| POSIX 文件及目录管理1 | 您所在的位置:网站首页 › stdlibh和stdioh有什么区别 › POSIX 文件及目录管理1 |
POSIX 文件及目录管理1
|
POSIX 文件及目录管理
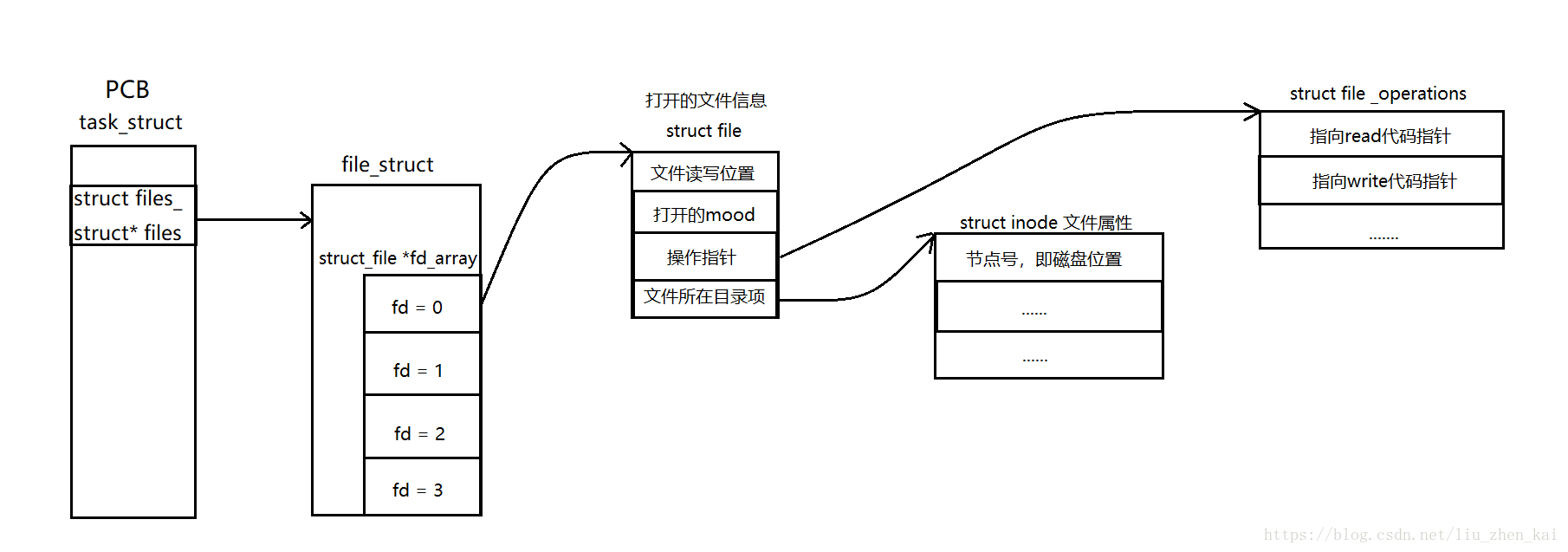
1.文件流与文件描述符的区别 在C库中,实现了对系统IO接口的封装,使得用户更加方便使用,但是不管如何实现,最终都要通过内核实现对文件的读写控制。 下面举个例子来看一下C库与系统中对于标准输入,标准输出与标准错误的头文件定义 //C库 [[email protected] /]$ cat /usr/include/stdio.h | grep '_IO_FILE*' struct _IO_FILE; typedef struct _IO_FILE FILE; typedef struct _IO_FILE __FILE; extern struct _IO_FILE *stdin; /* Standard input stream. */ extern struct _IO_FILE *stdout; /* Standard output stream. */ extern struct _IO_FILE *stderr; /* Standard error output stream. */ //POSIX [[email protected] /]$ cat /usr/include/unistd.h | grep 'STD' #ifndef _UNISTD_H #define _UNISTD_H 1 _LFS64_STDIO Standard I/O supports large files. #define STDIN_FILENO 0 /* Standard input. */ #define STDOUT_FILENO 1 /* Standard output. */ #define STDERR_FILENO 2 /* Standard error output. */文件描述符:数字(整形) 文件流:struct FILE* 结构体指针 关系:文件流的定义中包含有文件描述符,是C库对unistd.h的一种封装。 文件表结构图 在PCB中有结构体:struct files_struct*file,指向的就是进程文件的基本信息,而 file_struct 结构体就含有一个 struct file* fd数组,这个数组每个成员都记录着打开文件的信息,而数组的下标就是文件描述符。 POSIX标准下的IO管理 创建/打开/关闭文件 打开文件的系统调用接口是open函数 int open(const char *pathname, int flags); int open(const char *pathname, int flags, mode_t mode); 参数: pathname:打开文件的路径以及文件名 falgs:打开选项,也即是file struct_operations mode:创建的文件的权限,通常还和系统umask掩码有关。下面对于参数falgs的几个宏进行介绍 The argument flags must include one of the following access modes:O_RDONLY, O_WRONLY, or O_RDWR. These request opening the file read-only, write-only, or read/write, respectively. 对于参数falgs 有三个必选项: O_RDONLY : 只读方式打开 O_WRONLY : 只写方式打开 O_RDWR : 以读写方式打开 falgs还有一系列非必选项可以通过man手册查找 其中O_CREAT 选项是打开文件,若不存在则创建该文件open的使用 [liu@localhost 04]$ vim open.c 1 #include 2 #include 3 #include 4 5 int main(void) 6 { 7 int fd = open("./tmp.txt", O_RDWR|O_CREAT, 0644); 8 printf("fd is : %d\n", fd); 9 return 0; 10 }在运行可执行文件open之前可以看到只有open和open.c两个文件 [liu@localhost 04]$ cc open.c -o open [liu@localhost 04]$ ls open open.c运行open以后,创建了一个新文件tmp.txt [liu@localhost 04]$ ./open fd is : 3 [liu@localhost 04]$ ls open open.c tmp.txt查看文件权限 [[email protected] 04]$ ll tmp.txt -rw-r--r--. 1 liu liu 0 Aug 24 04:39 tmp.txt文件的权限就是644 但是在创建文件的时候,权限还是与umask掩码息息相关,若要创建权限大于系统默认权限的文件,那么需要在程序中改变umask掩码的值。 close的使用 close() closes a file descriptor, so that it no longer refers to any file and may be reused.