| elk(Elasticsearch、Kibana、Logstash )有这篇就够了,超级详细,包教会 | 您所在的位置:网站首页 › 找到这款mt4软件就够了 › elk(Elasticsearch、Kibana、Logstash )有这篇就够了,超级详细,包教会 |
elk(Elasticsearch、Kibana、Logstash )有这篇就够了,超级详细,包教会
|
目录 1. elk介绍 2. elk安装(windows版) 3. elk安装(linux版) 4. 收集springboot项目日志(windows版) 5. 收集springboot项目日志(linux版) 6. elk 补充(后台运行,开机自启) 1. elk介绍elastic中文官网: 免费且开放的搜索:Elasticsearch、ELK 和 Kibana 的开发者 | Elastic
Elasticsearch 是一个基于Lucene的搜索服务器。它提供了一个分布式多用户能力的全文搜索引擎,基于RESTful web接口。Elasticsearch是用Java语言开发的,并作为Apache许可条款下的开放源码发布,是一种流行的企业级搜索引擎。Elasticsearch用于云计算中,能够达到实时搜索,稳定,可靠,快速,安装使用方便。官方客户端在Java、.NET(C#)、PHP、Python、Apache Groovy、Ruby和许多其他语言中都是可用的。根据DB-Engines的排名显示,Elasticsearch是最受欢迎的企业搜索引擎,其次是Apache Solr,也是基于Lucene。 Kibana 是一款免费开源的前端应用程序,其基础是 Elastic Stack,可以为 Elasticsearch 中索引的数据提供搜索和数据可视化功能。尽管人们通常将 Kibana 视作 Elastic Stack(之前称作 ELK Stack,分别表示 Elasticsearch、Logstash 和 Kibana)的制图工具,但也可将 Kibana 作为用户界面来监测和管理 Elastic Stack 集群并确保集群安全性,还可将其作为基于 Elastic Stack 所开发内置解决方案的汇集中心。Elasticsearch 社区于 2013 年开发出了 Kibana,现在 Kibana 已发展成为 Elastic Stack 的窗口,是用户和公司的一个门户。 Logstash 是一个轻量级、开源的服务器端数据处理管道,允许您从各种来源收集数据,进行动态转换,并将数据发送到您希望的目标。它最常用作 Elasticsearch 的数据管道,Elasticsearch 是一个开源分析和搜索引擎。由于它与 Elasticsearch 紧密集成,具备强大的日志处理功能并提供 200 多个预构建的开源插件来帮助您轻松地索引数据,因此 Logstash 是将数据加载到 Elasticsearch 的常用工具。 网上的说都太官方了,我用大白话来描述一下这三个是主要的作用是什么,学一个东西首先要记住这几点: Elasticsearch 1、它是什么东西? 首先介绍一下它是什么东西,Elasticsearch是现在目前最流行的搜索引擎技术,BAT等很多大厂都在使用; 2、它能做什么? 搜索引擎就是把数据放到缓存中,在搜索时能够给快速的检索出来数据; 3、它怎么用? 需要安装和简单的配置上就可以了; logstash 1、它是什么东西? 是一个数据同步的脚本; 2、它能做什么? 帮我们同步数据,例如:把日志收集到es中 3、它怎么用? 需要安装和简单的配置上就可以了; kibana 1、它是什么东西? 展示数据,资源监控的程序;拥有很漂亮的ui; 2、它能做什么? 帮我们展示数据; 3、它怎么用? 需要安装和简单的配置上就可以了; 别嫌我啰嗦,学一个东西之前必须要知道这三点,什么东西、能做什么、怎么用,知道清楚这三点之后后面就比较容易理解了。 2. elk安装(windows版)1、下载地址:下载 Elastic 产品 | Elastic
主要需要下载下面这个三个:
点击下载
选择下载的版本
2、如果下载速度过慢,可以选择国内镜像,中文社区 下载中心 - Elastic 中文社区 点击需要的版本进行下载,可以下翻选择需要的版本;
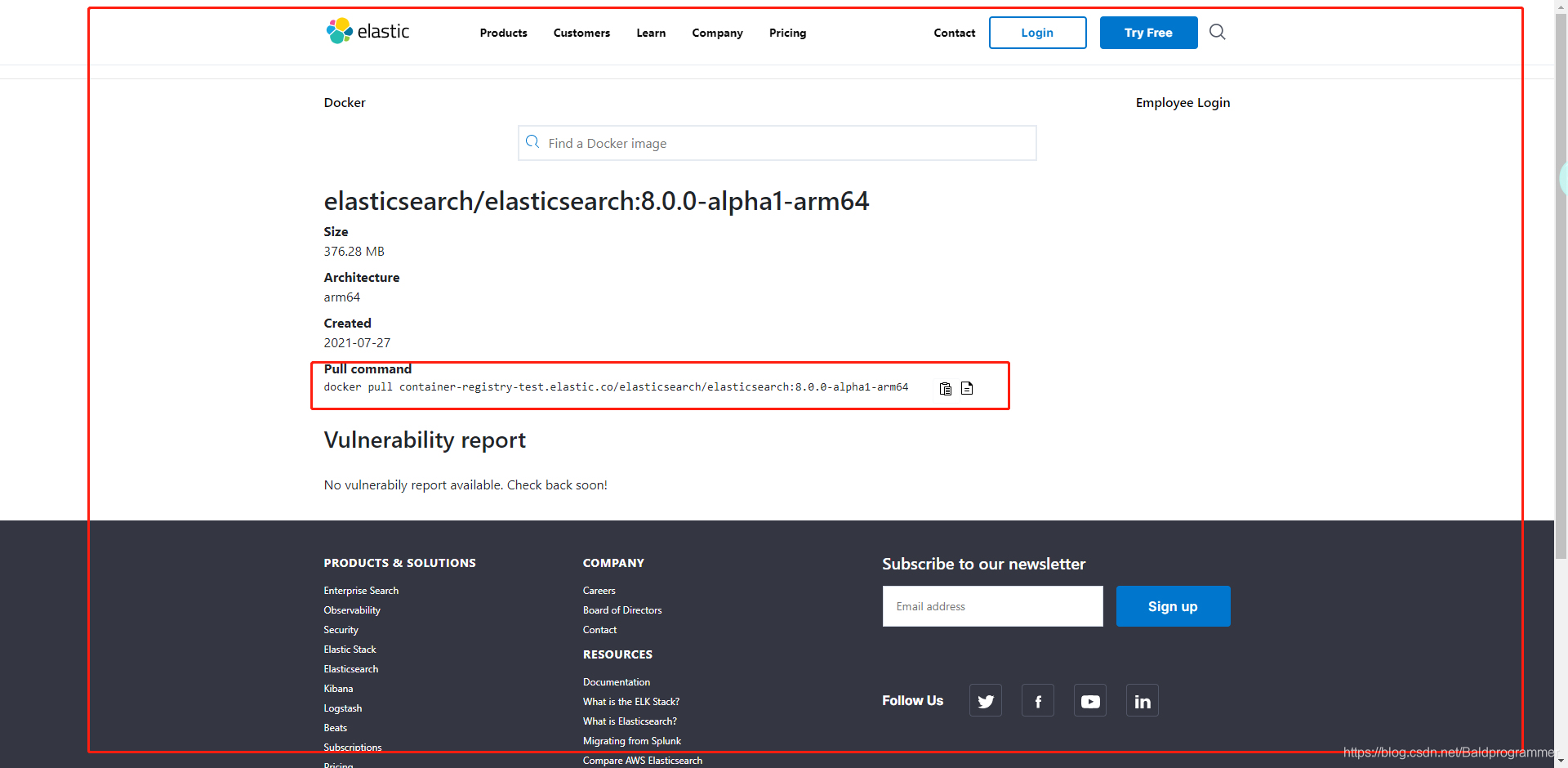
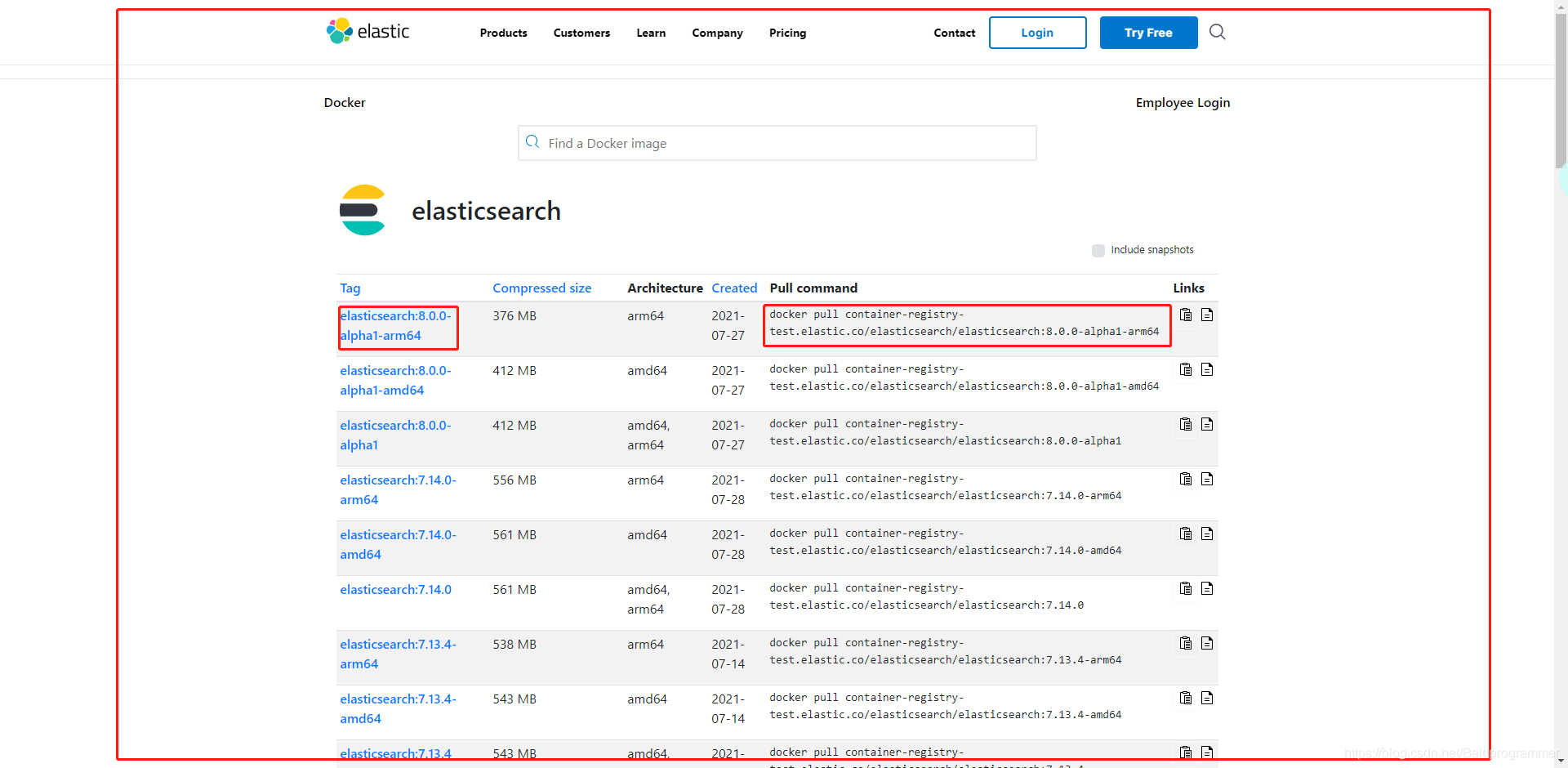
3、如果想要使用docker运行,打开:Docker @ Elastic
点击蓝色字进去使用里面的命令,或者使用外面的命令拉取镜像
4、如果下载的不顺利或者懒,那就直接百度网盘下载: ```bash windows版 链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1_frZlpRxLcuWC9KqUkgQdg 提取码:good ```###### 5、安装elk 1、已经获取到了安装包,把安装包放到一个位置,然后解压;
2、修改配置文件,把elk进行关联起来 1)修改elasticsearch-7.13.4配置 目录结构: 看这些目录是不是很熟悉,没错es是用java写的 bin目录:存放批处理文件 cofig目录:存放配置文件 data目录:存放es的数据 jdk目录:存放的就是jdk,因为es会默认带一个jdk lib目录:存放的就是一些jar包,相当于c或者python中的库 models目录:存放也是一些jar包依赖 plugins目录:存放的是插件,如果需要可以把插件放进去
编辑F:\elk7.13.4\elasticsearch-7.13.4\config\elasticsearch.yml文件
基础配置(也可以先不配置,使用默认的) #IP network.host: 192.168.0.101 #端口 http.port: 9200 #日志路径 path.logs: /path/to/logs #数据路径 path.data: /path/to/data详细配置 # ======================== Elasticsearch Configuration ========================= # # NOTE: Elasticsearch comes with reasonable defaults for most settings. # Before you set out to tweak and tune the configuration, make sure you # understand what are you trying to accomplish and the consequences. # # The primary way of configuring a node is via this file. This template lists # the most important settings you may want to configure for a production cluster. # # Please consult the documentation for further information on configuration options: # https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/index.html # # ---------------------------------- 集群配置 ----------------------------------- # ---------------------------------- Cluster ----------------------------------- # # Use a descriptive name for your cluster: # #cluster.name: my-application # # ------------------------------------ 节点 ------------------------------------ # ------------------------------------ Node ------------------------------------ # # 为节点使用描述性名称: # Use a descriptive name for the node: # #配置节点名 #node.name: n1 #node.name: n2 #node.name: node-1 # # 将自定义属性添加到节点 # Add custom attributes to the node: # #node.attr.rack: r1 # # ----------------------------------- 路径 ------------------------------------ # ----------------------------------- Paths ------------------------------------ # 存储数据的目录路径(多个目录用逗号分隔) # Path to directory where to store the data (separate multiple locations by comma): # #数据路径 #path.data: /path/to/data path.data: /path/to/data # # Path to log files: # #日志路径 #path.logs: /path/to/logs path.logs: /path/to/logs # # ----------------------------------- 内存 ----------------------------------- # ----------------------------------- Memory ----------------------------------- # 启动时锁定内存 # Lock the memory on startup: # #bootstrap.memory_lock: true # 确保堆大小设置为可用内存的一半左右,并且允许进程的所有者使用此限制。 # Make sure that the heap size is set to about half the memory available # on the system and that the owner of the process is allowed to use this # limit. # 当系统交换内存时,Elasticsearch性能不佳。 # Elasticsearch performs poorly when the system is swapping the memory. # # ---------------------------------- 网络 ----------------------------------- # ---------------------------------- Network ----------------------------------- # 默认只能在本机使用,需要配置局域网ip(在内网环境中访问) # By default Elasticsearch is only accessible on localhost. Set a different # address here to expose this node on the network: # #IP #network.host: 192.168.0.1 network.host: 192.168.0.101 # # By default Elasticsearch listens for HTTP traffic on the first free port it # finds starting at 9200. Set a specific HTTP port here: # #端口 #http.port: 9200 http.port: 9200 # For more information, consult the network module documentation. # # --------------------------------- 发现 ---------------------------------- # --------------------------------- Discovery ---------------------------------- # 在此节点启动时传递要执行查找的主机的初始列表: # 主机的默认列表为[“127.0.0.1”、“[::1]” # Pass an initial list of hosts to perform discovery when this node is started: # The default list of hosts is ["127.0.0.1", "[::1]"] # #配置多个主机去发现 #discovery.seed_主机:[“主机1”、“主机2”] #discovery.seed_hosts: ["192.168.1.1", "192.168.1.2"] #discovery.seed_hosts: ["host1", "host2"] # # Bootstrap the cluster using an initial set of master-eligible nodes: #使用初始节点引导集群 #cluster.initial_master_nodes: ["n1", "n2"] #cluster.initial_master_nodes: ["node-1", "node-2"] # # For more information, consult the discovery and cluster formation module documentation. # # ---------------------------------- 其他 ----------------------------------- # ---------------------------------- Various ----------------------------------- # 删除索引时需要显式名称 # Require explicit names when deleting indices: # #action.destructive_requires_name: true这里我使用默认配置,什么都不改,启动es(es为elasticsearch简称)
显示如下证明启动成功了
访问
2)修改kibana-7.13.4配置 目录介绍: kibana是基于node写的,在运行的使用需要node,不过也可以打包html+js bin目录:存放批处理文件 config目录:存放配置文件 data目录:存放数据文件 node目录:mode启动程序 plugins目录:存放插件 src目录:存放js文件 x-pack目录:作为kibana集成的监控安全共能
配置kibana的配置文件:F:\elk7.13.4\kibana-7.13.4-windows-x86_64\config\kibana.yml
