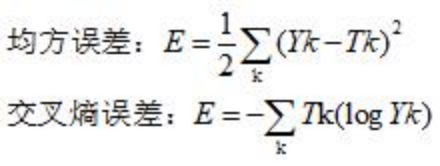| 基于BP神经网络对MNIST数据集检测识别(numpy版本) | 您所在的位置:网站首页 › mnist数据集最高准确率 › 基于BP神经网络对MNIST数据集检测识别(numpy版本) |
基于BP神经网络对MNIST数据集检测识别(numpy版本)
|
基于BP神经网络对MNIST数据集检测识别
1.作者介绍2.BP神经网络介绍2.1 BP神经网络
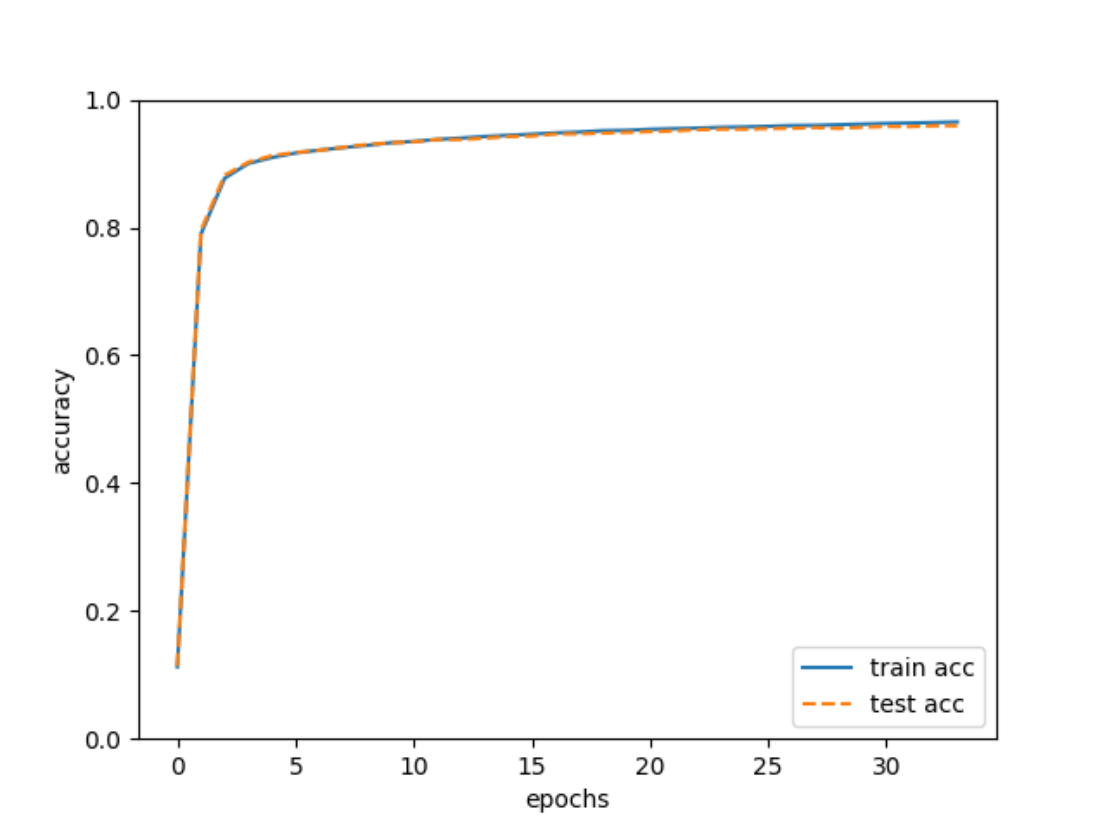
3.BP神经网络对MNIST数据集检测实验3.1 读取数据集3.2 前向传播3.3 损失函数3.4 构建神经网络3.5 训练3.6 模型推理
4.完整代码
1.作者介绍
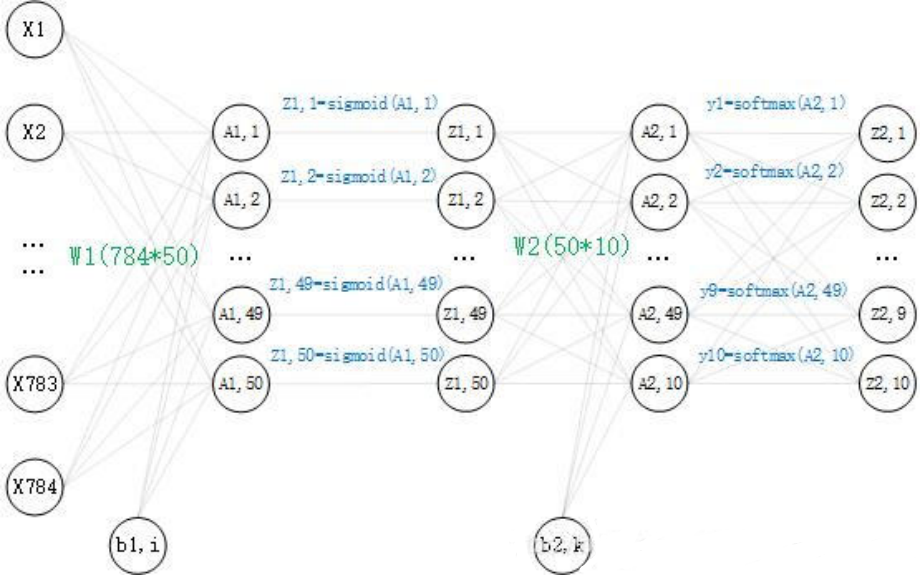
王凯,男,西安工程大学电子信息学院,2022级研究生 研究方向:机器视觉与人工智能 电子邮件:[email protected] 张思怡,女,西安工程大学电子信息学院,2022级研究生,张宏伟人工智能课题组 研究方向:机器视觉与人工智能 电子邮件:[email protected] 2.BP神经网络介绍 2.1 BP神经网络搭建一个两层(两个权重矩阵,一个隐藏层)的神经网络,其中输入节点和输出节点的个数是确定的,分别为 784 和 10。而隐藏层节点的个数还未确定,并没有明确要求隐藏层的节点个数,所以在这里取50个。现在神经网络的结构已经确定了,再看一下里面是怎么样的,这里画出了对一个数据的运算过程: 安装numpy :pip install numpy 安装matplotlib pip install matplotlib mnist是一个包含各种手写数字图片的数据集:其中有60000个训练数据和10000个测试时局,即60000个 train_img 和与之对应的 train_label,10000个 test_img 和 与之对应的test_label。 前向传播时,我们可以构造一个函数,输入数据,输出预测。 def predict(self, x): w1, w2 = self.dict['w1'], self.dict['w2'] b1, b2 = self.dict['b1'], self.dict['b2'] a1 = np.dot(x, w1) + b1 z1 = sigmoid(a1) a2 = np.dot(z1, w2) + b2 y = softmax(a2) 3.3 损失函数求出神经网络对一组数据的预测值,是一个1*10的矩阵。 其中,Yk表示的是第k个节点的预测值,Tk表示标签中第k个节点的one-hot值,举前面的eg:(手写数字5的图片预测值和5的标签) Yk=[0.01,0.01,0.01,0.04,0.8,0.01,0.1,0.01,0.01,0.01] Tk=[0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0] 值得一提的是,在交叉熵误差函数中,Tk的值只有一个1,其余为0,所以对于这个数据的交叉熵误差就为 E = -1(log0.8)。 在这里选用交叉熵误差作为损失函数,代码实现如下: def loss(self, y, t): t = t.argmax(axis=1) num = y.shape[0] s = y[np.arange(num), t] return -np.sum(np.log(s)) / num 3.4 构建神经网络前面我们定义了预测值predict, 损失函数loss, 识别精度accuracy, 梯度grad,下面构建一个神经网络的类,把这些方法添加到神经网络的类中: for i in range(epoch): batch_mask = np.random.choice(train_size, batch_size) # 从0到60000 随机选100个数 x_batch = x_train[batch_mask] y_batch = net.predict(x_batch) t_batch = t_train[batch_mask] grad = net.gradient(x_batch, t_batch) for key in ('w1', 'b1', 'w2', 'b2'): net.dict[key] -= lr * grad[key] loss = net.loss(y_batch, t_batch) train_loss_list.append(loss) # 每批数据记录一次精度和当前的损失值 if i % iter_per_epoch == 0: train_acc = net.accuracy(x_train, t_train) test_acc = net.accuracy(x_test, t_test) train_acc_list.append(train_acc) test_acc_list.append(test_acc) print( '第' + str(i/600) + '次迭代''train_acc, test_acc, loss :| ' + str(train_acc) + ", " + str(test_acc) + ',' + str( loss)) 3.5 训练 