|
在开始程序之前说一个困扰的几天的东西,在链表做形参的时候什么时候用(**p)什么时候用(*p)
答案:只要是要修改head指针必须传递head的地址(用**p),否则传递head值即可(*p)。这与普通变量类似,当需要修改普通变量的值,需传递其地址,否则传递普通变量的值即可(引用)
详细的解释可以在csdn查到,附上链接:关于链表问题, 什么时候用2级指针, 什么时候用1级指针?-CSDN论坛
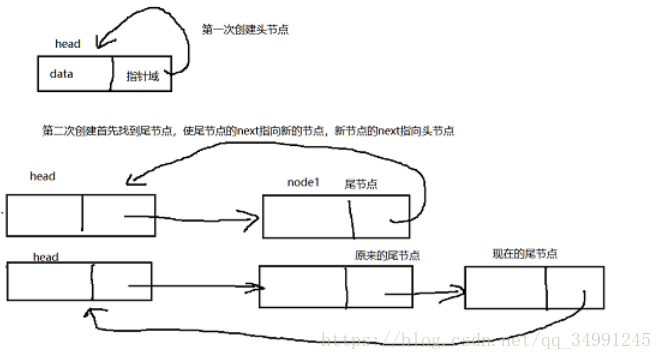
一、创建循环链表,结合下面的图片一起看几次就懂了
#include
#include
typedef struct List
{
int data;
struct List *next;
}list,*p_list;
void creat_list(list **p)//如果链表为空,则创建一个链表,指针域指向自己,否则寻找尾节点,将
{ //将尾节点的指针域指向这个新节点,新节点的指针域指向头结点
int item;
list *temp;
list *target;
printf("输入节点的值,输入0结束\n");
while(1)
{
scanf("%d",&item);
if(item==0)return;
if(*p==NULL) //如果输入的链表是空。则创建一个新的节点,使其next指针指向自己 (*head)->next=*head;
{
*p=(list *)malloc(sizeof(list));
if(!*p)exit(0);
(*p)->data=item;
(*p)->next=*p;
}
else //输入的链表不是空的,寻找链表的尾节点,使尾节点的next=新节点。新节点的next指向头节点
{
for(target=*p;target->next!=*p;target=target->next);//寻找尾节点
temp=(list *)malloc(sizeof(list));
if(!temp)exit(0);
temp->data=item;
temp->next=*p; //新节点指向头节点
target->next=temp;//尾节点指向新节点
}
}
}
图片和程序结合起来看
二、循环链表的遍历
void show(list *p)//遍历,循环链表的遍历最好用do while语句 ,因为头节点就有值
{
list *temp;
temp=p;
do
{
printf("%5d",temp->data);
temp=temp->next;
}
while(temp!=p);
printf("\n");
}
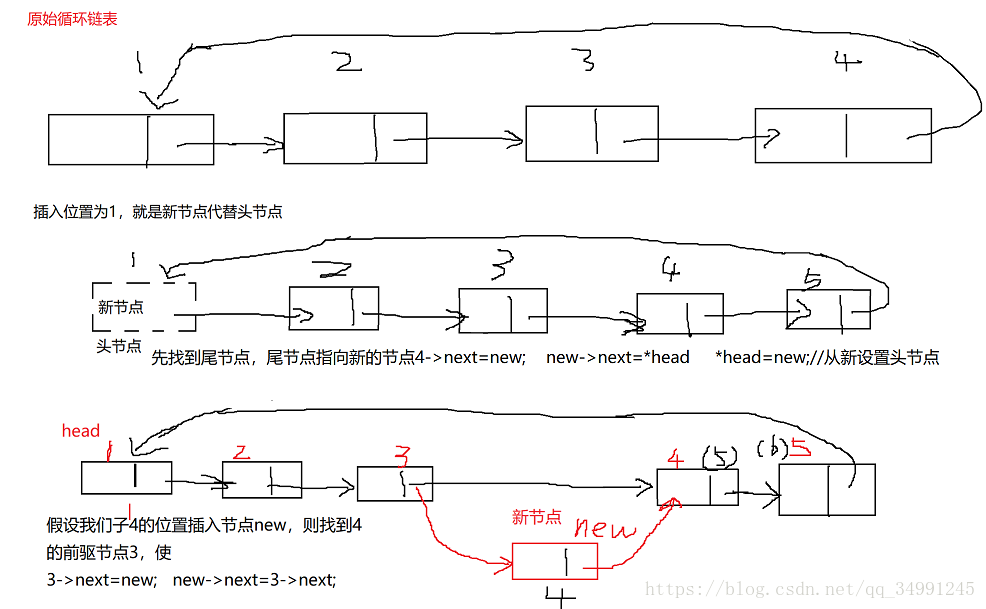
三、循环链表的插入
循环链表中最重要的是 头节点和尾节点,多数的操作都需要考虑到尾节点和头节点的特殊处理
代码
void insert(list **pNode,int place,int num) //链表的插入 place位置 num 数据
{
list *temp,*target;
int i;
if(place==1)//如果输入的数字是1,表示要插入头节点。应该特殊处理
{ //首先找到尾节点,让后让新节点的next指向头节点,尾节点指向新的头节点,在让头指针指向temp。这要特别注意
temp=(list *)malloc(sizeof(list));
if(!temp)exit(0);
temp->data=num;
for(target=*pNode;target->next!=*pNode;target=target->next);
temp->next=*pNode;
target->next=temp;
*pNode=temp;/特别注意
}
else//在其他的地方插入节点。 同样先找到要插入的位置,如果位置超出链表的长度,自动插入队尾。
{//找到要插入位置的前一个节点target,让target->next=temp,插入节点的前驱指向新节点,新节点指向target->next的地址
for(i=1,target=*pNode;target->next!=*pNode&&i!=place-1;target=target->next,i++);
temp=(list *)malloc(sizeof(list));
temp->data=num;
temp->next=target->next;
target->next=temp;
}
}
结合图片来看看
四、循环链表的删除
void Delete(list **pNode,int place) //删除操作
{
list *temp,*target;
int i;
temp=*pNode;
if(temp==NULL) //首先判断链表是否为空
{
printf("这是一个空指针 无法删除\n");
return;
}
