| 2.文件的打开及创建 | 您所在的位置:网站首页 › open函数能删除文件么 › 2.文件的打开及创建 |
2.文件的打开及创建
|
目录 一.open函数简介: 1.包含的头文件 2.open函数原型 3.函数参数说明: 4.open函数描述 5.打开一个文件(文件存在时),获取文件描述符: 6.打开一个文件,如果需要打开的文件不存在,那么创建该文件: 5. 参数mode为0600时,是什么意思? 二:文件打开创建的补充: 2.1:O_EXCL 的使用 2.2:O_APPEND 的使用 2.3:O_TRUNC 的使用 三:creat函数 3.1函数简介 3.2:运行代码demo,参数mode选择的创建模式是 S_IRWXU。可读、写、执行 3.3:运行结果 一.open函数简介: 1.包含的头文件#include #include #include 2.open函数原型int open(const char *pathname, int flags); int open(const char *pathname, int flags, mode_t mode); int creat(const char *pathname, mode_t mode); 3.函数参数说明:pathname:要打开的文件名(含路径) flags : O_RDONLY 只读打开,O_WRONLY 只写打开,O_RDWR 可读可写打开 当我们附带了权限后,打开的文件就只能按照这种权限来操作。 以上这三个参数中应当只指定一个。下列参数是可选择的: O-CREAT :若文件不存在则创建它。使用此选项时,需要同时说明第三个参数mode.用其说明该新文件的存取许可权限。O_EXCL :以这种属性去打开文件时,如果同时指定了O_CREAT,而文件已经存在,则打开文件失败(也可以说返回值是-1)。O_APPEND :以这种属性去打开文件时,每次写时都加到文件的尾端。(不想写入时文件被覆盖,用这个flag,正常写入没有加其他条件的话,原来文件中的数据内容会被覆盖,注意是覆盖,覆盖本身的字节长度,没有覆盖的会保留,不是删除)O_TRUNC :以这种属性去打开文件时,如果这个文件中本来是有内容的,而且为只读或只写成功打开,则将其长度截短为0,通俗点的意思就是把原来的文件中的内容干掉,写入你自己要的数据内容Mode:一定是在flags中使用了 O-CREAT 标志,mode 记录待创建的文件的访问权限,(比如:给的是0600时,则文件所有者给的权限是 可读可写) 4.open函数描述DESCRIPTION Given a pathname for a file, open() returns a file descriptor, a small, nonnegative integer for use in subsequent system calls(read(2), write(2), lseek(2), fcntl(2), etc.). The file descriptor returned by a successful call will be the lowest-numbered file descriptor not currently open for the process. 给定一个文件的路径名,open()返回一个文件描述符,一个小的非负整数,用于后续的系统调用(read(2), write(2), Iseek(2), fcntl(2),等等)。成功调用返回的文件描述符将是进程当前未打开的编号最低的文件描述符。失败:返回 -1 5.打开一个文件(文件存在时),获取文件描述符: #include #include #include #include int main() { int fd; fd = open("./file1",O_RDWR); printf("fd = %d \n",fd); return 0; } 6.打开一个文件,如果需要打开的文件不存在,那么创建该文件:【 在参数flags 中使用了 O-CREAT 标志,参数mode 中就要给出文件的访问权限 0600 (或者其他),这两个是配着使用的】 #include #include #include #include int main() { int fd; fd = open("./file1",O_RDWR); if(fd == -1){ printf("open file1 fail \n"); fd = open("./file1",O_RDWR|O_CREAT,0600); if(fd > 0){ printf("creat file1 success \n"); } } printf("open file1 success:fd = %d \n",fd); return 0; } 5. 参数mode为0600时,是什么意思?
对应两个图看:即可知道0600是让我们以文件所有者的身份给了file1文件可读可写的权限。 开头的第一个 - 是普通文件的意思。 二:文件打开创建的补充: 2.1:O_EXCL 的使用以这种属性去打开文件时,如果同时指定了O_CREAT,而文件已经存在,则打开文件失败(也可以说返回值是-1)。 #include #include #include #include int main() { int fd; fd = open("./file",O_RDWR|O_CREAT|O_EXCL,0600); if(fd == -1){ printf("file1 exist \n"); } return 0; } 2.2:O_APPEND 的使用以这种属性去打开文件时,每次写时都加到文件的尾端。(不想写入时文件被覆盖,用这个flag,正常写入没有加其他条件的话,原来文件中的数据内容会被覆盖,注意是覆盖,覆盖本身的字节长度,没有覆盖的会保留,不是删除)
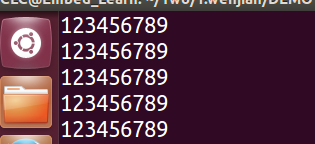
首先:没有添加O_APPEND之前:我们手动touch新建一个文件file1,并设置文件file1里面有一堆的内容。
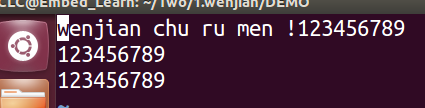
然后我们打开文件的时候只是以可读可写O_RDWR打开。并且向文件file1里面写入一串字符串,代码如下: #include #include #include #include #include #include #include int main() { int fd; char *buf = "wenjian chu ru men !"; fd = open("./file1",O_RDWR); //ssize_t write(int fd, const void *buf, size_t count); int n_write = write(fd,buf,strlen(buf)); printf("write %d byte to file1 \n",n_write); close(fd); return 0; }运行结果显示,file1里面的内容被覆盖。
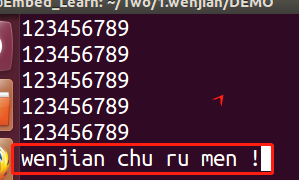
当我们添加O_APPEND使用之后,代码如下: #include #include #include #include #include #include #include int main() { int fd; char *buf = "wenjian chu ru men !"; fd = open("./file1",O_RDWR|O_APPEND); //在open添加 //ssize_t write(int fd, const void *buf, size_t count); int n_write = write(fd,buf,strlen(buf)); printf("write %d byte to file1 \n",n_write); close(fd); return 0; }运行结果如下:在文件内容的尾巴另起一行写入字符串。
以这种属性去打开文件时,如果这个文件中本来是有内容的,而且为只读或只写成功打开,则将其长度截短为0,通俗点的意思就是把原来的文件中的内容干掉,写入你自己要的数据内容
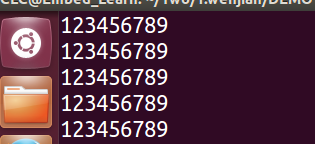
首先,touch新建一个文件file1里面有很多的内容。
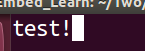
然后添加 O_TRUNC使用之后,代码如下: #include #include #include #include #include #include #include int main() { int fd; char *buf = "test!"; fd = open("./file1",O_RDWR|O_TRUNC); //在open添加 //ssize_t write(int fd, const void *buf, size_t count); int n_write = write(fd,buf,strlen(buf)); printf("write %d byte to file1 \n",n_write); close(fd); return 0; }运行结果显示,新建的文件file1中的内容被全部删除,并且被写入的字符串取代:
r : 意思是可读 w:意思是可写 x:意思是可执行 对应了代码中,参数mode选择的创建模式是 S_IRWXU。可读、写、执行。 |
【本文地址】