基础配置 # 提供服务的IP #server.host: "localhost" # 提供服务的端口 #server.port: 5601 #es服务的地址 #elasticsearch.hosts: ["http://localhost:9200"]详细配置 # 提供服务的端口 # Kibana is served by a back end server. This setting specifies the port to use. #server.port: 5601 # 提供服务的IP # Specifies the address to which the Kibana server will bind. IP addresses and host names are both valid values. # The default is 'localhost', which usually means remote machines will not be able to connect. # To allow connections from remote users, set this parameter to a non-loopback address. #server.host: "localhost" # 配置代理路径 # Enables you to specify a path to mount Kibana at if you are running behind a proxy. # Use the `server.rewriteBasePath` setting to tell Kibana if it should remove the basePath # from requests it receives, and to prevent a deprecation warning at startup. # This setting cannot end in a slash. #server.basePath: "" # 指定Kibana是否应重写前缀为的请求,或要求它们由反向代理重写 # Specifies whether Kibana should rewrite requests that are prefixed with # `server.basePath` or require that they are rewritten by your reverse proxy. # This setting was effectively always `false` before Kibana 6.3 and will # default to `true` starting in Kibana 7.0. #server.rewriteBasePath: false # 指定最终用户可以使用Kibana的公共URL。如果 # 已配置“server.basePath”。此URL应以相同的basePath结尾。 # Specifies the public URL at which Kibana is available for end users. If # `server.basePath` is configured this URL should end with the same basePath. #server.publicBaseUrl: "" # 传入服务器请求的最大负载大小(以字节为单位)。 # The maximum payload size in bytes for incoming server requests. #server.maxPayload: 1048576 # es服务的地址 # The URLs of the Elasticsearch instances to use for all your queries. #elasticsearch.hosts: ["http://localhost:9200"] # Kibana在Elasticsearch中使用索引来存储保存的搜索、可视化和仪表盘。如果索引不存在,Kibana将创建一个新索引。 # Kibana uses an index in Elasticsearch to store saved searches, visualizations and # dashboards. Kibana creates a new index if the index doesn't already exist. #kibana.index: ".kibana" # 加载默认应用 # The default application to load. #kibana.defaultAppId: "home" # 如果es设置了账号和密码,在下面配置 # If your Elasticsearch is protected with basic authentication, these settings provide # the username and password that the Kibana server uses to perform maintenance on the Kibana # index at startup. Your Kibana users still need to authenticate with Elasticsearch, which # is proxied through the Kibana server. # 账号 #elasticsearch.username: "kibana_system" # 密码 #elasticsearch.password: "pass" # 配置ssl证书和ssl密钥 # Enables SSL and paths to the PEM-format SSL certificate and SSL key files, respectively. # These settings enable SSL for outgoing requests from the Kibana server to the browser. #server.ssl.enabled: false #server.ssl.certificate: /path/to/your/server.crt #server.ssl.key: /path/to/your/server.key # 这些文件用于向Elasticsearch验证Kibana的身份,并且在以下情况下是必需的 # Optional settings that provide the paths to the PEM-format SSL certificate and key files. # These files are used to verify the identity of Kibana to Elasticsearch and are required when # xpack.security.http.ssl.client_authentication in Elasticsearch is set to required. #elasticsearch.ssl.certificate: /path/to/your/client.crt #elasticsearch.ssl.key: /path/to/your/client.key # 可选设置,允许您为证书指定PEM文件的路径 # Optional setting that enables you to specify a path to the PEM file for the certificate # authority for your Elasticsearch instance. #elasticsearch.ssl.certificateAuthorities: [ "/path/to/your/CA.pem" ] #若要忽略SSL证书的有效性,请将此设置的值更改为“无”。 # To disregard the validity of SSL certificates, change this setting's value to 'none'. #elasticsearch.ssl.verificationMode: full #等待Elasticsearch响应ping的时间(毫秒)。默认为的值 # Time in milliseconds to wait for Elasticsearch to respond to pings. Defaults to the value of # the elasticsearch.requestTimeout setting. #elasticsearch.pingTimeout: 1500 #等待后端或Elasticsearch响应的时间(毫秒)。此值 #必须是正整数。 # Time in milliseconds to wait for responses from the back end or Elasticsearch. This value # must be a positive integer. #elasticsearch.requestTimeout: 30000 #要发送到Elasticsearch的Kibana客户端头列表。发送*否*客户端 #标题,将此值设置为[](空列表)。 # List of Kibana client-side headers to send to Elasticsearch. To send *no* client-side # headers, set this value to [] (an empty list). #elasticsearch.requestHeadersWhitelist: [ authorization ] #发送到Elasticsearch的标题名称和值。无法覆盖任何自定义标题 #通过客户端头,而不考虑elasticsearch.requestHeadersWhitelist配置。 # Header names and values that are sent to Elasticsearch. Any custom headers cannot be overwritten # by client-side headers, regardless of the elasticsearch.requestHeadersWhitelist configuration. #elasticsearch.customHeaders: {} #Elasticsearch等待碎片响应的时间(毫秒)。设置为0以禁用。 #elasticsearch.shardTimeout:30000 # Time in milliseconds for Elasticsearch to wait for responses from shards. Set to 0 to disable. #elasticsearch.shardTimeout: 30000 #记录发送到Elasticsearch的查询。需要将logging.verbose设置为true # Logs queries sent to Elasticsearch. Requires logging.verbose set to true. #elasticsearch.logQueries: false #指定Kibana创建进程ID文件的路径 # Specifies the path where Kibana creates the process ID file. #pid.file: /run/kibana/kibana.pid #允许您指定Kibana存储日志输出的文件 # Enables you to specify a file where Kibana stores log output. #logging.dest: stdout #将此设置的值设置为true以抑制所有日志记录输出。 # Set the value of this setting to true to suppress all logging output. #logging.silent: false #将此设置的值设置为true以抑制除错误消息以外的所有日志输出。 # Set the value of this setting to true to suppress all logging output other than error messages. #logging.quiet: false #将此设置的值设置为true以记录所有事件,包括系统使用信息以及所有的请求。 # Set the value of this setting to true to log all events, including system usage information # and all requests. #logging.verbose: false #设置采样系统和进程性能的间隔(以毫秒为单位) # Set the interval in milliseconds to sample system and process performance # metrics. Minimum is 100ms. Defaults to 5000. #ops.interval: 5000 #指定用于所有可本地化字符串、日期和数字格式的区域设置。 #支持的语言如下:英语-en,默认情况下为中文-zh-CN。 # Specifies locale to be used for all localizable strings, dates and number formats. # Supported languages are the following: English - en , by default , Chinese - zh-CN . #i18n.locale: "en"这里我使用默认配置,然后启动kibana,访问
访问http://localhost:5601/ 显示如下,表示成功
点击 add data添加一些数据
可以看出来支持很多服务日志的收集
为了看起来方便,改配置:i18n.locale: "zh-CN" 重启kibana ctrl+c关闭,然后启动
现在访问就是中文的了
添加数据,感受一下kibana的界面
3)修改logstash-7.13.4配置 目录介绍: bin目录:存放批处理脚本 目录结构: 看这些目录是不是很熟悉,没错es是用java写的 bin目录:存放批处理文件 cofig目录:存放配置文件 data目录:存放es的数据 jdk目录:存放的就是jdk,因为es会默认带一个jdk lib目录:存放的就是一些jar包,相当于c或者python中的库 models目录:存放也是一些jar包依赖 plugins目录:存放的是插件,如果需要可以把插件放进去 tools目录:存放自带的工具jar包