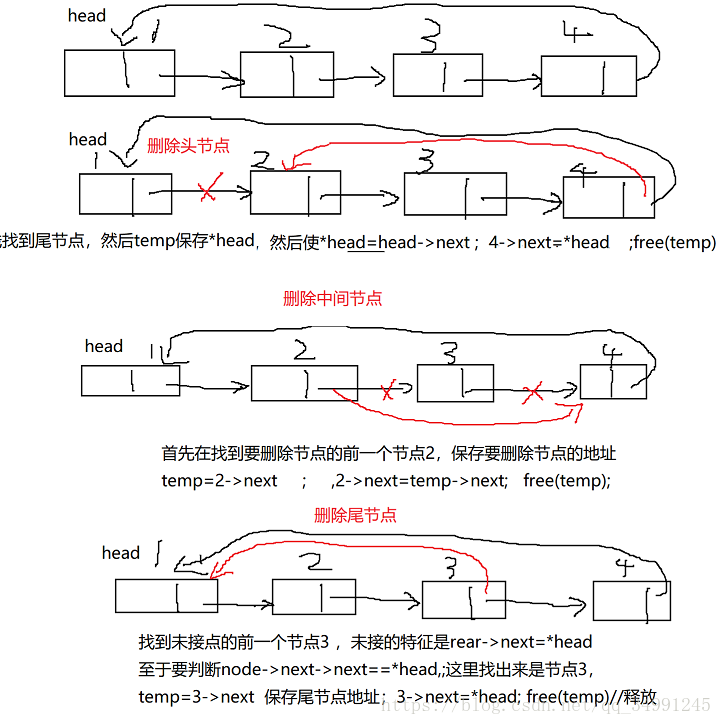
if(place==1) //如果删除的是头节点
{ //应当特殊处理,找到尾节点,使尾节点的next指向头节点的下一个节点
// rear->next=(*head)->next;然后让新节点作为头节点,释放原来的头节点
for(target=*pNode;target->next!=*pNode;target=target->next);
temp=*pNode;
*pNode=(*pNode)->next;
target->next=*pNode;
free(temp);
}
else //删除其他节点
{ //首先找出尾节点
for(i=1,target=*pNode;target->next!=*pNode&&i!=place-1;target=target->next,i++);
if(target->next==*pNode) //判断要删除的位置是否大于链表长度,若大于链表长度,
//特殊处理直接删除尾节点
{
//找出尾节的前一个节点
for(target=*pNode;target->next->next!=*pNode;target=target->next);
temp=target->next; // 尾节点的前一个节点直接指向头节点 释放原来的尾节点
target->next=*pNode;
printf("数字太大删除尾巴\n");
free(temp);
}
else
{
temp=target->next;// 删除普通节点 找到要删除节点的前一个节点target,
//使target指向要删除节点的下一个节点 转存删除节点地址
target->next=temp->next; // 然后释放这个节点
free(temp);
}
}
}
看看流程图
五、查找值
int findval(list *pNode,int val) //寻找值 返回位置
{
int i=1; //从一开始,因为头节点也有值
list *node;
node=pNode;
while(node->data!=val&&node->next!=pNode)
{
i++;
node=node->next;
}
if(node->next==pNode&&node->data!=val)//尾节点指向头节点就跳出,因此还要检测一次为节点的data
{
return -1;
}
return i;
}
完整代码
#include
#include
typedef struct List
{
int data;
struct List *next;
}list,*p_list;
void creat_list(list **p)//如果链表为空,则创建一个链表,指针域指向自己,否则寻找尾节点,将
{ //将尾节点的指针域指向这个新节点,新节点的指针域指向头结点
int item;
list *temp;
list *target;
printf("输入节点的值,输入0结束\n");
while(1)
{
scanf("%d",&item);
if(item==0)break;
if(*p==NULL) //如果输入的链表是空。则创建一个新的节点,使其next指针指向自己 (*head)->next=*head;
{
*p=(list *)malloc(sizeof(list));
if(!*p)exit(0);
(*p)->data=item;
(*p)->next=*p;
}
else //输入的链表不是空的,寻找链表的尾节点,使尾节点的next=新节点。新节点的next指向头节点
{
for(target=*p;target->next!=*p;target=target->next);//寻找尾节点
temp=(list *)malloc(sizeof(list));
if(!temp)exit(0);
temp->data=item;
temp->next=*p; //新节点指向头节点
target->next=temp;//尾节点指向新节点
}
}
}
void insert(list **pNode,int place,int num) //链表的插入
{
list *temp,*target;
int i;
if(place==1) //如果输入的数字是1,表示要插入头节点。应该特殊处理
{ //首先找到尾节点,让后让新节点的next指向头节点,尾节点指向新的头节点,在让头指针指向temp。这要特别注意
temp=(list *)malloc(sizeof(list));
if(!temp)exit(0);
temp->data=num;
for(target=*pNode;target->next!=*pNode;target=target->next);
temp->next=*pNode;
target->next=temp;