import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from TwoLayerNet import TwoLayerNet from mnist import load_mnist (x_train, t_train), (x_test, t_test) = load_mnist(normalize=True, one_hot_label=True) net = TwoLayerNet(input_size=784, hidden_size=50, output_size=10, weight_init_std=0.01) epoch = 20400 batch_size = 100 lr = 0.1 train_size = x_train.shape[0] # 60000 iter_per_epoch = max(train_size / batch_size, 1) # 600 train_loss_list = [] train_acc_list = [] test_acc_list = []保存权重: np.save('w1.npy', net.dict['w1']) np.save('b1.npy', net.dict['b1']) np.save('w2.npy', net.dict['w2']) np.save('b2.npy', net.dict['b2'])结果可视化: 运行python reasoning.py 可以看到模型拥有较高的准确率。 4.完整代码训练 import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from TwoLayerNet import TwoLayerNet from mnist import load_mnist (x_train, t_train), (x_test, t_test) = load_mnist(normalize=True, one_hot_label=True) net = TwoLayerNet(input_size=784, hidden_size=50, output_size=10, weight_init_std=0.01) epoch = 20400 batch_size = 100 lr = 0.1 train_size = x_train.shape[0] # 60000 iter_per_epoch = max(train_size / batch_size, 1) # 600 train_loss_list = [] train_acc_list = [] test_acc_list = [] for i in range(epoch): batch_mask = np.random.choice(train_size, batch_size) # 从0到60000 随机选100个数 x_batch = x_train[batch_mask] y_batch = net.predict(x_batch) t_batch = t_train[batch_mask] grad = net.gradient(x_batch, t_batch) for key in ('w1', 'b1', 'w2', 'b2'): net.dict[key] -= lr * grad[key] loss = net.loss(y_batch, t_batch) train_loss_list.append(loss) # 每批数据记录一次精度和当前的损失值 if i % iter_per_epoch == 0: train_acc = net.accuracy(x_train, t_train) test_acc = net.accuracy(x_test, t_test) train_acc_list.append(train_acc) test_acc_list.append(test_acc) print( '第' + str(i/600) + '次迭代''train_acc, test_acc, loss :| ' + str(train_acc) + ", " + str(test_acc) + ',' + str( loss)) np.save('w1.npy', net.dict['w1']) np.save('b1.npy', net.dict['b1']) np.save('w2.npy', net.dict['w2']) np.save('b2.npy', net.dict['b2']) markers = {'train': 'o', 'test': 's'} x = np.arange(len(train_acc_list)) plt.plot(x, train_acc_list, label='train acc') plt.plot(x, test_acc_list, label='test acc', linestyle='--') plt.xlabel("epochs") plt.ylabel("accuracy") plt.ylim(0, 1.0) plt.legend(loc='lower right') plt.show()测试 import numpy as