linux等待队列wait |
您所在的位置:网站首页 › 文房四宝笔墨纸砚什么意思看动画 › linux等待队列wait |
linux等待队列wait
|
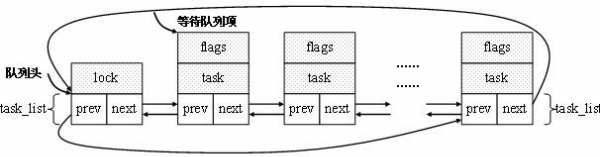
本文转自 reille博客: http://velep.com/archives/815.html 等待队列在linux内核中有着举足轻重的作用,很多linux驱动都或多或少涉及到了等待队列。因此,对于linux内核及驱动开发者来说,掌握等待队列是必须课之一。 Linux内核的等待队列是以双循环链表为基础数据结构,与进程调度机制紧密结合,能够用于实现核心的异步事件通知机制。它有两种数据结构:等待队列头(wait_queue_head_t)和等待队列项(wait_queue_t)。等待队列头和等待队列项中都包含一个list_head类型的域作为”连接件”。它通过一个双链表和把等待task的头,和等待的进程列表链接起来。下面具体介绍。 一、定义: 头文件:/include/linux/wait.h 1 struct __wait_queue_head { 2 spinlock_t lock; 3 struct list_head task_list; 4 }; 5 typedef struct __wait_queue_head wait_queue_head_t;二、作用: 在内核里面,等待队列是有很多用处的,尤其是在中断处理、进程同步、定时等场合。可以使用等待队列在实现阻塞进程的唤醒。它以队列为基础数据结构,与进程调度机制紧密结合,能够用于实现内核中的异步事件通知机制,同步对系统资源的访问等。 三、字段详解: 1、spinlock_t lock; 在对task_list与操作的过程中,使用该锁实现对等待队列的互斥访问。 2、srtuct list_head_t task_list; 双向循环链表,存放等待的进程。 三、操作: 1、定义并初始化: (1) 1 wait_queue_head_t my_queue; 2 init_waitqueue_head(&my_queue);直接定义并初始化。init_waitqueue_head()函数会将自旋锁初始化为未锁,等待队列初始化为空的双向循环链表。 (2) DECLARE_WAIT_QUEUE_HEAD(my_queue); 定义并初始化,相当于(1)。 (3) 定义等待队列: DECLARE_WAITQUEUE(name,tsk); 注意此处是定义一个wait_queue_t类型的变量name,并将其private与设置为tsk。wait_queue_t类型定义如下: 1 typedef struct __wait_queue wait_queue_t; 2 3 struct __wait_queue { 4 unsigned int flags; 5 #define WQ_FLAG_EXCLUSIVE 0x01 6 void *private; 7 wait_queue_func_t func; 8 struct list_head task_list; 9 }; 其中flags域指明该等待的进程是互斥进程还是非互斥进程。其中0是非互斥进程,WQ_FLAG_EXCLUSIVE(0×01)是互斥进程。等待队列(wait_queue_t)和等待对列头(wait_queue_head_t)的区别是等待队列是等待队列头的成员。也就是说等待队列头的task_list域链接的成员就是等待队列类型的(wait_queue_t)。 2、(从等待队列头中)添加/移出等待队列: (1) add_wait_queue()函数: 01 void add_wait_queue(wait_queue_head_t *q, wait_queue_t *wait) 02 { 03 unsigned long flags; 04 05 wait->flags &= ~WQ_FLAG_EXCLUSIVE; 06 spin_lock_irqsave(&q->lock, flags); 07 __add_wait_queue(q, wait); 08 spin_unlock_irqrestore(&q->lock, flags); 09 } 10 EXPORT_SYMBOL(add_wait_queue);设置等待的进程为非互斥进程,并将其添加进等待队列头(q)的队头中。 01 void add_wait_queue_exclusive(wait_queue_head_t *q, wait_queue_t *wait) 02 { 03 unsigned long flags; 04 05 wait->flags |= WQ_FLAG_EXCLUSIVE; 06 spin_lock_irqsave(&q->lock, flags); 07 __add_wait_queue_tail(q, wait); 08 spin_unlock_irqrestore(&q->lock, flags); 09 } 10 EXPORT_SYMBOL(add_wait_queue_exclusive);该函数也和add_wait_queue()函数功能基本一样,只不过它是将等待的进程(wait)设置为互斥进程。 (2)remove_wait_queue()函数: 1 void remove_wait_queue(wait_queue_head_t *q, wait_queue_t *wait) 2 { 3 unsigned long flags; 4 5 spin_lock_irqsave(&q->lock, flags); 6 __remove_wait_queue(q, wait); 7 spin_unlock_irqrestore(&q->lock, flags); 8 } 9 EXPORT_SYMBOL(remove_wait_queue);在等待的资源或事件满足时,进程被唤醒,使用该函数被从等待头中删除。 