*pNode=temp;//特别注意
}
else //在其他的地方插入节点。 同样先找到要插入的位置,如果位置超出链表的长度,自动插入队尾。 tar new 原来是2
{ //找到要插入位置的前一个节点target,让target->next=temp,插入节点的前驱指向新节点,新节点指向target->next的地址 1 2 3
for(i=1,target=*pNode;target->next!=*pNode&&i!=place-1;target=target->next,i++);
temp=(list *)malloc(sizeof(list));
temp->data=num;
temp->next=target->next;
target->next=temp;
}
}
void Delete(list **pNode,int place) //删除操作
{
list *temp,*target;
int i;
temp=*pNode;
if(temp==NULL) //首先判断链表是否为空
{
printf("这是一个空指针 无法删除\n");
return;
}
if(place==1) //如果删除的是头节点
{ //应当特殊处理,找到尾节点,使尾节点的next指向头节点的下一个节点 rear->next=(*head)->next;然后让新节点作为头节点,释放原来的头节点
for(target=*pNode;target->next!=*pNode;target=target->next);
temp=*pNode;
*pNode=(*pNode)->next;
target->next=*pNode;
free(temp);
}
else
{ //删除其他节点
for(i=1,target=*pNode;target->next!=*pNode&&i!=place-1;target=target->next,i++); //首先找出尾节点
if(target->next==*pNode) //判断要删除的位置是否大于链表长度,若大于链表长度,特殊处理直接删除尾节点
{
for(target=*pNode;target->next->next!=*pNode;target=target->next);//找出尾节的前一个节点
temp=target->next; // 尾节点的前一个节点直接指向头节点 释放原来的尾节点
target->next=*pNode;
printf("数字太大删除尾巴\n");
free(temp);
}
else
{
temp=target->next;// 删除普通节点 找到要删除节点的前一个节点target,使target指向要删除节点的下一个节点 转存删除节点地址
target->next=temp->next; // 然后释放这个节点
free(temp);
}
}
}
int findval(list *pNode,int val) //寻找值
{
int i=1;
list *node;
node=pNode;
while(node->data!=val&&node->next!=pNode)
{
i++;
node=node->next;
}
if(node->next==pNode&&node->data!=val)//尾节点指向头节点就跳出,因此还要检测一次为节点的data
{
return -1;
}
return i;
}
void show(list *p)//遍历,循环链表的遍历最好用do while语句 ,因为头节点就有值
{
list *temp;
temp=p;
do
{
printf("%5d",temp->data);
temp=temp->next;
}
while(temp!=p);
printf("\n");
}
int main()
{
list *head=NULL;
//list *val;
int place,num;
creat_list(&head);
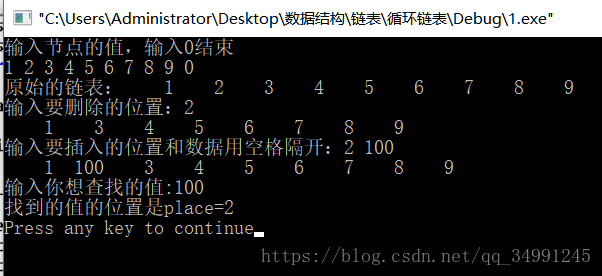
printf("原始的链表:");
show(head);
printf("输入要删除的位置:");
scanf("%d",&place);
Delete(&head,place);
show(head);
printf("输入要插入的位置和数据用空格隔开:");
scanf("%d %d",&place,&num);
insert(&head,place,num);
show(head);
printf("输入你想查找的值:");
scanf("%d",&num);
place=findval(head,num);
if(place!=-1)printf("找到的值的位置是place=%d\n",place);
else printf("没找到值\n");
return 0;
}
运行结果
|



