| Windows/Linux获取Mac地址和CPU序列号实现 | 您所在的位置:网站首页 › 因特尔硬盘序列号 › Windows/Linux获取Mac地址和CPU序列号实现 |
Windows/Linux获取Mac地址和CPU序列号实现
|
UUID(Universally Unique Identifier)即通用唯一标识符,是指在一台机器上生成的数字,保证在全球范围的唯一性。可用的开源库如libuuid,可参考https://blog.csdn.net/fengbingchun/article/details/94590406。 UDID(Unique Device Identifier)即设备唯一标识符。一般可通过获取设备的MAC地址+设备的CPU序列号作为设备的唯一标识符。 MAC地址(Media Access Control Address),直译为媒体访问控制地址,也称为局域网地址(LAN Address),以太网地址(Ethernet Address)或物理地址(Physical Address),它是一个用来确认网络设备位置的地址。在OSI模型中,第三层网络层负责IP地址,第二层数据链路层则负责MAC地址。MAC地址用于在网络中唯一标示一个网卡,一台设备若有一或多个网卡,则每个网卡都需要并会有一个唯一的MAC地址。 MAC地址共48位(6个字节),以十六进制表示。第1Bit为广播地址(0)/群播地址(1),第2Bit为广域地址(0)/区域地址(1)。前3~24位由IEEE决定如何分配给每一家制造商,且不重复,后24位由实际生产该网络设备的厂商自行指定且不重复。 通过命令查看MAC地址: (1). Windows:打开命令提示符(cmd.exe),运行ipconfig/all命令,执行结果如下所示:如果计算机上有多个网络设备(无论物理或虚拟),则会有多组信息及MAC地址,需辨识相应的设备。
(2). Linux:第一种方法运行ifconfig命令;第二种方法运行ip link show命令,执行结果如下所示:eth0为第一块物理网卡,HWaddr 2c:fd:a1:bc:1f:44就是MAC地址,lo为本地回环地址。
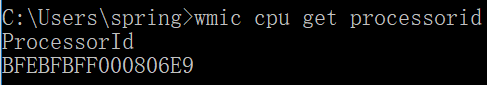
修改MAC地址:网卡MAC地址可以通过Windows设备管理员或其他工具修改。对于某些手机、平板电脑设备来说,其MAC地址/产品序号均由厂方连同销售或保修时的客户资料一并记录在案,而有关的MAC地址也不可通过常规手段来修改。 注:以上MAC地址内容主要来自 维基百科 CPU都有一个唯一的ID号,称CPUID,即CPU序列号,是在制造CPU的时候,由厂家置入到CPU内部的。但是近年的Intel CPU不再区分同一批次中各个CPU的序列号,这样就有可能两台电脑获得的CPU序列号是一样的。 通过命令查看CPU序列号: (1). Windows:打开命令提示符,运行wmic cpu get processorid命令,执行结果如下图所示:
(2). Linux:第一种方法运行dmidecode -t 4 | grep ID命令;第二种方法运行cpuid -r命令,执行结果如下图所示:
以下是代码段通过C++获取Mac地址和CPU序列号的实现: namespace { #ifdef __linux__ // reference: https://stackoverflow.com/questions/6491566/getting-the-machine-serial-number-and-cpu-id-using-c-c-in-linux inline void native_cpuid(unsigned int *eax, unsigned int *ebx, unsigned int *ecx, unsigned int *edx) { // ecx is often an input as well as an output asm volatile("cpuid" : "=a" (*eax), "=b" (*ebx), "=c" (*ecx), "=d" (*edx) : "0" (*eax), "2" (*ecx)); } #endif } // namespace int get_mac_and_cpuid() { // get mac #ifdef _MSC_VER // reference: https://stackoverflow.com/questions/13646621/how-to-get-mac-address-in-windows-with-c PIP_ADAPTER_INFO AdapterInfo = (IP_ADAPTER_INFO *)malloc(sizeof(IP_ADAPTER_INFO)); if (AdapterInfo == nullptr) { fprintf(stderr, "fail to malloc\n"); return -1; } DWORD dwBufLen = sizeof(IP_ADAPTER_INFO); std::unique_ptr mac_addr(new char[18]); // Make an initial call to GetAdaptersInfo to get the necessary size into the dwBufLen variable if (GetAdaptersInfo(AdapterInfo, &dwBufLen) == ERROR_BUFFER_OVERFLOW) { free(AdapterInfo); AdapterInfo = (IP_ADAPTER_INFO *)malloc(dwBufLen); if (AdapterInfo == nullptr) { fprintf(stderr, "fail to malloc\n"); return -1; } } if (GetAdaptersInfo(AdapterInfo, &dwBufLen) == NO_ERROR) { for (PIP_ADAPTER_INFO pAdapterInfo = AdapterInfo; pAdapterInfo != nullptr; pAdapterInfo = pAdapterInfo->Next) { // technically should look at pAdapterInfo->AddressLength and not assume it is 6. if (pAdapterInfo->AddressLength != 6) continue; if (pAdapterInfo->Type != MIB_IF_TYPE_ETHERNET) continue; sprintf(mac_addr.get(), "%02X:%02X:%02X:%02X:%02X:%02X", pAdapterInfo->Address[0], pAdapterInfo->Address[1], pAdapterInfo->Address[2], pAdapterInfo->Address[3], pAdapterInfo->Address[4], pAdapterInfo->Address[5]); fprintf(stdout, "mac address: %s\n", mac_addr.get()); break; } } free(AdapterInfo); #else // reference: https://stackoverflow.com/questions/1779715/how-to-get-mac-address-of-your-machine-using-a-c-program/35242525 int sock = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_DGRAM, 0); if (sock < 0) { fprintf(stderr, "fail to socket: %d\n", sock); return -1; }; struct ifconf ifc; char buf[1024]; int success = 0; ifc.ifc_len = sizeof(buf); ifc.ifc_buf = buf; if (ioctl(sock, SIOCGIFCONF, &ifc) == -1) { fprintf(stderr, "fail to ioctl: SIOCGIFCONF\n"); return -1; } struct ifreq* it = ifc.ifc_req; const struct ifreq* const end = it + (ifc.ifc_len / sizeof(struct ifreq)); struct ifreq ifr; for (; it != end; ++it) { strcpy(ifr.ifr_name, it->ifr_name); if (ioctl(sock, SIOCGIFFLAGS, &ifr) == 0) { if (!(ifr.ifr_flags & IFF_LOOPBACK)) { // don't count loopback if (ioctl(sock, SIOCGIFHWADDR, &ifr) == 0) { success = 1; break; } } } else { fprintf(stderr, "fail to ioctl: SIOCGIFFLAGS\n"); return -1; } } unsigned char mac_address[6]; if (success) memcpy(mac_address, ifr.ifr_hwaddr.sa_data, 6); fprintf(stdout, "mac address: %02X:%02X:%02X:%02X:%02X:%02X\n", mac_address[0], mac_address[1], mac_address[2], mac_address[3], mac_address[4], mac_address[5]); #endif // Capture vendor string char vendor[0x20]; memset(vendor, 0, sizeof(vendor)); // get cpid #ifdef _MSC_VER // reference: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/cpp/intrinsics/cpuid-cpuidex?view=vs-2019 std::array cpui; // Calling __cpuid with 0x0 as the function_id argument gets the number of the highest valid function ID __cpuid(cpui.data(), 0); int nIds_ = cpui[0]; std::vector data_; for (int i = 0; i |
【本文地址】