编辑F:\elk7.13.4\logstash-7.13.4\config\logstash.yml文件 基础配置 # IP # http.host: 127.0.0.1 # 端口 # http.port: 9600详细配置 #可以使用分层形式进行设置 # Settings file in YAML # # Settings can be specified either in hierarchical form, e.g.: #通道 # pipeline: #批次 # batch: #大小 # size: 125 #延时 # delay: 5 # # Or as flat keys: # #一行一行的配置属性值 # pipeline.batch.size: 125 # pipeline.batch.delay: 5 # # ------------ 节点标识 ------------ # ------------ Node identity ------------ # # Use a descriptive name for the node: # 节点名称 # node.name: test # 如果省略,节点名称将默认为计算机的主机名 # If omitted the node name will default to the machine's host name # # ------------ 数据路径 ------------------ # ------------ Data path ------------------ # #logstash及其插件应该使用哪个目录对于任何持续的需求。默认为LOGSTASH_HOME/data # Which directory should be used by logstash and its plugins # for any persistent needs. Defaults to LOGSTASH_HOME/data # # path.data: # # ------------ 管道设置 -------------- # ------------ Pipeline Settings -------------- # 管道的ID。 # The ID of the pipeline. # 管道id:main # pipeline.id: main # 设置并行执行过滤器+输出的工作人员数量 管道阶段。 # Set the number of workers that will, in parallel, execute the filters+outputs # stage of the pipeline. # 这默认为主机的CPU核心数。 # This defaults to the number of the host's CPU cores. # 管道工人:2名 # pipeline.workers: 2 # 在发送到筛选器+工作者之前,要从输入中检索多少事件 # How many events to retrieve from inputs before sending to filters+workers # 管道.批次.尺寸:125 # pipeline.batch.size: 125 # 轮询下一个事件时等待的时间(毫秒) # How long to wait in milliseconds while polling for the next event # 在将较小的批次分配到过滤器+输出之前 # before dispatching an undersized batch to filters+outputs # 管道.批次.延迟:50 # pipeline.batch.delay: 50 # 在停机期间强制Logstash退出记忆中的事件 # 默认情况下,logstash将拒绝退出,直到所有已将接收到的事件推送到输出。 # Force Logstash to exit during shutdown even if there are still inflight # events in memory. By default, logstash will refuse to quit until all # received events have been pushed to the outputs. # 警告:启用此选项可能会导致关机期间数据丢失 # WARNING: enabling this can lead to data loss during shutdown # pipeline.unsafe_shutdown: false # 设置管道事件顺序。选项有“自动”(默认)、“真”或“假”。 # Set the pipeline event ordering. Options are "auto" (the default), "true" or "false". # "auto" will automatically enable ordering if the 'pipeline.workers' setting # is also set to '1'. # "true" will enforce ordering on the pipeline and prevent logstash from starting # if there are multiple workers. # "false" will disable any extra processing necessary for preserving ordering. # pipeline.ordered: auto # # ------------ Pipeline Configuration Settings -------------- # ------------ 管道配置设置 -------------- # # Where to fetch the pipeline configuration for the main pipeline # 从何处获取主管道的管道配置 # path.config: # 主管道的管道配置字符串 # Pipeline configuration string for the main pipeline # # config.string: # 启动时,测试配置是否有效并退出(干运行) # At startup, test if the configuration is valid and exit (dry run) # # config.test_and_exit: false # 定期检查配置是否已更改并重新加载管道这也可以通过SIGHUP信号手动触发 # Periodically check if the configuration has changed and reload the pipeline # This can also be triggered manually through the SIGHUP signal # # config.reload.automatic: false # # 不建议以这种方式设置间隔,在以后的版本中可能会更改 # How often to check if the pipeline configuration has changed (in seconds) # Note that the unit value (s) is required. Values without a qualifier (e.g. 60) # are treated as nanoseconds. # Setting the interval this way is not recommended and might change in later versions. # # config.reload.interval: 3s # 将完全编译的配置显示为调试日志消息 # Show fully compiled configuration as debug log message # NOTE: --log.level must be 'debug' # 注意:--log.level必须为“调试” # 是否启动debugger模式 # config.debug: false # # 启用时,处理中字符串中的转义字符,如\n和\“ # When enabled, process escaped characters such as \n and \" in strings in the # pipeline configuration files. # # config.support_escapes: false # # ------------HTTP API设置 ------------- # ------------ HTTP API Settings ------------- # Define settings related to the HTTP API here. # # 默认情况下启用HTTP API。它可以被禁用,但功能依赖于它不会按预期工作。 # The HTTP API is enabled by default. It can be disabled, but features that rely # on it will not work as intended. # http.enabled: true # 默认情况下,HTTP API仅绑定到主机的本地环回接口,确保网络的其余部分无法访问它。因为API # 既不包括身份验证,也不包括授权,并且尚未加固或删除测试用作可公开访问的API,绑定到可公开访问的IP应尽可能避免。 # By default, the HTTP API is bound to only the host's local loopback interface, # ensuring that it is not accessible to the rest of the network. Because the API # includes neither authentication nor authorization and has not been hardened or # tested for use as a publicly-reachable API, binding to publicly accessible IPs # should be avoided where possible. # IP # http.host: 127.0.0.1 # # The HTTP API web server will listen on an available port from the given range. # Values can be specified as a single port (e.g., `9600`), or an inclusive range # of ports (e.g., `9600-9700`). # 端口 # http.port: 9600-9700 # # ------------ 模块设置 --------------- # ------------ Module Settings --------------- #在这里定义模块。模块定义必须定义为数组。 #查看这一点的简单方法是在每个'name'前面加上一个'-',并保留 #与之关联的`name`下的所有关联变量,以及 #在下一个上面,像这样: # Define modules here. Modules definitions must be defined as an array. # The simple way to see this is to prepend each `name` with a `-`, and keep # all associated variables under the `name` they are associated with, and # above the next, like this: # # modules: # - name: MODULE_NAME # var.PLUGINTYPE1.PLUGINNAME1.KEY1: VALUE # var.PLUGINTYPE1.PLUGINNAME1.KEY2: VALUE # var.PLUGINTYPE2.PLUGINNAME1.KEY1: VALUE # var.PLUGINTYPE3.PLUGINNAME3.KEY1: VALUE # # Module variable names must be in the format of # # var.PLUGIN_TYPE.PLUGIN_NAME.KEY # # modules: # # ------------ 云设置 --------------- # ------------ Cloud Settings --------------- # Define Elastic Cloud settings here. # cloud.id的格式为base64值,例如dXMtZWFzdC0xLmF3cy5mb3VuZC5pbyRub3RhcmVhbCRpZGVudGlmaWVy # Format of cloud.id is a base64 value e.g. dXMtZWFzdC0xLmF3cy5mb3VuZC5pbyRub3RhcmVhbCRpZGVudGlmaWVy # and it may have an label prefix e.g. staging:dXMtZ... # 它可能有一个标签前缀,例如staging:dXMtZ。。。 # This will overwrite 'var.elasticsearch.hosts' and 'var.kibana.host' # cloud.id: # # Format of cloud.auth is: : # This is optional # 如果提供,这将覆盖“var.elasticsearch.username”和“var.elasticsearch.password” # If supplied this will overwrite 'var.elasticsearch.username' and 'var.elasticsearch.password' # If supplied this will overwrite 'var.kibana.username' and 'var.kibana.password' # cloud.auth: elastic: # # ------------ 队列设置 -------------- # ------------ Queuing Settings -------------- # 可以配置在硬盘或者内存中执行,默认为内存 # Internal queuing model, "memory" for legacy in-memory based queuing and # "persisted" for disk-based acked queueing. Defaults is memory # # queue.type: memory # # 如果类型(queue.type)使用硬盘,此路径(path.queue:)则为数据文件的目录 # If using queue.type: persisted, the directory path where the data files will be stored. # Default is path.data/queue # # path.queue: # # If using queue.type: persisted, the page data files size. The queue data consists of # append-only data files separated into pages. Default is 64mb # 仅追加分隔为页面的数据文件。默认值为64mb # queue.page_capacity: 64mb # 如果使用queue.type:persistend,则为队列中未读事件的最大数量。 # If using queue.type: persisted, the maximum number of unread events in the queue. # Default is 0 (unlimited) # # queue.max_events: 0 # # # If using queue.type: persisted, the total capacity of the queue in number of bytes. # If you would like more unacked events to be buffered in Logstash, you can increase the # capacity using this setting. Please make sure your disk drive has capacity greater than # the size specified here. If both max_bytes and max_events are specified, Logstash will pick # whichever criteria is reached first # Default is 1024mb or 1gb # 队列容量 # queue.max_bytes: 1024mb # # If using queue.type: persisted, the maximum number of acked events before forcing a checkpoint # Default is 1024, 0 for unlimited # 强制检查点之前已确认的最大事件数 # queue.checkpoint.acks: 1024 # # If using queue.type: persisted, the maximum number of written events before forcing a checkpoint # Default is 1024, 0 for unlimited # 则为强制检查点之前写入的最大事件数 默认值为1024,0表示无限制 # queue.checkpoint.writes: 1024 # # If using queue.type: persisted, the interval in milliseconds when a checkpoint is forced on the head page # Default is 1000, 0 for no periodic checkpoint. # 如果使用queue.type:persisted,则在头页上强制设置检查点的间隔(以毫秒为单位)默认值为1000,0表示无定期检查点。 # queue.checkpoint.interval: 1000 # # ------------ 死信队列设置 -------------- # ------------ Dead-Letter Queue Settings -------------- # Flag to turn on dead-letter queue. # 死信队列。启用:false # dead_letter_queue.enable: false # 如果使用死信队列。enable:true,每个死信队列的最大大小。条目 # If using dead_letter_queue.enable: true, the maximum size of each dead letter queue. Entries # 如果将死信队列的大小增加到超出此设置,则将删除 # will be dropped if they would increase the size of the dead letter queue beyond this setting. # #默认值为1024mb # Default is 1024mb # 死信队列。最大字节数:1024mb # dead_letter_queue.max_bytes: 1024mb # 如果使用dead_letter_queue.enable:true,如果没有符合DLQ条件的其他事件,则间隔(以毫秒为单位) # 创建后,将写入死信队列文件。这里的值越低,意味着队列文件越多、越小 # 可以写入,而较大的值将在“写入”死信队列的项目之间引入更多延迟,并且 # 当项目不经常写入时,死信队列输入可以读取。 # 默认值为5000。 # If using dead_letter_queue.enable: true, the interval in milliseconds where if no further events eligible for the DLQ # have been created, a dead letter queue file will be written. A low value here will mean that more, smaller, queue files # may be written, while a larger value will introduce more latency between items being "written" to the dead letter queue, and # being available to be read by the dead_letter_queue input when items are are written infrequently. # Default is 5000. # 死信队列。刷新间隔:5000 # dead_letter_queue.flush_interval: 5000 # 如果使用dead_letter_queue.enable:true,则为存储数据文件的目录路径。 # If using dead_letter_queue.enable: true, the directory path where the data files will be stored. # Default is path.data/dead_letter_queue # # path.dead_letter_queue: # # ------------- 指标设置 -------------- # ------------ Metrics Settings -------------- # # Bind address for the metrics REST endpoint # IP # http.host: "127.0.0.1" # # Bind port for the metrics REST endpoint, this option also accept a range # (9600-9700) and logstash will pick up the first available ports. # 端口 # http.port: 9600-9700 # # ------------ 调试设置 -------------- # ------------ Debugging Settings -------------- # 启动模式 # Options for log.level: # * fatal # * error # * warn # * info (default) # * debug # * trace # 日志级别 # log.level: info # path.logs: # # ------------ 其他设置 -------------- # ------------ Other Settings -------------- # 在哪里可以找到自定义插件 # Where to find custom plugins # path.plugins: [] # # 在单独的日志文件中输出每个管道的日志行的标志。每个日志文件名都包含pipeline.name默认值为false # Flag to output log lines of each pipeline in its separate log file. Each log filename contains the pipeline.name # Default is false # pipeline.separate_logs: false # # X-Pack设置(不适用于OSS构建) # ------------ X-Pack Settings (not applicable for OSS build)-------------- # X-Pack监控 # X-Pack Monitoring # https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/logstash/current/monitoring-logstash.html #xpack.monitoring.enabled: false #xpack.monitoring.elasticsearch.username: logstash_system #xpack.monitoring.elasticsearch.password: password #xpack.monitoring.elasticsearch.proxy: ["http://proxy:port"] #xpack.monitoring.elasticsearch.hosts: ["https://es1:9200", "https://es2:9200"] # 主机+用户名/密码设置的替代方法是使用 # an alternative to hosts + username/password settings is to use cloud_id/cloud_auth #xpack.monitoring.elasticsearch.cloud_id: monitoring_cluster_id:xxxxxxxxxx #xpack.monitoring.elasticsearch.cloud_auth: logstash_system:password # 另一种身份验证方法是使用Elasticsearch API密钥 # another authentication alternative is to use an Elasticsearch API key #xpack.monitoring.elasticsearch.api_key: "id:api_key" #xpack.monitoring.elasticsearch.ssl.certificate_authority: [ "/path/to/ca.crt" ] #xpack.monitoring.elasticsearch.ssl.truststore.path: path/to/file #xpack.monitoring.elasticsearch.ssl.truststore.password: password #xpack.monitoring.elasticsearch.ssl.keystore.path: /path/to/file #xpack.monitoring.elasticsearch.ssl.keystore.password: password #xpack.monitoring.elasticsearch.ssl.verification_mode: certificate #xpack.monitoring.elasticsearch.sniffing: false #xpack.monitoring.collection.interval: 10s #xpack.monitoring.collection.pipeline.details.enabled: true # X-Pack管理 # X-Pack Management # https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/logstash/current/logstash-centralized-pipeline-management.html #xpack.management.enabled: false #xpack.management.pipeline.id: ["main", "apache_logs"] #xpack.management.elasticsearch.username: logstash_admin_user #xpack.management.elasticsearch.password: password #xpack.management.elasticsearch.proxy: ["http://proxy:port"] #xpack.management.elasticsearch.hosts: ["https://es1:9200", "https://es2:9200"] # 主机+用户名/密码设置的替代方法是使用 # an alternative to hosts + username/password settings is to use cloud_id/cloud_auth #xpack.management.elasticsearch.cloud_id: management_cluster_id:xxxxxxxxxx #xpack.management.elasticsearch.cloud_auth: logstash_admin_user:password # 另一种身份验证方法是使用Elasticsearch API密钥 # another authentication alternative is to use an Elasticsearch API key #xpack.management.elasticsearch.api_key: "id:api_key" #xpack.management.elasticsearch.ssl.certificate_authority: [ "/path/to/ca.crt" ] #xpack.management.elasticsearch.ssl.truststore.path: /path/to/file #xpack.management.elasticsearch.ssl.truststore.password: password #xpack.management.elasticsearch.ssl.keystore.path: /path/to/file #xpack.management.elasticsearch.ssl.keystore.password: password #xpack.management.elasticsearch.ssl.verification_mode: certificate #xpack.management.elasticsearch.sniffing: false #xpack.management.logstash.poll_interval: 5s3、需要注意注意启动顺序: es ——》 logstash ——》 kibana 3. elk安装(linux版)1、下载地址:下载 Elastic 产品 | Elastic
主要需要下载下面这个三个:
点击下载
选择下载的版本
2、如果下载速度过慢,可以选择国内镜像,中文社区 下载中心 - Elastic 中文社区 点击需要的版本进行下载,可以下翻选择需要的版本;
3、如果想要使用docker运行,打开:Docker @ Elastic
点击蓝色字进去使用里面的命令,或者使用外面的命令拉取镜像
4、如果下载的不顺利或者懒,那就直接百度网盘下载: linux版 链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1K0946mrLk40aRsY7RtiIjg 提取码:good5、安装elk 首先创建用户组和用户(因为es不可以使用root用户启动) groupadd es useradd es -g es passwd es
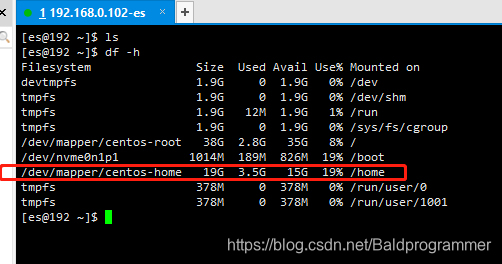
1、df -h #查看是否可用的位置,或者是否有足够的空间
2、 创建elk目录,进入elk目录 mkdir elk cd elk 3、把下载下来的安装包放到elk目录
