| 基于深度学习的人脸表情识别系统(PyQT+代码+训练数据集) | 您所在的位置:网站首页 › 人脸表情识别应用于智能汽车的应用 › 基于深度学习的人脸表情识别系统(PyQT+代码+训练数据集) |
基于深度学习的人脸表情识别系统(PyQT+代码+训练数据集)
|
基于深度学习的人脸表情识别系统(PyQT+代码+训练数据集)
前言一、数据集1.1 数据集介绍1.2 数据预处理
二、模型搭建三、训练与测试3.1 模型训练3.2 模型测试
四、PyQt界面实现
前言
本项目是基于mini_Xception深度学习网络模型的人脸表情识别系统,核心采用CNN卷积神经网络搭建,详述了数据集处理、模型构建、训练代码、以及基于PyQt5的应用界面设计。在应用中可以支持图像、视频和实时摄像头进行人脸表情识别。本文附带了完整的应用界面设计、深度学习模型代码和训练数据集的下载链接。 完整资源下载链接:博主在面包多网站上的完整资源下载页 项目演示视频: 【项目分享】基于深度学习的人脸表情识别系统(含PyQt界面) 一、数据集 1.1 数据集介绍Fer2013人脸表情数据集由35886张人脸表情图片组成,其中,测试图(Training)28708张,公共验证图(PublicTest)和私有验证图(PrivateTest)各3589张,每张图片是由大小固定为48×48的灰度图像组成,共有7种表情,分别对应于数字标签0-6,具体表情对应的标签和中英文如下:0 anger 生气; 1 disgust 厌恶; 2 fear 恐惧; 3 happy 开心; 4 sad 伤心;5 surprised 惊讶; 6 normal 中性。 数据给的是一个csv文件,其中的表情数据并没有直接给图片,而是给了像素值。我们需要在整理的时候顺便转换成图片就好,这里我们使用getpic.py。 # getpic.py 生成图像数据 import codecs import cv2 from tqdm import tqdm import numpy as np f = codecs.open('fer2013.csv','r','utf8').readlines()[1:] labelfile = codecs.open('label.txt','w','utf8') index = 0 for line in tqdm(f): flist = line.split(',') label = flist[0] img = flist[1].split(' ') img = [int(i) for i in img] img = np.array(img) img = img.reshape((48,48)) cv2.imwrite('ferpic/'+str(index)+'.png',img) labelfile.write(str(index)+'\t'+label+'\n') index += 1将像素值归一化到[0, 1]的范围内有助于训练模型时梯度更加稳定,从而更容易收敛到较好的解。归一化可以避免某些像素值过大或过小导致的梯度爆炸或梯度消失问题。使用utils.py对图像进行预处理,以便在神经网络中使用。根据参数v2的不同取值,可以选择不同的预处理方式。 # utils.py def preprocess_input(x, v2=True): x = x.astype('float32') x = x / 255.0 if v2: x = x - 0.5 x = x * 2.0 return x这个预处理方法主要包含两个步骤:归一化和零均值化。归一化:通过将像素值除以255.0,将输入的图像数据归一化到[0, 1]的范围内。这一步可以确保所有的像素值都在相似的数值范围内,有利于模型训练的稳定性。零均值化:如果参数v2为True,那么将对图像进行零均值化。零均值化的过程包括两个操作:将像素值减去0.5,这样可以将像素值平移至以0.5为中心,即像素值的均值为0.5。这一步使得图像数据的中心点在零点附近,有利于模型的收敛速度。将像素值乘以2.0,将像素值缩放到[-1, 1]的范围内。这一步可以确保图像数据的值域适合一些需要对称分布输入数据的模型,同时提高了模型对输入数据的鲁棒性。 最后使用dataset.py文件将处理好的数据集封装成data.hdf5文件方面后面训练模型使用。 # dataset.py import codecs import cv2 import numpy as np from maketwo import Detecttwo from tqdm import tqdm datapath = '/unsullied/sharefs/lh/isilon-home/fer2013/ferpic/' label = '/unsullied/sharefs/lh/isilon-home/fer2013/label.txt' label = codecs.open(label,'r','utf8').readlines() label = [i.split('\t') for i in label] label = [ [i[0] ,int(i[1]) ] for i in label] #print(label[0:5]) X = [] Y = [] for i in tqdm(label): picname = datapath+i[0]+'.png' img = cv2.imread(picname,0) img = np.expand_dims(img,axis=2)#224*224*1 img = cv2.resize(img, (48,48), interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR) #cv2.imwrite('1.png',img) img = np.expand_dims(img,axis=2)#224*224*1 X.append(img) y = [0,0,0,0,0,0,0] y[i[1]]=1 y = np.array(y) Y.append(y) X = np.array(X) Y = np.array(Y) print(X.shape,Y.shape) print(X[0],Y[0:5]) import h5py f = h5py.File("Data.hdf5",'w') f.create_dataset('X',data=X) f.create_dataset('Y',data=Y) f.close() #np.save('X.npy',X) #np.save('Y.npy',Y) 二、模型搭建我们使用的是基于CNN实现的网络模型mini_XCEPTION。Xception网络模型是由Google提出的,它在Inception v3的基础上进行了进一步的优化。主要是采用深度可分离的卷积(depthwise separable convolution)来替换原来Inception v3中的卷积操作。XCEPTION的网络结构在ImageNet数据集(Inception v3的设计解决目标)上略优于Inception v3,并且在包含3.5亿个图像甚至更大的图像分类数据集上明显优于Inception v3,而两个结构保持了相同数目的参数,性能增益来自于更加有效地使用模型参数,详细可参考论文:Real-time Convolutional Neural Networks for Emotion and Gender Classification–O Arriaga。网络结构图,如下图所示: 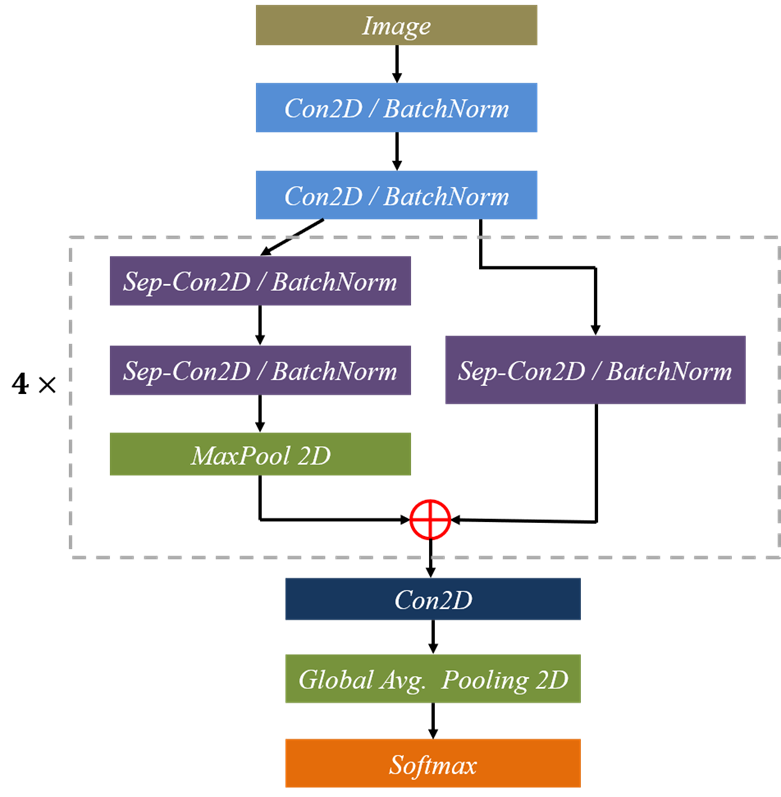
基于CNN的模型实现代码如下: # 模型实现代码 def mini_XCEPTION(input_shape, num_classes, l2_regularization=0.01): regularization = l2(l2_regularization) # base img_input = Input(input_shape) x = Conv2D(8, (3, 3), strides=(1, 1), kernel_regularizer=regularization, use_bias=False)(img_input) x = BatchNormalization()(x) x = Activation('relu')(x) x = Conv2D(8, (3, 3), strides=(1, 1), kernel_regularizer=regularization, use_bias=False)(x) x = BatchNormalization()(x) x = Activation('relu')(x) # module 1 residual = Conv2D(16, (1, 1), strides=(2, 2), padding='same', use_bias=False)(x) residual = BatchNormalization()(residual) x = SeparableConv2D(16, (3, 3), padding='same', kernel_regularizer=regularization, use_bias=False)(x) x = BatchNormalization()(x) x = Activation('relu')(x) x = SeparableConv2D(16, (3, 3), padding='same', kernel_regularizer=regularization, use_bias=False)(x) x = BatchNormalization()(x) x = MaxPooling2D((3, 3), strides=(2, 2), padding='same')(x) x = layers.add([x, residual]) # module 2 residual = Conv2D(32, (1, 1), strides=(2, 2), padding='same', use_bias=False)(x) residual = BatchNormalization()(residual) x = SeparableConv2D(32, (3, 3), padding='same', kernel_regularizer=regularization, use_bias=False)(x) x = BatchNormalization()(x) x = Activation('relu')(x) x = SeparableConv2D(32, (3, 3), padding='same', kernel_regularizer=regularization, use_bias=False)(x) x = BatchNormalization()(x) x = MaxPooling2D((3, 3), strides=(2, 2), padding='same')(x) x = layers.add([x, residual]) # module 3 residual = Conv2D(64, (1, 1), strides=(2, 2), padding='same', use_bias=False)(x) residual = BatchNormalization()(residual) x = SeparableConv2D(64, (3, 3), padding='same', kernel_regularizer=regularization, use_bias=False)(x) x = BatchNormalization()(x) x = Activation('relu')(x) x = SeparableConv2D(64, (3, 3), padding='same', kernel_regularizer=regularization, use_bias=False)(x) x = BatchNormalization()(x) x = MaxPooling2D((3, 3), strides=(2, 2), padding='same')(x) x = layers.add([x, residual]) # module 4 residual = Conv2D(128, (1, 1), strides=(2, 2), padding='same', use_bias=False)(x) residual = BatchNormalization()(residual) x = SeparableConv2D(128, (3, 3), padding='same', kernel_regularizer=regularization, use_bias=False)(x) x = BatchNormalization()(x) x = Activation('relu')(x) x = SeparableConv2D(128, (3, 3), padding='same', kernel_regularizer=regularization, use_bias=False)(x) x = BatchNormalization()(x) x = MaxPooling2D((3, 3), strides=(2, 2), padding='same')(x) x = layers.add([x, residual]) x = Conv2D(num_classes, (3, 3), #kernel_regularizer=regularization, padding='same')(x) x = GlobalAveragePooling2D()(x) output = Activation('softmax',name='predictions')(x) model = Model(img_input, output) return model 三、训练与测试 3.1 模型训练使用Keras库和自定义的mini_XCEPTION模型进行情绪识别的训练。首先,设置了一些关键的训练参数,如批量大小、训练周期、输入数据的维度、验证集的比例、类别数目等参数。 # parameters batch_size = 32 num_epochs = 800 input_shape = (48, 48, 1) validation_split = 0.1 num_classes = 7 patience = 50 base_path = 'trained_models/float_models/'接着,通过ImageDataGenerator类创建了一个数据生成器,用于在训练过程中对图像进行数据增强,包括旋转、平移、缩放和翻转等操作。 # data generator data_generator = ImageDataGenerator( featurewise_center=False, featurewise_std_normalization=False, rotation_range=10, width_shift_range=0.1, height_shift_range=0.1, zoom_range=.1, horizontal_flip=True)然后,定义了mini_XCEPTION模型,并使用Adam优化器和分类交叉熵损失函数进行编译。 # model parameters/compilation model = mini_XCEPTION(input_shape, num_classes) model.compile(optimizer='adam', loss='categorical_crossentropy', metrics=['accuracy']) model.summary()随后,为训练过程设置了回调函数,包括CSVLogger用于记录日志、EarlyStopping用于提前终止训练、ReduceLROnPlateau用于在验证损失不再下降时减少学习率,以及ModelCheckpoint用于保存最佳模型。在加载数据集后,使用train_test_split函数将数据分为训练集和测试集,并开始训练模型。训练过程中,通过flow方法从数据生成器中获取数据,并在每个epoch后进行验证,直至达到指定的训练周期或满足提前终止的条件。最终,模型的性能通过准确率等指标进行评估,并保存最佳模型以供后续使用。 for dataset_name in datasets: print('Training dataset:', dataset_name) # callbacks log_file_path = base_path + dataset_name + '_emotion_training.log' csv_logger = CSVLogger(log_file_path, append=False) early_stop = EarlyStopping('val_loss', patience=patience) reduce_lr = ReduceLROnPlateau('val_loss', factor=0.1, patience=int(patience/4), verbose=1) trained_models_path = base_path + dataset_name + '_mini_XCEPTION' model_names = trained_models_path + '.