np from mnist import load_mnist from functions import sigmoid, softmax import cv2 ######################################数据的预处理 (x_train, t_train), (x_test, t_test) = load_mnist(normalize=True, one_hot_label=True) batch_mask = np.random.choice(100,1) # 从0到60000 随机选100个数 #print(batch_mask) x_batch = x_train[batch_mask] #####################################转成图片 arr = x_batch.reshape(28,28) cv2.imshow('wk',arr) key = cv2.waitKey(10000) #np.savetxt('batch_mask.txt',arr) #print(x_batch) #train_size = x_batch.shape[0] #print(train_size) ########################################进入模型预测 w1 = np.load('w1.npy') b1 = np.load('b1.npy') w2 = np.load('w2.npy') b2 = np.load('b2.npy') a1 = np.dot(x_batch,w1) + b1 z1 = sigmoid(a1) a2 = np.dot(z1,w2) + b2 y = softmax(a2) p = np.argmax(y, axis=1) print(p) |
【本文地址】
 数学公式:
数学公式: 
 其中的 train_img 和 test_img 就是这种图片的形式,train_img 是为了训练神经网络算法的训练数据,test_img 是为了测试神经网络算法的测试数据,每一张图片为2828,将图片转换为2828=784个像素点,每个像素点的值为0到255,像素点值的大小代表灰度,从而构成一个1784的矩阵,作为神经网络的输入,而神经网络的输出形式为110的矩阵,个:eg:[0.01,0.01,0.01,0.04,0.8,0.01,0.1,0.01,0.01,0.01],矩阵里的数字代表神经网络预测值的概率,比如0.8代表第五个数的预测值概率。 其中 train_label 和 test_label 是 对应训练数据和测试数据的标签,可以理解为一个1*10的矩阵,用one-hot-vectors(只有正确解表示为1)表示,one_hot_label为True的情况下,标签作为one-hot数组返回,one-hot数组 例:[0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0],即矩阵里的数字1代表第五个数为True,也就是这个标签代表数字5。 数据集的读取: load_mnist(normalize=True, flatten=True, one_hot_label=False):中, normalize : 是否将图像的像素值正规化为0.0~1.0(将像素值正规化有利于提高精度)。flatten : 是否将图像展开为一维数组。 one_hot_label:是否采用one-hot表示。
其中的 train_img 和 test_img 就是这种图片的形式,train_img 是为了训练神经网络算法的训练数据,test_img 是为了测试神经网络算法的测试数据,每一张图片为2828,将图片转换为2828=784个像素点,每个像素点的值为0到255,像素点值的大小代表灰度,从而构成一个1784的矩阵,作为神经网络的输入,而神经网络的输出形式为110的矩阵,个:eg:[0.01,0.01,0.01,0.04,0.8,0.01,0.1,0.01,0.01,0.01],矩阵里的数字代表神经网络预测值的概率,比如0.8代表第五个数的预测值概率。 其中 train_label 和 test_label 是 对应训练数据和测试数据的标签,可以理解为一个1*10的矩阵,用one-hot-vectors(只有正确解表示为1)表示,one_hot_label为True的情况下,标签作为one-hot数组返回,one-hot数组 例:[0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0],即矩阵里的数字1代表第五个数为True,也就是这个标签代表数字5。 数据集的读取: load_mnist(normalize=True, flatten=True, one_hot_label=False):中, normalize : 是否将图像的像素值正规化为0.0~1.0(将像素值正规化有利于提高精度)。flatten : 是否将图像展开为一维数组。 one_hot_label:是否采用one-hot表示。  完整代码及数据集下载:https://gitee.com/wang-kai-ya/bp.git
完整代码及数据集下载:https://gitee.com/wang-kai-ya/bp.git