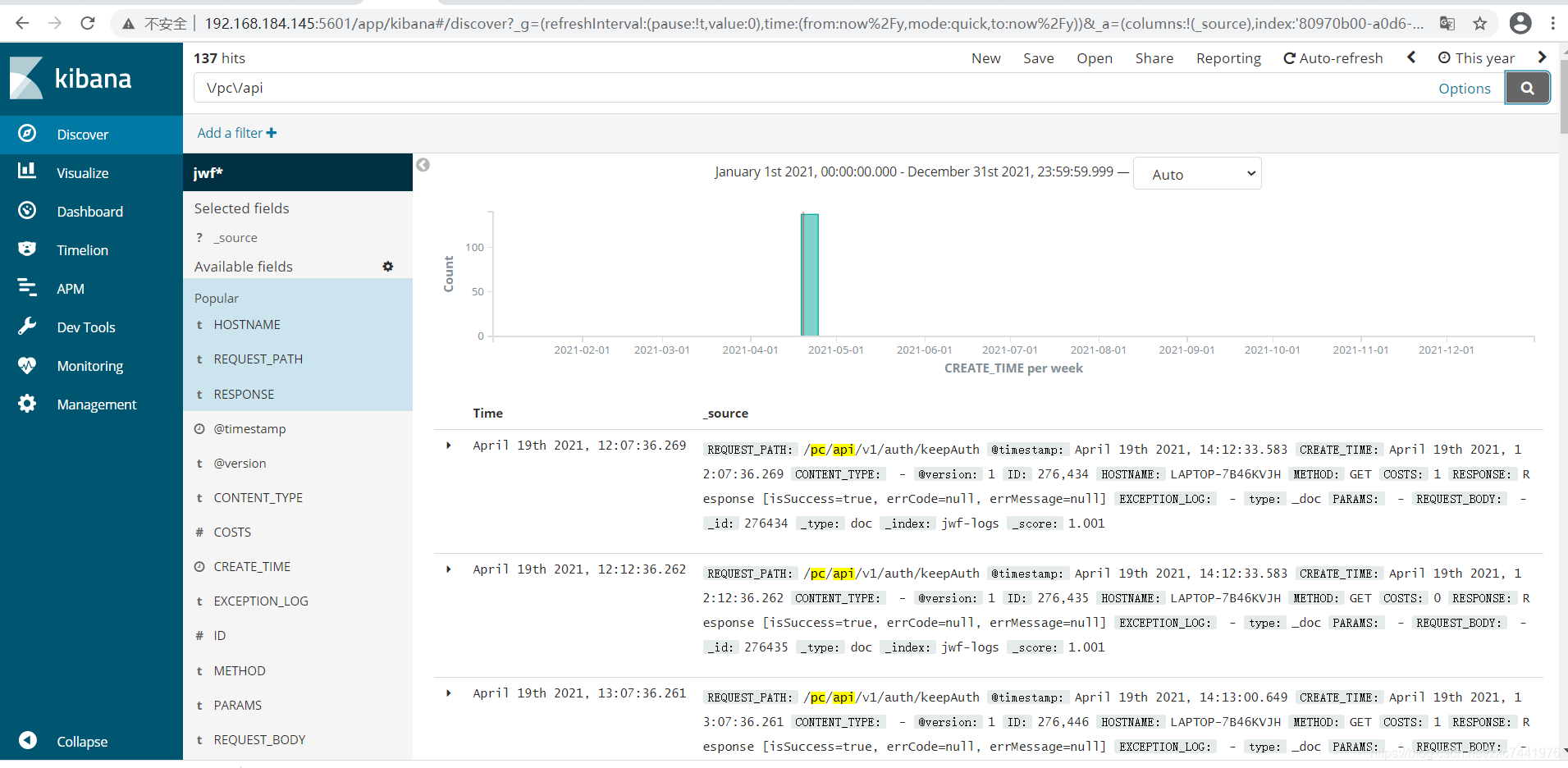 支持监控图表和仪表盘自定义 支持监控图表和仪表盘自定义  注意: ELK中涉及的各组件,版本要保持一致,否则可能会出现匹配错误。 注意: ELK中涉及的各组件,版本要保持一致,否则可能会出现匹配错误。
|
【本文地址】