3、等待事件: (1)wait_event()宏: 01 /** 02 * wait_event - sleep until a condition gets true 03 * @wq: the waitqueue to wait on 04 * @condition: a C expression for the event to wait for 05 * 06 * The process is put to sleep (TASK_UNINTERRUPTIBLE) until the 07 * @condition evaluates to true. The @condition is checked each time 08 * the waitqueue @wq is woken up. 09 * 10 * wake_up() has to be called after changing any variable that could 11 * change the result of the wait condition. 12 */ 13 #define wait_event(wq, condition) \ 14 do { \ 15 if (condition) \ 16 break; \ 17 __wait_event(wq, condition); \ 18 } while (0)在等待会列中睡眠直到condition为真。在等待的期间,进程会被置为TASK_UNINTERRUPTIBLE进入睡眠,直到condition变量变为真。每次进程被唤醒的时候都会检查condition的值. (2)wait_event_interruptible()函数: 和wait_event()的区别是调用该宏在等待的过程中当前进程会被设置为TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE状态.在每次被唤醒的时候,首先检查condition是否为真,如果为真则返回,否则检查如果进程是被信号唤醒,会返回-ERESTARTSYS错误码.如果是condition为真,则返回0. (3)wait_event_timeout()宏: 也与wait_event()类似.不过如果所给的睡眠时间为负数则立即返回.如果在睡眠期间被唤醒,且condition为真则返回剩余的睡眠时间,否则继续睡眠直到到达或超过给定的睡眠时间,然后返回0. (4)wait_event_interruptible_timeout()宏: 与wait_event_timeout()类似,不过如果在睡眠期间被信号打断则返回ERESTARTSYS错误码. (5) wait_event_interruptible_exclusive()宏 同样和wait_event_interruptible()一样,不过该睡眠的进程是一个互斥进程. 5、唤醒队列: (1)wake_up()函数: 01 #define wake_up(x) __wake_up(x, TASK_NORMAL, 1, NULL) 02 03 /** 04 * __wake_up - wake up threads blocked on a waitqueue. 05 * @q: the waitqueue 06 * @mode: which threads 07 * @nr_exclusive: how many wake-one or wake-many threads to wake up 08 * @key: is directly passed to the wakeup function 09 */ 10 void __wake_up(wait_queue_head_t *q, unsigned int mode, 11 int nr_exclusive, void *key) 12 { 13 unsigned long flags; 14 15 spin_lock_irqsave(&q->lock, flags); 16 __wake_up_common(q, mode, nr_exclusive, 0, key); 17 spin_unlock_irqrestore(&q->lock, flags); 18 } 19 EXPORT_SYMBOL(__wake_up);唤醒等待队列.可唤醒处于TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE和TASK_UNINTERUPTIBLE状态的进程,和wait_event/wait_event_timeout成对使用. (2)wake_up_interruptible()函数: 1 #define wake_up_interruptible(x) __wake_up(x, TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE, 1, NULL)和wake_up()唯一的区别是它只能唤醒TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE状态的进程.,与wait_event_interruptible/wait_event_interruptible_timeout/ wait_event_interruptible_exclusive成对使用. (3) 1 #define wake_up_all(x) __wake_up(x, TASK_NORMAL, 0, NULL) 2 3 #define wake_up_interruptible_nr(x, nr) __wake_up(x, TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE, nr, NULL) 4 #define wake_up_interruptible_all(x) __wake_up(x, TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE, 0, NULL)这些也基本都和wake_up/wake_up_interruptible一样. 6、在等待队列上睡眠: (1) sleep_on()函数: 01 void __sched sleep_on(wait_queue_head_t *q) 02 { 03 sleep_on_common(q, TASK_UNINTERRUPTIBLE, MAX_SCHEDULE_TIMEOUT); 04 } 05 06 static long __sched 07 sleep_on_common(wait_queue_head_t *q, int state, long timeout) 08 { 09 unsigned long flags; 10 wait_queue_t wait; 11 12 init_waitqueue_entry(&wait, current); 13 14 __set_current_state(state); 15 16 spin_lock_irqsave(&q->lock, flags); 17 __add_wait_queue(q, &wait); 18 spin_unlock(&q->lock); 19 timeout = schedule_timeout(timeout); 20 spin_lock_irq(&q->lock); 21 __remove_wait_queue(q, &wait); 22 spin_unlock_irqrestore(&q->lock, flags); 23 24 return timeout; 25 }该函数的作用是定义一个等待队列(wait),并将当前进程添加到等待队列中(wait),然后将当前进程的状态置为TASK_UNINTERRUPTIBLE,并将等待队列(wait)添加到等待队列头(q)中。之后就被挂起直到资源可以获取,才被从等待队列头(q)中唤醒,从等待队列头中移出。在被挂起等待资源期间,该进程不能被信号唤醒。 (2)sleep_on_timeout()函数: 1 long __sched sleep_on_timeout(wait_queue_head_t *q, long timeout) 2 { 3 return sleep_on_common(q, TASK_UNINTERRUPTIBLE, timeout); 4 } 5 EXPORT_SYMBOL(sleep_on_timeout);与sleep_on()函数的区别在于调用该函数时,如果在指定的时间内(timeout)没有获得等待的资源就会返回。实际上是调用schedule_timeout()函数实现的。值得注意的是如果所给的睡眠时间(timeout)小于0,则不会睡眠。该函数返回的是真正的睡眠时间。 (3)interruptible_sleep_on()函数: 1 void __sched interruptible_sleep_on(wait_queue_head_t *q) 2 { 3 sleep_on_common(q, TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE, MAX_SCHEDULE_TIMEOUT); 4 } 5 EXPORT_SYMBOL(interruptible_sleep_on);该函数和sleep_on()函数唯一的区别是将当前进程的状态置为TASK_INTERRUPTINLE,这意味在睡眠如果该进程收到信号则会被唤醒。 (4)interruptible_sleep_on_timeout()函数: 1 long __sched 2 interruptible_sleep_on_timeout(wait_queue_head_t *q, long timeout) 3 { 4 return sleep_on_common(q, TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE, timeout); 5 } 6 EXPORT_SYMBOL(interruptible_sleep_on_timeout);类似于sleep_on_timeout()函数。进程在睡眠中可能在等待的时间没有到达就被信号打断而被唤醒,也可能是等待的时间到达而被唤醒。
以上四个函数都是让进程在等待队列上睡眠,不过是小有诧异而已。在实际用的过程中,根据需要选择合适的函数使用就是了。例如在对软驱数据的读写中,如果设备没有就绪则调用sleep_on()函数睡眠直到数据可读(可写),在打开串口的时候,如果串口端口处于关闭状态则调用interruptible_sleep_on()函数尝试等待其打开。在声卡驱动中,读取声音数据时,如果没有数据可读,就会等待足够常的时间直到可读取。 |
【本文地址】
今日新闻 |
点击排行 |
|
推荐新闻 |
图片新闻 |
|
专题文章 |