为串联机械臂写一个ROS控制器 |
您所在的位置:网站首页 › 机械臂三个字怎么写 › 为串联机械臂写一个ROS控制器 |
为串联机械臂写一个ROS控制器
|
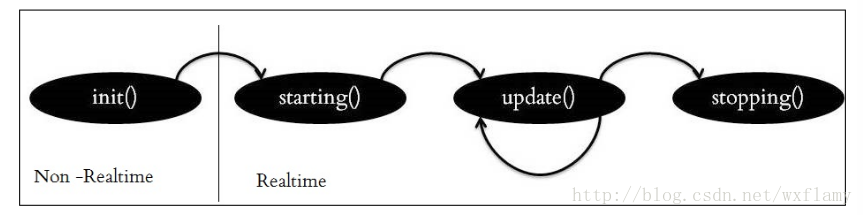
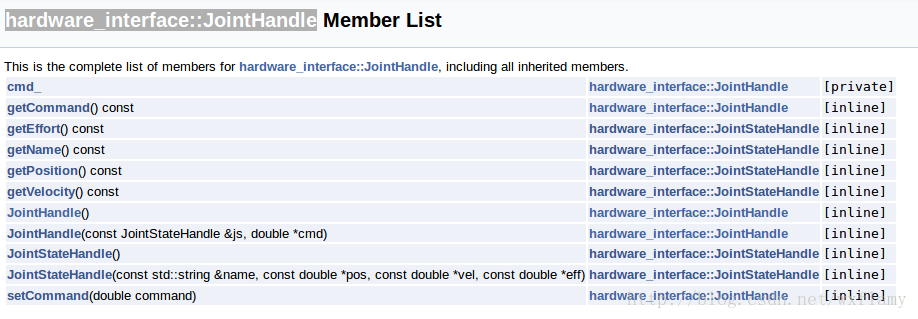
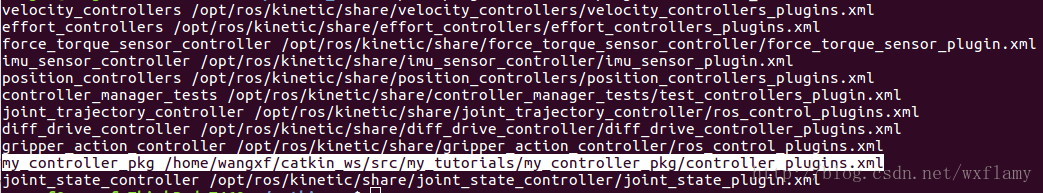
上一篇博客中,实现了gazebo中控制器的应用,但是由于PID调的不好,控制效果实在是不好意思贴出图来,作为一个控制理论与控制工程毕业的人,我怎么忍得了。今天就试着来编一编控制器。当然是参考了一些教程。12 ROS中有一些标准的控制器,比如joint state, position, trajectory,这些在gazebo仿真中也用到了一部分。 以下是控制器的工作流程 加载控制器后,第一个执行的函数就是初始化int(),这并不是启动控制器,初始化函数的参数包括机器人的状态参数和Nodehandle。初始化函数只执行一次。 启动控制器函数starting(),也只执行一次,用于控制器的启动。 update()函数保证了控制器的活跃状态。以1000Hz的频率执行代码,意味着一微秒就要计算完成一个执行周期。 最后stop()停止控制器命令也只执行一次。 建立一个控制器的过程需要以下几个步骤: 新建一个带有必要依赖的ROS包;编写控制器C++代码;将C++类注册或者发布为一个插件;在XML文件中定义插件; 更新package.xml来发布插件;编写CMakeLists.txt编译代码 为控制器参数编写配置文件 在gazebo中进行仿真 使用controller manager加载控制器。 创建控制器功能包 $ catkin_create_pkg my_controller_pkg roscpp pluginlib controller_interface hardware_interface 建立一个控制器的头文件 #include #include #include #include #include #include #include #include #include #include #include #include #include #include namespace my_controller_pkg{ class MyControllerClass: public controller_interface::Controller { private: hardware_interface::JointHandle joint_; double init_pos_; ros::Subscriber sub_command_; public: /** * \brief Store position and velocity command in struct to allow easier realtime buffer usage */ struct Commands { double position_; // Last commanded position double velocity_; // Last commanded velocity bool has_velocity_; // false if no velocity command has been specified }; realtime_tools::RealtimeBuffer command_; Commands command_struct_; // pre-allocated memory that is re-used to set the realtime buffer virtual bool init(hardware_interface::EffortJointInterface *robot, ros::NodeHandle &n); virtual void starting(); virtual void update(const ros::Time& time, const ros::Duration& period); virtual void stopping(); void setCommandCB(const std_msgs::Float64ConstPtr& msg); /*! * \brief Give set position of the joint for next update: revolute (angle) and prismatic (position) * * \param command */ void setCommand(double pos_target); /*! * \brief Give set position of the joint for next update: revolute (angle) and prismatic (position) * Also supports a target velocity * * \param pos_target - position setpoint * \param vel_target - velocity setpoint */ void setCommand(double pos_target, double vel_target); }; } 建立代码文件 #include "my_controller_pkg/my_controller_file.h" #include namespace my_controller_pkg { /// Controller initialization in non-realtime bool MyControllerClass::init(hardware_interface::EffortJointInterface *robot, ros::NodeHandle &n) { std::string joint_name; if (!n.getParam("joint_name", joint_name)) { ROS_ERROR("No joint given in namespace: '%s')", n.getNamespace().c_str()); return false; } joint_ = robot->getHandle(joint_name); // if (!joint_) // { // ROS_ERROR("MyController could not find joint named '%s'", // joint_name.c_str()); // return false; // } // Start command subscriber sub_command_ = n.subscribe("command", 1, &MyControllerClass::setCommandCB, this); return true; } /// Controller startup in realtime void MyControllerClass::starting() { init_pos_ = joint_.getPosition(); } /// Controller update loop in realtime void