{epoch:02d}-{accuracy:.2f}.hdf5' model_checkpoint = ModelCheckpoint(model_names, 'val_loss', verbose=1, save_best_only=True) callbacks = [model_checkpoint, csv_logger, early_stop, reduce_lr] # loading dataset f = h5py.File('Data.hdf5','r') X = f['X'][()] X = preprocess_input(X) Y = f['Y'][()] f.close() #X = np.load('X.npy') #Y = np.load('Y.npy') train_X,test_X,train_Y,test_Y = train_test_split(X,Y,test_size=validation_split,random_state=0) model.fit_generator(data_generator.flow(train_X, train_Y, batch_size), steps_per_epoch=len(train_X) / batch_size, epochs=num_epochs, verbose=1, callbacks=callbacks, validation_data=(test_X,test_Y))使用train.py文件进行训练,训练好的模型文件会被保存下如下目录中
使用image_demo.py对图像进行测试,具体的代码实现如下: (1)初始化加载两个检测模型 config = ConfigProto() config.gpu_options.allow_growth = True session = InteractiveSession(config=config) emotion_model_path = 'trained_models/float_models/fer2013_mini_XCEPTION.33-0.65.hdf5' emotion_labels = {0:'angry',1:'disgust',2:'fear',3:'happy', 4:'sad',5:'surprise',6:'neutral'} detection_model_path = 'trained_models/facemodel/haarcascade_frontalface_default.xml' emotion_classifier = load_model(emotion_model_path, compile=False) face_detection = cv2.CascadeClassifier(detection_model_path) emotion_target_size = emotion_classifier.input_shape[1:3](2)使用opencv检测人脸 gray_image = np.expand_dims(imggray,axis=2)#224*224*1 faces = face_detection.detectMultiScale(imggray, 1.3, 5) res = [] if len(faces)==0: print('No face') return None(3)调用Xception网络对框选出的人脸进行表情检测 for face_coordinates in faces: x1,y1,width,height = face_coordinates x1,y1,x2,y2 = x1,y1,x1+width,y1+height gray_face = gray_image[y1:y2, x1:x2] try: gray_face = cv2.resize(gray_face, (emotion_target_size)) except: continue gray_face = preprocess_input(gray_face, True) gray_face = np.expand_dims(gray_face, 0) gray_face = np.expand_dims(gray_face, -1) emotion_prediction = emotion_classifier.predict(gray_face) #emotion_probability = np.max(emotion_prediction) emotion_label_arg = np.argmax(emotion_prediction) res.append([emotion_label_arg,x1,y1,x2,y2])(4)在图像上绘制检测况以及相关信息 def save_predict(imgurl,targeturl='images/predicted_test_image.png'): imggray = cv2.imread(imgurl,0) imgcolor = cv2.imread(imgurl,1) ress = general_predict(imggray,imgcolor) if ress==None: print('No face and no image saved') for res in ress: label = emotion_labels[res[0]] lx,ly,rx,ry = res[1],res[2],res[3],res[4] cv2.rectangle(imgcolor,(lx,ly),(rx,ry),(0,0,255),2) cv2.putText(imgcolor,label,(lx,ly),cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX,2,(0,0,255),2,cv2.LINE_AA) # cv2.imwrite('images/res_1.png', imgcolor) cv2.imwrite('res.png', imgcolor)识别前后的效果图 当整个项目构建完成后,使用PyQt5编写可视化界面,可以支持图像、视频和实时摄像头进行人脸表情识别。 整个界面文件框架如下: 1)connect.py: 主运行文件,连接各个子界面 # connect.py class jiemian2(QtWidgets.QMainWindow,Ui_MainWindow2): def __init__(self): super(jiemian2,self).__init__() self.setupUi(self) #加载相机识别模块 camera.py self.file.clicked.connect(self.back) #返回主界面功能按钮 连接下面的back函数 def back(self): self.hide() #隐藏此窗口 self.log = loginWindow() self.log.show() #显示登录窗口 #必须加上self class jiemian3(QtWidgets.QMainWindow,Ui_MainWindow3): def __init__(self): super(jiemian3,self).__init__() self.setupUi(self) #加载视频文件识别模块 file.py self.file.clicked.connect(self.back) #返回主界面功能按钮 连接下面的back函数 def back(self): self.hide() #隐藏此窗口 self.log = loginWindow() self.log.show() #显示登录窗口 class jiemian4(QtWidgets.QMainWindow,Ui_MainWindow4): def __init__(self): super(jiemian4,self).__init__() self.setupUi(self) self.file.clicked.connect(self.back) #返回主界面功能按钮 连接下面的back函数 def back(self): self.hide() #隐藏此窗口 self.log = loginWindow() self.log.show() #显示登录窗口 #主界面 class loginWindow(QtWidgets.QMainWindow,Ui_MainWindow): def __init__(self): super(loginWindow,self).__init__() self.setupUi(self) self.pushButton.clicked.connect(self.camera) #相机检测按钮 连接下面的camera_detect功能函数 self.pushButton_2.clicked.connect(self.file_detect) #视频文件检测按钮 连接下面的file_detect函数 self.pushButton_3.clicked.connect(self.photo_detect) # def camera_detect(self): # self.hide() #隐藏本界面 # self.jiemian2 = jiemian2(model=self.model,model_gender=self.model_gender) #加载相机识别界面 # # self.jiemian2.show()#显示相机识别界面 def file_detect(self): self.hide() self.jiemian3 = jiemian3() #加载视频文件识别界面 self.jiemian3.show() def camera(self): self.hide() self.jiemian2 = jiemian2() #加载视频文件识别界面 self.jiemian2.show() def photo_detect(self): self.hide() self.jiemian4 = jiemian4() #加载视频文件识别界面 self.jiemian4.show()2)main.py: 连接各个功能模块 3)实时检测: camera.py |
【本文地址】


 对于视频流的识别处理,则使用Video_demo.py调用摄像头对人脸表情进行实时检测,其文件程序逻辑与图像的相同,只不过是调用摄像头取其中的每一帧做检测。
对于视频流的识别处理,则使用Video_demo.py调用摄像头对人脸表情进行实时检测,其文件程序逻辑与图像的相同,只不过是调用摄像头取其中的每一帧做检测。
 4)图像检测photo.py
4)图像检测photo.py  5)视频检测file.py
5)视频检测file.py 