| Python numpy.log2() | 您所在的位置:网站首页 › log2-x的图像 › Python numpy.log2() |
Python numpy.log2()
|
Python numpy.log2()
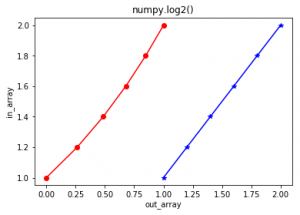
numpy.log2(arr, out = None, *, where = True, casting = ‘same_kind’, order = ‘K’, dtype = None, ufunc ‘ log1p’ ) : 这个数学函数可以帮助用户计算出 x的基数-2对数其中x属于所有的输入阵列元素。 参数 : array : [array_like]输入数组或对象。 out : [ndarray, optional]输出数组,其尺寸与输入数组相同,与结果放在一起。 **kwargs : 允许你向一个函数传递长度可变的关键字参数。当我们想在一个函数中处理命名的参数时,它就会被使用。 where : [array_like, optional]真值意味着在该位置计算通用函数(ufunc),假值意味着在输出中不考虑该值。 返回 : 一个以x为基数的对数数组。 其中x属于输入数组的所有元素。 代码1: # Python program explaining # log2() function import numpy as np in_array = [1, 3, 5, 2**8] print ("Input array : ", in_array) out_array = np.log2(in_array) print ("Output array : ", out_array) print("\nnp.log2(4**4) : ", np.log2(4**4)) print("np.log2(2**8) : ", np.log2(2**8))输出 : Input array : [1, 3, 5, 256] Output array : [ 0. 1.5849625 2.32192809 8. ] np.log2(4**4) : 8.0 np.log2(2**8) : 8.0代码2:图形表示法 # Python program showing # Graphical representation of # log2() function import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt in_array = [1, 1.2, 1.4, 1.6, 1.8, 2] out_array = np.log2(in_array) print ("out_array : ", out_array) plt.plot(in_array, in_array, color = 'blue', marker = "*") # red for numpy.log2() plt.plot(out_array, in_array, color = 'red', marker = "o") plt.title("numpy.log2()") plt.xlabel("out_array") plt.ylabel("in_array") plt.show()输出 : out_array : [ 0. 0.26303441 0.48542683 0.67807191 0.84799691 1. ]
|
【本文地址】
公司简介
联系我们