MyControllerClass::update(const ros::Time& time, const ros::Duration& period) { command_struct_ = *(command_.readFromRT()); double command_position = command_struct_.position_; double desired_pos = init_pos_ + 0.5 * sin(ros::Time::now().toSec()); double current_pos = joint_.getPosition(); double commanded_effort = -1000 * (current_pos - command_position); //joint_.commanded_effort_ = -10 * (current_pos - desired_pos); joint_.setCommand(commanded_effort); } /// Controller stopping in realtime void MyControllerClass::stopping() {} void MyControllerClass::setCommandCB(const std_msgs::Float64ConstPtr& msg) { setCommand(msg->data); } // Set the joint position command void MyControllerClass::setCommand(double pos_command) { command_struct_.position_ = pos_command; command_struct_.has_velocity_ = false; // Flag to ignore the velocity command since our setCommand method did not include it // the writeFromNonRT can be used in RT, if you have the guarantee that // * no non-rt thread is calling the same function (we're not subscribing to ros callbacks) // * there is only one single rt thread command_.writeFromNonRT(command_struct_); } // Set the joint position command with a velocity command as well void MyControllerClass::setCommand(double pos_command, double vel_command) { command_struct_.position_ = pos_command; command_struct_.velocity_ = vel_command; command_struct_.has_velocity_ = true; command_.writeFromNonRT(command_struct_); } } // namespace // Register controller to pluginlib PLUGINLIB_EXPORT_CLASS(my_controller_pkg::MyControllerClass, controller_interface::ControllerBase);其中hardware_interface::JointHandle可以参考:http://docs.ros.org/jade/api/hardware_interface/html/c++/classhardware__interface_1_1JointHandle-members.html 等我以后插在代码注释里 建立插件描述文件 My test. 更新package.xml文件 更新CMakeLists.txt文件 ## my_controller_file library add_library(my_controller_lib src/my_controller_file.cpp) target_link_libraries(my_controller_lib ${catkin_LIBRARIES}) 建立控制器使用catkin_make命令编译。然后用下列命令可以查看控制器是否编译成了一个插件 rospack plugins --attrib=plugin controller_interface在上一文章的yaml基础上修改,让新编的控制器控制joint1 myfirstrobot: # Publish all joint states ----------------------------------- joint_state_controller: type: joint_state_controller/JointStateController publish_rate: 50 # Position Controllers --------------------------------------- joint2_position_controller: type: effort_controllers/JointPositionController joint: joint2 pid: {p: 120.0, i: 10.01, d: 20.0} # Position Controllers --------------------------------------- joint1_position_controller: type: my_controller_pkg/MyControllerClass joint_name: joint1其他跟上一博客中的内容一致。 在gazebo中应用运行roslaunch myurdf gazebo.launch,会启动gazebo和rviz,运行以下命令,改变joint1的目标值 rostopic pub -1 /myfirstrobot/joint1_position_controller/command std_msgs/Float64 "data: 1" rostopic pub -1 /myfirstrobot/joint1_position_controller/command std_msgs/Float64 "data: 0"效果如下: 当然作为一个控制专业毕业的,怎么能受得了,这次能看出超调吗? 扰动也不惧啊 |
【本文地址】
今日新闻 |
点击排行 |
|
推荐新闻 |
图片新闻 |
|
专题文章 |
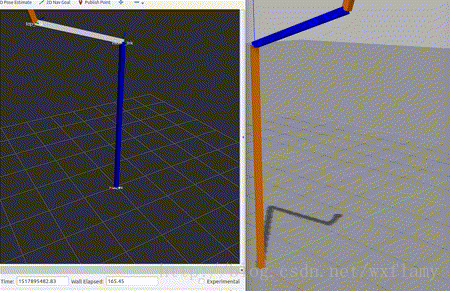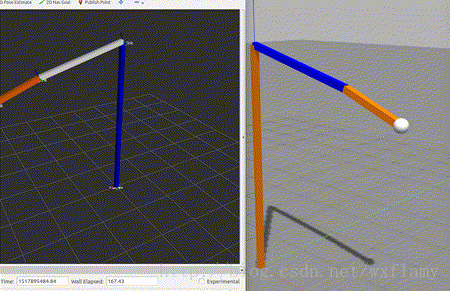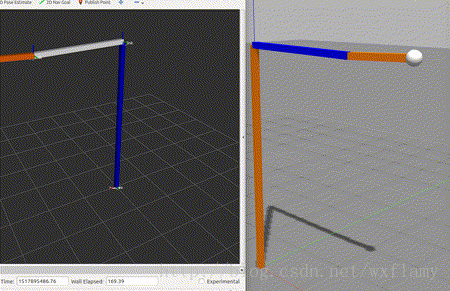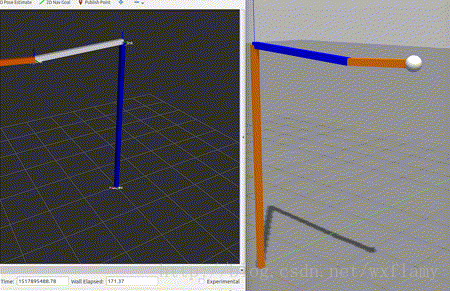 毕竟是个比例控制,不要有强迫症。 …………
毕竟是个比例控制,不要有强迫症。 …………


