| JavaScript实现二叉树前中后序遍历(递归和非递归分别实现) | 您所在的位置:网站首页 › 前序遍历后序遍历什么意思 › JavaScript实现二叉树前中后序遍历(递归和非递归分别实现) |
JavaScript实现二叉树前中后序遍历(递归和非递归分别实现)
|
JavaScript实现二叉树的前中后序遍历(递归和非递归) 一、来一棵绿绿的二叉树 1、binary-tree.js const binaryTree = { val: 'a', left: { val: 'b', left: { val: 'd', left: null, right: null }, right: { val: 'e', left: null, right: null } }, right: { val: 'c', left: { val: 'f', left: null, right: null }, right: { val: 'g', left: null, right: null } } } module.exports = { binaryTree } 2、给它画一下
递归实现非常简单,快速写完,在这个内卷的时代,四舍五入就是人均有手就会写,知道自己在干嘛就可以了 基本上就是前序就是最开始打印再递归左孩子,再递归右孩子; 中序就是递归左孩子,再打印结点值,再递归右孩子; 后序就是递归左孩子,递归右孩子,再打印结点值 1、前序遍历 const { binaryTree } = require('./binary-tree') const pre_order = root => { // 结点是空的,直接返回 if (!root) return; console.log(root.val) pre_order(root.left) pre_order(root.right) } pre_order(binaryTree) // a b d e c f g
ctrl(command) + shift + L把pre_order改成in_order,再调下打印的顺序 const { binaryTree } = require('./binary-tree') const in_order = root => { // 结点是空的,直接返回 if (!root) return; in_order(root.left) console.log(root.val) in_order(root.right) } in_order(binaryTree) // d b e a f c g
稍微有一丢丢难度的来啦~ 前中后都用栈来实现一下 1、非递归前序遍历再看下前面画的图 为什么这里要先push右结点再push左结点呢?因为栈是先进后出的, 在前面递归实现的时候,我们已经知道结果是 a b d e c f g了 可见左结点是要先打印的,所以先把结点的右孩子压栈,再压左孩子,这样就可以先pop出来左孩子了 底下会写后序遍历,就是跟这个反过来的,可以结合起来食用 2、非递归实现中序遍历从上面递归算法及图示可以看出,中序遍历首先会找到最左边边的孩子结点 这里可以借助一个指针配合栈来实现 const { binaryTree } = require('./binary-tree') const nonrec_inorder = root => { // 结点是空的,直接返回 if (!root) return; // 定义一个指针指向root let p = root; // 定义一个栈 const stack = []; // 这里地方要|| p是因为不加的话,最开始它就不跑进来了 while(stack.length || p) { // 只要p不为空,就一直去找左节点,压栈 while(p) { stack.push(p) p = p.left; } // 第一轮的这个时候已经找到最左边边的结点了,给它pop出来 const node = stack.pop(); console.log(node.val) // 这个时候左结点和根结点都已经pop出来了,要去遍历右节点 p = node.right; } } nonrec_inorder(binaryTree)
后序遍历的结果是d e b f g c a 是吧 假如一开始先把前序遍历翻过来,先从右边“前序遍历” 所以按照这个思路 只要先翻过来从右边实现一遍“前序遍历”,再把这个结果放在一个栈里面,先进后出就输出正确结果了有木有! const { binaryTree } = require('./binary-tree') const nonrec_postorder = root => { // 结点是空的,直接返回 if (!root) return; // 这个是跟前序遍历的那个栈一样作用 const stack = [root]; // 这个是用来给最后结果反一下的 const out_stack = []; while(stack.length) { const node = stack.pop(); // 每次把这个pop出来的结果收集起来,放在输出结果的那个栈里 out_stack.push(node); if(node.left) stack.push(node.left); if(node.right) stack.push(node.right); } // 输出栈再pop打印一下就好啦 while(out_stack.length) { const n = out_stack.pop(); console.log(n.val) } } nonrec_postorder(binaryTree)好啦~完结撒花✿✿ヽ(°▽°)ノ✿虽然图丑,但是是用心画的 如果你随手点个赞,那么这个星球上就会多一个开心可爱又热爱分享的女程序媛~ |
【本文地址】
公司简介
联系我们



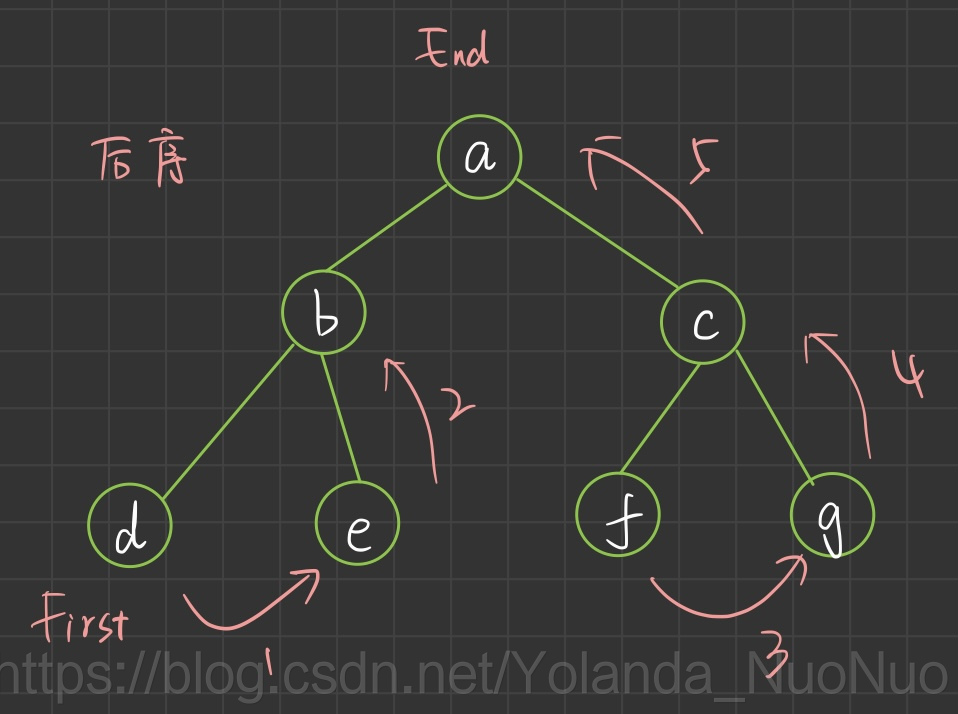 可以肉眼看到递归编码实现只是递归和打印的顺序,需要掌握的是三种顺序遍历是什么意思,是怎么遍历的
可以肉眼看到递归编码实现只是递归和打印的顺序,需要掌握的是三种顺序遍历是什么意思,是怎么遍历的 这样就是a c g f b e d 你把这个反过来读,不就是后序遍历的结果嘛!
这样就是a c g f b e d 你把这个反过来读,不就是后序遍历的结果嘛!