用于关闭一个打开的文件,通常与open成对使用 函数原型:int open(int fd) 成功返回0,失败返回-1 写入/读取文件 当文件被open打开或者创建之后,open会规定文件的打开方式,下面需要用到文件操作函数对其进行写入或读取的操作write系统调用接口 ssize_t write(int fd, const void *buf, size_t count); write() writes up to count bytes from the buffer pointed buf to the file referred to by the file descriptor fd.向指定的文件描述符对应的文件写入数据 1 #include 2 #include 3 #include 4 #include 5 6 int main(void) 7 { 8 int fd = open("./tmp.txt", O_RDWR|O_CREAT, 0644); 9 10 11 const char* arr = "this is form function open\n"; 12 //向tmp中写入内容 13 int ret = write(fd, arr, strlen(arr)); 14 if(ret < 0) 15 { 16 perror("write:"), 17 exit(1); 18 } 19 20 return 0; 21 }编译运行后发现tmp文件被写入了信息 [liu@localhost 04]$ gcc open.c -o read [liu@localhost 04]$ ls open open.c read tmp.txt [liu@localhost 04]$ ./read [liu@localhost 04]$ ls open open.c read tmp.txt [liu@localhost 04]$ cat tmp.txt this is form function openread系统调用接口 1 #include 2 #include 3 #include 4 #include 5 6 int main(void) 7 { 8 int fd = open("./open.c", O_RDWR|O_CREAT, 0644); 9 10 char buff[1024] = {}; 11 int ret = read(fd,buff, 1023); 12 if(ret < 0) 13 { 14 perror("write:"), 15 exit(1); 16 } 17 printf("%s", buff); 18 19 return 0; 20 }运行结果打印在屏幕上文件内容 [liu@localhost 04]$ gcc open.c -o read [liu@localhost 04]$ ./read #include #include #include #include int main(void) { int fd = open("./open.c", O_RDWR|O_CREAT, 0644); char buff[1024] = {}; int ret = read(fd,buff, 1023); if(ret < 0) { perror("write:"), exit(1); } printf("%s", buff); return 0; } 文件读写指针偏移 lseek用于文件读写指针偏移 off_t lseek(int fd//文件描述符, off_t offset//偏移量, int whence//偏移起始位置); The lseek() function repositions the offset of the open file associated with the file descriptor fd to the argument offset according to the direc- tive whence as follows: SEEK_SET 起始位置开始偏移 The offset is set to offset bytes. SEEK_CUR 当前位置开始偏移 The offset is set to its current location plus offset bytes. SEEK_END 结尾位置开始偏移 The offset is set to the size of the file plus offset bytes. 1 #include 2 #include 3 #include 4 #include 5 6 int main(void) 7 { 8 int fd = open("./open.c", O_RDWR|O_CREAT, 0644); 9 lseek(fd, 70, SEEK_SET); 10 char buff[1024] = {}; 11 int ret = read(fd,buff, 1023); 12 if(ret < 0) 13 { 14 perror("write:"), 15 exit(1); 16 } 17 printf("%s", buff); 18 19 return 0; 20 } [liu@localhost 04]$ ./lseek ring.h> int main(void) { int fd = open("./open.c", O_RDWR|O_CREAT, 0644); lseek(fd, 70, SEEK_SET); char buff[1024] = {}; int ret = read(fd,buff, 1023); if(ret < 0) { perror("write:"), exit(1); } printf("%s", buff); return 0; } |
【本文地址】
公司简介
联系我们