4、解压安装包 (或者使用for tar in *.tar.gz; do tar xvf $tar; done解压所有gz包) tar -zvxf elasticsearch-7.13.4-linux-x86_64.tar.gz tar -zvxf kibana-7.13.4-linux-x86_64.tar.gz tar -zvxf logstash-7.13.4-linux-x86_64.tar.gz 5、修改配置文件启动es 1)进入es目录 cd elasticsearch-7.13.4/config vim elasticsearch.yml #如果没有vim命令可以使用vi命令或者yum install vim 安装 基础配置 #IP network.host: 192.168.0.101 #端口 http.port: 9200 #日志路径 path.logs: /path/to/logs #数据路径 path.data: /path/to/data详细配置 # ======================== Elasticsearch Configuration ========================= # # NOTE: Elasticsearch comes with reasonable defaults for most settings. # Before you set out to tweak and tune the configuration, make sure you # understand what are you trying to accomplish and the consequences. # # The primary way of configuring a node is via this file. This template lists # the most important settings you may want to configure for a production cluster. # # Please consult the documentation for further information on configuration options: # https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/index.html # # ---------------------------------- 集群配置 ----------------------------------- # ---------------------------------- Cluster ----------------------------------- # # Use a descriptive name for your cluster: # #cluster.name: my-application # # ------------------------------------ 节点 ------------------------------------ # ------------------------------------ Node ------------------------------------ # # 为节点使用描述性名称: # Use a descriptive name for the node: # #配置节点名 #node.name: n1 #node.name: n2 #node.name: node-1 # # 将自定义属性添加到节点 # Add custom attributes to the node: # #node.attr.rack: r1 # # ----------------------------------- 路径 ------------------------------------ # ----------------------------------- Paths ------------------------------------ # 存储数据的目录路径(多个目录用逗号分隔) # Path to directory where to store the data (separate multiple locations by comma): # #数据路径 #path.data: /path/to/data path.data: /path/to/data # # Path to log files: # #日志路径 #path.logs: /path/to/logs path.logs: /path/to/logs # # ----------------------------------- 内存 ----------------------------------- # ----------------------------------- Memory ----------------------------------- # 启动时锁定内存 # Lock the memory on startup: # #bootstrap.memory_lock: true # 确保堆大小设置为可用内存的一半左右,并且允许进程的所有者使用此限制。 # Make sure that the heap size is set to about half the memory available # on the system and that the owner of the process is allowed to use this # limit. # 当系统交换内存时,Elasticsearch性能不佳。 # Elasticsearch performs poorly when the system is swapping the memory. # # ---------------------------------- 网络 ----------------------------------- # ---------------------------------- Network ----------------------------------- # 默认只能在本机使用,需要配置局域网ip(在内网环境中访问) # By default Elasticsearch is only accessible on localhost. Set a different # address here to expose this node on the network: # #IP #network.host: 192.168.0.1 network.host: 192.168.0.101 # # By default Elasticsearch listens for HTTP traffic on the first free port it # finds starting at 9200. Set a specific HTTP port here: # #端口 #http.port: 9200 http.port: 9200 # For more information, consult the network module documentation. # # --------------------------------- 发现 ---------------------------------- # --------------------------------- Discovery ---------------------------------- # 在此节点启动时传递要执行查找的主机的初始列表: # 主机的默认列表为[“127.0.0.1”、“[::1]” # Pass an initial list of hosts to perform discovery when this node is started: # The default list of hosts is ["127.0.0.1", "[::1]"] # #配置多个主机去发现 #discovery.seed_主机:[“主机1”、“主机2”] #discovery.seed_hosts: ["192.168.1.1", "192.168.1.2"] #discovery.seed_hosts: ["host1", "host2"] # # Bootstrap the cluster using an initial set of master-eligible nodes: #使用初始节点引导集群 #cluster.initial_master_nodes: ["n1", "n2"] #cluster.initial_master_nodes: ["node-1", "node-2"] # # For more information, consult the discovery and cluster formation module documentation. # # ---------------------------------- 其他 ----------------------------------- # ---------------------------------- Various ----------------------------------- # 删除索引时需要显式名称 # Require explicit names when deleting indices: # #action.destructive_requires_name: true把ip和端口的注释打开,修改ip为内网ip
添加配置: node.name: node-1 进入 es目录,启动es发现jdk找不到
安装JDK(如果启动不报错,或者已经安装省略这一步) 链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1PvT39Sa2O2YQBZ5PPLp2xg 提取码:good放到es目录解压 tar -zvxf jdk-8u65-linux-x64.tar.gz 配置环境变量 编辑profile文件()添加如下: JAVA_HOME=/home/es/jdk1.8.0_65 export PATH=$JAVA_HOME/bin:$PATH
测试是否可用 java --version
启动前的配置 sudo vim /etc/security/limits.conf 追加如下: * soft nofile 65536 * hard nofile 65536
vim /etc/sysctl.conf 追加如下: vm.max_map_count=655360
执行 sysctl -p 退连接工具重新登陆 启动es cd elasticsearch-7.13.4/bin ./elasticsearch 访问 http://192.168.0.102:9200/
6、修改配置文件启动kibana cd /home/es/elk/kibana-7.13.4-linux-x86_64/config vim kibana.yml 添加配置 server.port: 5601 elasticsearch.hosts: ["http://0.0.0.0:9200"] i18n.locale: "zh-CN" server.host: "0.0.0.0"
配置说明: 基础配置 # 提供服务的IP #server.host: "localhost" # 提供服务的端口 #server.port: 5601 #es服务的地址 #elasticsearch.hosts: ["http://localhost:9200"] #设置语言为中文 i18n.locale: "zh-CN"详细配置 # 提供服务的端口 # Kibana is served by a back end server. This setting specifies the port to use. #server.port: 5601 # 提供服务的IP # Specifies the address to which the Kibana server will bind. IP addresses and host names are both valid values. # The default is 'localhost', which usually means remote machines will not be able to connect. # To allow connections from remote users, set this parameter to a non-loopback address. #server.host: "localhost" # 配置代理路径 # Enables you to specify a path to mount Kibana at if you are running behind a proxy. # Use the `server.rewriteBasePath` setting to tell Kibana if it should remove the basePath # from requests it receives, and to prevent a deprecation warning at startup. # This setting cannot end in a slash. #server.basePath: "" # 指定Kibana是否应重写前缀为的请求,或要求它们由反向代理重写 # Specifies whether Kibana should rewrite requests that are prefixed with # `server.basePath` or require that they are rewritten by your reverse proxy. # This setting was effectively always `false` before Kibana 6.3 and will # default to `true` starting in Kibana 7.0. #server.rewriteBasePath: false # 指定最终用户可以使用Kibana的公共URL。如果 # 已配置“server.basePath”。此URL应以相同的basePath结尾。 # Specifies the public URL at which Kibana is available for end users. If # `server.basePath` is configured this URL should end with the same basePath. #server.publicBaseUrl: "" # 传入服务器请求的最大负载大小(以字节为单位)。 # The maximum payload size in bytes for incoming server requests. #server.maxPayload: 1048576 # es服务的地址 # The URLs of the Elasticsearch instances to use for all your queries. #elasticsearch.hosts: ["http://localhost:9200"] # Kibana在Elasticsearch中使用索引来存储保存的搜索、可视化和仪表盘。如果索引不存在,Kibana将创建一个新索引。 # Kibana uses an index in Elasticsearch to store saved searches, visualizations and # dashboards. Kibana creates a new index if the index doesn't already exist. #kibana.index: ".kibana" # 加载默认应用 # The default application to load. #kibana.defaultAppId: "home" # 如果es设置了账号和密码,在下面配置 # If your Elasticsearch is protected with basic authentication, these settings provide # the username and password that the Kibana server uses to perform maintenance on the Kibana # index at startup. Your Kibana users still need to authenticate with Elasticsearch, which # is proxied through the Kibana server. # 账号 #elasticsearch.username: "kibana_system" # 密码 #elasticsearch.password: "pass" # 配置ssl证书和ssl密钥 # Enables SSL and paths to the PEM-format SSL certificate and SSL key files, respectively. # These settings enable SSL for outgoing requests from the Kibana server to the browser. #server.ssl.enabled: false #server.ssl.certificate: /path/to/your/server.crt #server.ssl.key: /path/to/your/server.key # 这些文件用于向Elasticsearch验证Kibana的身份,并且在以下情况下是必需的 # Optional settings that provide the paths to the PEM-format SSL certificate and key files. # These files are used to verify the identity of Kibana to Elasticsearch and are required when # xpack.security.http.ssl.client_authentication in Elasticsearch is set to required. #elasticsearch.ssl.certificate: /path/to/your/client.crt #elasticsearch.ssl.key: /path/to/your/client.key # 可选设置,允许您为证书指定PEM文件的路径 # Optional setting that enables you to specify a path to the PEM file for the certificate # authority for your Elasticsearch instance. #elasticsearch.ssl.certificateAuthorities: [ "/path/to/your/CA.pem" ] #若要忽略SSL证书的有效性,请将此设置的值更改为“无”。 # To disregard the validity of SSL certificates, change this setting's value to 'none'. #elasticsearch.ssl.verificationMode: full #等待Elasticsearch响应ping的时间(毫秒)。默认为的值 # Time in milliseconds to wait for Elasticsearch to respond to pings. Defaults to the value of # the elasticsearch.requestTimeout setting. #elasticsearch.pingTimeout: 1500 #等待后端或Elasticsearch响应的时间(毫秒)。此值 #必须是正整数。 # Time in milliseconds to wait for responses from the back end or Elasticsearch. This value # must be a positive integer. #elasticsearch.requestTimeout: 30000 #要发送到Elasticsearch的Kibana客户端头列表。发送*否*客户端 #标题,将此值设置为[](空列表)。 # List of Kibana client-side headers to send to Elasticsearch. To send *no* client-side # headers, set this value to [] (an empty list). #elasticsearch.requestHeadersWhitelist: [ authorization ] #发送到Elasticsearch的标题名称和值。无法覆盖任何自定义标题 #通过客户端头,而不考虑elasticsearch.requestHeadersWhitelist配置。 # Header names and values that are sent to Elasticsearch. Any custom headers cannot be overwritten # by client-side headers, regardless of the elasticsearch.requestHeadersWhitelist configuration. #elasticsearch.customHeaders: {} #Elasticsearch等待碎片响应的时间(毫秒)。设置为0以禁用。 #elasticsearch.shardTimeout:30000 # Time in milliseconds for Elasticsearch to wait for responses from shards. Set to 0 to disable. #elasticsearch.shardTimeout: 30000 #记录发送到Elasticsearch的查询。需要将logging.verbose设置为true # Logs queries sent to Elasticsearch. Requires logging.verbose set to true. #elasticsearch.logQueries: false #指定Kibana创建进程ID文件的路径 # Specifies the path where Kibana creates the process ID file. #pid.file: /run/kibana/kibana.pid #允许您指定Kibana存储日志输出的文件 # Enables you to specify a file where Kibana stores log output. #logging.dest: stdout #将此设置的值设置为true以抑制所有日志记录输出。 # Set the value of this setting to true to suppress all logging output. #logging.silent: false #将此设置的值设置为true以抑制除错误消息以外的所有日志输出。 # Set the value of this setting to true to suppress all logging output other than error messages. #logging.quiet: false #将此设置的值设置为true以记录所有事件,包括系统使用信息以及所有的请求。 # Set the value of this setting to true to log all events, including system usage information # and all requests. #logging.verbose: false #设置采样系统和进程性能的间隔(以毫秒为单位) # Set the interval in milliseconds to sample system and process performance # metrics. Minimum is 100ms. Defaults to 5000. #ops.interval: 5000 #指定用于所有可本地化字符串、日期和数字格式的区域设置。 #支持的语言如下:英语-en,默认情况下为中文-zh-CN。 # Specifies locale to be used for all localizable strings, dates and number formats. # Supported languages are the following: English - en , by default , Chinese - zh-CN . #i18n.locale: "en"启动kibana 进入bin目录启动 cd /home/es/elk/kibana-7.13.4-linux-x86_64/bin ./kibana 访问 http://192.168.0.102:5601/
添加数据,感受一下kibana的界面
7、配置启动logstash 基础配置 # IP # http.host: 127.0.0.1 # 端口 # http.port: 9600详细配置 #可以使用分层形式进行设置 # Settings file in YAML # # Settings can be specified either in hierarchical form, e.g.: #通道 # pipeline: #批次 # batch: #大小 # size: 125 #延时 # delay: 5 # # Or as flat keys: # #一行一行的配置属性值 # pipeline.batch.size: 125 # pipeline.batch.delay: 5 # # ------------ 节点标识 ------------ # ------------ Node identity ------------ # # Use a descriptive name for the node: # 节点名称 # node.name: test # 如果省略,节点名称将默认为计算机的主机名 # If omitted the node name will default to the machine's host name # # ------------ 数据路径 ------------------ # ------------ Data path ------------------ # #logstash及其插件应该使用哪个目录对于任何持续的需求。默认为LOGSTASH_HOME/data # Which directory should be used by logstash and its plugins # for any persistent needs. Defaults to LOGSTASH_HOME/data # # path.data: # # ------------ 管道设置 -------------- # ------------ Pipeline Settings -------------- # 管道的ID。 # The ID of the pipeline. # 管道id:main # pipeline.id: main # 设置并行执行过滤器+输出的工作人员数量 管道阶段。 # Set the number of workers that will, in parallel, execute the filters+outputs # stage of the pipeline. # 这默认为主机的CPU核心数。 # This defaults to the number of the host's CPU cores. # 管道工人:2名 # pipeline.workers: 2 # 在发送到筛选器+工作者之前,要从输入中检索多少事件 # How many events to retrieve from inputs before sending to filters+workers # 管道.批次.尺寸:125 # pipeline.batch.size: 125 # 轮询下一个事件时等待的时间(毫秒) # How long to wait in milliseconds while polling for the next event # 在将较小的批次分配到过滤器+输出之前 # before dispatching an undersized batch to filters+outputs # 管道.批次.延迟:50 # pipeline.batch.delay: 50 # 在停机期间强制Logstash退出记忆中的事件 # 默认情况下,logstash将拒绝退出,直到所有已将接收到的事件推送到输出。 # Force Logstash to exit during shutdown even if there are still inflight # events in memory. By default, logstash will refuse to quit until all # received events have been pushed to the outputs. # 警告:启用此选项可能会导致关机期间数据丢失 # WARNING: enabling this can lead to data loss during shutdown # pipeline.unsafe_shutdown: false # 设置管道事件顺序。选项有“自动”(默认)、“真”或“假”。 # Set the pipeline event ordering. Options are "auto" (the default), "true" or "false". # "auto" will automatically enable ordering if the 'pipeline.workers' setting # is also set to '1'. # "true" will enforce ordering on the pipeline and prevent logstash from starting # if there are multiple workers. # "false" will disable any extra processing necessary for preserving ordering. # pipeline.ordered: auto # # ------------ Pipeline Configuration Settings -------------- # ------------ 管道配置设置 -------------- # # Where to fetch the pipeline configuration for the main pipeline # 从何处获取主管道的管道配置 # path.config: # 主管道的管道配置字符串 # Pipeline configuration string for the main pipeline # # config.string: # 启动时,测试配置是否有效并退出(干运行) # At startup, test if the configuration is valid and exit (dry run) # # config.test_and_exit: false # 定期检查配置是否已更改并重新加载管道这也可以通过SIGHUP信号手动触发 # Periodically check if the configuration has changed and reload the pipeline # This can also be triggered manually through the SIGHUP signal # # config.reload.automatic: false # # 不建议以这种方式设置间隔,在以后的版本中可能会更改 # How often to check if the pipeline configuration has changed (in seconds) # Note that the unit value (s) is required. Values without a qualifier (e.g. 60) # are treated as nanoseconds. # Setting the interval this way is not recommended and might change in later versions. # # config.reload.interval: 3s # 将完全编译的配置显示为调试日志消息 # Show fully compiled configuration as debug log message # NOTE: --log.level must be 'debug' # 注意:--log.level必须为“调试” # 是否启动debugger模式 # config.debug: false # # 启用时,处理中字符串中的转义字符,如\n和\“ # When enabled, process escaped characters such as \n and \" in strings in the # pipeline configuration files. # # config.support_escapes: false # # ------------HTTP API设置 ------------- # ------------ HTTP API Settings ------------- # Define settings related to the HTTP API here. # # 默认情况下启用HTTP API。它可以被禁用,但功能依赖于它不会按预期工作。 # The HTTP API is enabled by default. It can be disabled, but features that rely # on it will not work as intended. # http.enabled: true # 默认情况下,HTTP API仅绑定到主机的本地环回接口,确保网络的其余部分无法访问它。因为API # 既不包括身份验证,也不包括授权,并且尚未加固或删除测试用作可公开访问的API,绑定到可公开访问的IP应尽可能避免。 # By default, the HTTP API is bound to only the host's local loopback interface, # ensuring that it is not accessible to the rest of the network. Because the API # includes neither authentication nor authorization and has not been hardened or # tested for use as a publicly-reachable API, binding to publicly accessible IPs # should be avoided where possible. # IP # http.host: 127.0.0.1 # # The HTTP API web server will listen on an available port from the given range. # Values can be specified as a single port (e.g., `9600`), or an inclusive range # of ports (e.g., `9600-9700`). # 端口 # http.port: 9600-9700 # # ------------ 模块设置 --------------- # ------------ Module Settings --------------- #在这里定义模块。模块定义必须定义为数组。 #查看这一点的简单方法是在每个'name'前面加上一个'-',并保留 #与之关联的`name`下的所有关联变量,以及 #在下一个上面,像这样: # Define modules here. Modules definitions must be defined as an array. # The simple way to see this is to prepend each `name` with a `-`, and keep # all associated variables under the `name` they are associated with, and # above the next, like this: # # modules: # - name: MODULE_NAME # var.PLUGINTYPE1.PLUGINNAME1.KEY1: VALUE # var.PLUGINTYPE1.PLUGINNAME1.KEY2: VALUE # var.PLUGINTYPE2.PLUGINNAME1.KEY1: VALUE # var.PLUGINTYPE3.PLUGINNAME3.KEY1: VALUE # # Module variable names must be in the format of # # var.PLUGIN_TYPE.PLUGIN_NAME.KEY # # modules: # # ------------ 云设置 --------------- # ------------ Cloud Settings --------------- # Define Elastic Cloud settings here. # cloud.id的格式为base64值,例如dXMtZWFzdC0xLmF3cy5mb3VuZC5pbyRub3RhcmVhbCRpZGVudGlmaWVy # Format of cloud.id is a base64 value e.g. dXMtZWFzdC0xLmF3cy5mb3VuZC5pbyRub3RhcmVhbCRpZGVudGlmaWVy # and it may have an label prefix e.g. staging:dXMtZ... # 它可能有一个标签前缀,例如staging:dXMtZ。。。 # This will overwrite 'var.elasticsearch.hosts' and 'var.kibana.host' # cloud.id: # # Format of cloud.auth is: : # This is optional # 如果提供,这将覆盖“var.elasticsearch.username”和“var.elasticsearch.password” # If supplied this will overwrite 'var.elasticsearch.username' and 'var.elasticsearch.password' # If supplied this will overwrite 'var.kibana.username' and 'var.kibana.password' # cloud.auth: elastic: # # ------------ 队列设置 -------------- # ------------ Queuing Settings -------------- # 可以配置在硬盘或者内存中执行,默认为内存 # Internal queuing model, "memory" for legacy in-memory based queuing and # "persisted" for disk-based acked queueing. Defaults is memory # # queue.type: memory # # 如果类型(queue.type)使用硬盘,此路径(path.queue:)则为数据文件的目录 # If using queue.type: persisted, the directory path where the data files will be stored. # Default is path.data/queue # # path.queue: # # If using queue.type: persisted, the page data files size. The queue data consists of # append-only data files separated into pages. Default is 64mb # 仅追加分隔为页面的数据文件。默认值为64mb # queue.page_capacity: 64mb # 如果使用queue.type:persistend,则为队列中未读事件的最大数量。 # If using queue.type: persisted, the maximum number of unread events in the queue. # Default is 0 (unlimited) # # queue.max_events: 0 # # # If using queue.type: persisted, the total capacity of the queue in number of bytes. # If you would like more unacked events to be buffered in Logstash, you can increase the # capacity using this setting. Please make sure your disk drive has capacity greater than # the size specified here. If both max_bytes and max_events are specified, Logstash will pick # whichever criteria is reached first # Default is 1024mb or 1gb # 队列容量 # queue.max_bytes: 1024mb # # If using queue.type: persisted, the maximum number of acked events before forcing a checkpoint # Default is 1024, 0 for unlimited # 强制检查点之前已确认的最大事件数 # queue.checkpoint.acks: 1024 # # If using queue.type: persisted, the maximum number of written events before forcing a checkpoint # Default is 1024, 0 for unlimited # 则为强制检查点之前写入的最大事件数 默认值为1024,0表示无限制 # queue.checkpoint.writes: 1024 # # If using queue.type: persisted, the interval in milliseconds when a checkpoint is forced on the head page # Default is 1000, 0 for no periodic checkpoint. # 如果使用queue.type:persisted,则在头页上强制设置检查点的间隔(以毫秒为单位)默认值为1000,0表示无定期检查点。 # queue.checkpoint.interval: 1000 # # ------------ 死信队列设置 -------------- # ------------ Dead-Letter Queue Settings -------------- # Flag to turn on dead-letter queue. # 死信队列。启用:false # dead_letter_queue.enable: false # 如果使用死信队列。enable:true,每个死信队列的最大大小。条目 # If using dead_letter_queue.enable: true, the maximum size of each dead letter queue. Entries # 如果将死信队列的大小增加到超出此设置,则将删除 # will be dropped if they would increase the size of the dead letter queue beyond this setting. # #默认值为1024mb # Default is 1024mb # 死信队列。最大字节数:1024mb # dead_letter_queue.max_bytes: 1024mb # 如果使用dead_letter_queue.enable:true,如果没有符合DLQ条件的其他事件,则间隔(以毫秒为单位) # 创建后,将写入死信队列文件。这里的值越低,意味着队列文件越多、越小 # 可以写入,而较大的值将在“写入”死信队列的项目之间引入更多延迟,并且 # 当项目不经常写入时,死信队列输入可以读取。 # 默认值为5000。 # If using dead_letter_queue.enable: true, the interval in milliseconds where if no further events eligible for the DLQ # have been created, a dead letter queue file will be written. A low value here will mean that more, smaller, queue files # may be written, while a larger value will introduce more latency between items being "written" to the dead letter queue, and # being available to be read by the dead_letter_queue input when items are are written infrequently. # Default is 5000. # 死信队列。刷新间隔:5000 # dead_letter_queue.flush_interval: 5000 # 如果使用dead_letter_queue.enable:true,则为存储数据文件的目录路径。 # If using dead_letter_queue.enable: true, the directory path where the data files will be stored. # Default is path.data/dead_letter_queue # # path.dead_letter_queue: # # ------------- 指标设置 -------------- # ------------ Metrics Settings -------------- # # Bind address for the metrics REST endpoint # IP # http.host: "127.0.0.1" # # Bind port for the metrics REST endpoint, this option also accept a range # (9600-9700) and logstash will pick up the first available ports. # 端口 # http.port: 9600-9700 # # ------------ 调试设置 -------------- # ------------ Debugging Settings -------------- # 启动模式 # Options for log.level: # * fatal # * error # * warn # * info (default) # * debug # * trace # 日志级别 # log.level: info # path.logs: # # ------------ 其他设置 -------------- # ------------ Other Settings -------------- # 在哪里可以找到自定义插件 # Where to find custom plugins # path.plugins: [] # # 在单独的日志文件中输出每个管道的日志行的标志。每个日志文件名都包含pipeline.name默认值为false # Flag to output log lines of each pipeline in its separate log file. Each log filename contains the pipeline.name # Default is false # pipeline.separate_logs: false # # X-Pack设置(不适用于OSS构建) # ------------ X-Pack Settings (not applicable for OSS build)-------------- # X-Pack监控 # X-Pack Monitoring # https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/logstash/current/monitoring-logstash.html #xpack.monitoring.enabled: false #xpack.monitoring.elasticsearch.username: logstash_system #xpack.monitoring.elasticsearch.password: password #xpack.monitoring.elasticsearch.proxy: ["http://proxy:port"] #xpack.monitoring.elasticsearch.hosts: ["https://es1:9200", "https://es2:9200"] # 主机+用户名/密码设置的替代方法是使用 # an alternative to hosts + username/password settings is to use cloud_id/cloud_auth #xpack.monitoring.elasticsearch.cloud_id: monitoring_cluster_id:xxxxxxxxxx #xpack.monitoring.elasticsearch.cloud_auth: logstash_system:password # 另一种身份验证方法是使用Elasticsearch API密钥 # another authentication alternative is to use an Elasticsearch API key #xpack.monitoring.elasticsearch.api_key: "id:api_key" #xpack.monitoring.elasticsearch.ssl.certificate_authority: [ "/path/to/ca.crt" ] #xpack.monitoring.elasticsearch.ssl.truststore.path: path/to/file #xpack.monitoring.elasticsearch.ssl.truststore.password: password #xpack.monitoring.elasticsearch.ssl.keystore.path: /path/to/file #xpack.monitoring.elasticsearch.ssl.keystore.password: password #xpack.monitoring.elasticsearch.ssl.verification_mode: certificate #xpack.monitoring.elasticsearch.sniffing: false #xpack.monitoring.collection.interval: 10s #xpack.monitoring.collection.pipeline.details.enabled: true # X-Pack管理 # X-Pack Management # https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/logstash/current/logstash-centralized-pipeline-management.html #xpack.management.enabled: false #xpack.management.pipeline.id: ["main", "apache_logs"] #xpack.management.elasticsearch.username: logstash_admin_user #xpack.management.elasticsearch.password: password #xpack.management.elasticsearch.proxy: ["http://proxy:port"] #xpack.management.elasticsearch.hosts: ["https://es1:9200", "https://es2:9200"] # 主机+用户名/密码设置的替代方法是使用 # an alternative to hosts + username/password settings is to use cloud_id/cloud_auth #xpack.management.elasticsearch.cloud_id: management_cluster_id:xxxxxxxxxx #xpack.management.elasticsearch.cloud_auth: logstash_admin_user:password # 另一种身份验证方法是使用Elasticsearch API密钥 # another authentication alternative is to use an Elasticsearch API key #xpack.management.elasticsearch.api_key: "id:api_key" #xpack.management.elasticsearch.ssl.certificate_authority: [ "/path/to/ca.crt" ] #xpack.management.elasticsearch.ssl.truststore.path: /path/to/file #xpack.management.elasticsearch.ssl.truststore.password: password #xpack.management.elasticsearch.ssl.keystore.path: /path/to/file #xpack.management.elasticsearch.ssl.keystore.password: password #xpack.management.elasticsearch.ssl.verification_mode: certificate #xpack.management.elasticsearch.sniffing: false #xpack.management.logstash.poll_interval: 5s 4. 收集springboot项目日志(windows版)1、收集springboot项目日志 进入logstash配置目录,新建logstash.conf
input表示输入日志的服务,output是同步到es的服务地址
创建启动脚本
springboot项目中导入pom文件 net.logstash.logback logstash-logback-encoder 6.1创建logstash同步文件
在application.yml配置 logging: config: classpath:logstash-spring.xml注意:xml中的端口要和logstash.conf输入日志的端口相同 #启动springboot项目 -》启动start-logstash.bat脚本 启动成功命令行中会有信息输出:
查看同步的数据
1、收集springboot项目日志 进入logstash配置目录,新建logstash.conf cd logstash-7.13.4/config vi logstash.conf 输入内容如下 input{ tcp { mode => "server" host => "0.0.0.0" #我这里是本地 port => 9061 #开放这个端口进行采集 codec => json_lines # 编解码器 有的版本需要独自安装 } } output{ elasticsearch{ #es地址 hosts=>["127.0.0.1:9200"] # 在es里产生的index的名称 index => "springboot-study-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}" } stdout{codec => rubydebug} }输入:wq!保存 input表示输入日志的服务,output是同步到es的服务地址
创建启动脚本 cd /home/es/elk/logstash-7.13.4/bin vi start-logstash.sh 输入如下: ./logstash -f ../config/logstash.conf 保存 :wq! 赋权 chmod u+x start-logstash.sh
springboot项目中导入pom文件 net.logstash.logback logstash-logback-encoder 6.1创建logstash同步文件
在application.yml配置 logging: config: classpath:logstash-spring.xml注意:xml中的端口要和logstash.conf输入日志的端口相同 #打包springboot项目 部署到linux中,启动springboot项目-》启动start-logstash.sh 打包springboot项目
上传jar包
启动jar包,查看实时日志 nohup java -jar network-0804.jar > network-0804.log & tail -f network-0804.log
启动start-logstash.sh cd logstash-7.13.4/bin/ ./start-logstash.sh
查看同步的数据
1、后台运行 : 在linux环境下,如果想要后台启动,需要在执行启动脚本是后面加一个"&"符号表示后台运行,例如:后台运行es 进入es的bin目录,执行./elasticsearch &,如果想要生成运行的日志nohup ./elasticsearch > es.log &, 如果想要查看es.log日志可以,可以使用vi vim cat 查看静态日志,也可以通过tail -f 查看动态日志; 例如:tail -f es.log 2、开机启动 cd /etc/init.d #进入目录 sudo touch elasticsearch logstash kibana #创建启动脚本 sudo chmod +x elasticsearch logstash kibana #设置可执行权限 编辑文件分别保存进去 elasticsearch #!/bin/bash # chkconfig: 2345 21 89 # description: elasticsearch es_home=/home/es/elk/elasticsearch-7.13.4 case $1 in start) sudo -iu elk $es_home/bin/elasticsearch &;; *) echo "require start" ;; esac
kibana #!/bin/bash # chkconfig: 2345 98 02 # description: kibana kibana_home=/home/es/elk/kibana-7.13.4-linux-x86_64 case $1 in start) sudo -iu elk $kibana_home/bin/kibana &;; *) echo "require start" ;; esac
logstash #!/bin/bash # chkconfig: 2345 50 50 # description: logstash logstash_home=/home/es/elk/logstash-7.13.4 case $1 in start) sudo -iu elk $elk_home/bin/elasticsearch &;; *) echo "require start" ;; esac
添加到开机启动 sudo chkconfig --add elasticsearch sudo chkconfig --add logstash sudo chkconfig --add kibana 配置java环境变量 sudo vim /etc/profile JAVA_HOME=/home/es/jdk1.8.0_65 JRE_HOME=$JAVA_HOME/jre PATH=$PATH:$JAVA_HOME/bin:/sbin:/usr/bin:/usr/sbin CLASSPATH=.:$JAVA_HOME/lib/dt.jar:$JAVA_HOME/lib/tools.jar export JAVA_HOME export JRE_HOME export PATH export CLASSPATH
刷新环境变量文件:source /etc/profile 重启服务器 reboot |
【本文地址】