| Java switch支持类型详解 | 您所在的位置:网站首页 › java语句switch › Java switch支持类型详解 |
Java switch支持类型详解
|
switch支持哪些类型? (1)最早时,只支持int、char、byte、short这样的整型的基本类型或对应的包装类型Integer、Character、Byte、Short常量,包装类型最终也会经过拆箱为基本类型,本质上还是只支持基本类型 (2)JDK1.5开始支持enum,原理是给枚举值进行了内部的编号,进行编号和枚举值的映射 (3)JDK1.7开始支持String,但不允许为null,原理是借助 hashcode( ) 来实现。 我们首先看下Jdk的官方文档。官方文档中对于switch有如下描述。 Compilation of switch statements uses the tableswitch and lookupswitch instructions. The tableswitch instruction is used when the cases of the switch can be efficiently represented as indices into a table of target offsets. The default target of the switch is used if the value of the expression of the switch falls outside the range of valid indices. The Java Virtual Machine's tableswitch and lookupswitch instructions operate only on int data. Because operations on byte, char, or short values are internally promoted to int, a switch whose expression evaluates to one of those types is compiled as though it evaluated to type int. If the chooseNear method had been written using type short, the same Java Virtual Machine instructions would have been generated as when using type int. Other numeric types must be narrowed to type int for use in a switch. Where the cases of the switch are sparse, the table representation of the tableswitch instruction becomes inefficient in terms of space. The lookupswitch instruction may be used instead. The lookupswitch instruction pairs int keys (the values of the case labels) with target offsets in a table. When a lookupswitch instruction is executed, the value of the expression of the switch is compared against the keys in the table. If one of the keys matches the value of the expression, execution continues at the associated target offset. If no key matches, execution continues at the default target. The Java Virtual Machine specifies that the table of the lookupswitch instruction must be sorted by key so that implementations may use searches more efficient than a linear scan. Even so, the lookupswitch instruction must search its keys for a match rather than simply perform a bounds check and index into a table like tableswitch. Thus, a tableswitch instruction is probably more efficient than a lookupswitch where space considerations permit a choice. 大概意思就是以下几点: 1、switch使用tableswitch 和lookupswitch 指令来实现 2、Java虚拟机的 tableswitch 和 lookupswitch 指令只能作用在int类型的数据 3、byte、char 和 short类型可以安全转换为int,所以switch(key)的key类型可以为byte、char和short。long和double等类型是不能安全的转换为int,所以key的类型不能为long和double 4、如果cases对应的值比较稀疏时,使用tableswitch 会导致空间的利用率低下,此时可以使用 5、lookupswitch指令时,要求按照key进行排序,方便对key的搜索进行优化,比如可以采用二分查找等进行优化。 从字节码层面查看下包装类型时处理方式。 public void integerSwitch(Integer integer) { switch (integer) { case 1: System.out.println(1); break; default: break; } } 生成的字节码如下(有省略): public void integerSwitch(java.lang.Integer); descriptor: (Ljava/lang/Integer;)V flags: ACC_PUBLIC Code: stack=2, locals=2, args_size=2 0: aload_1 1: invokevirtual #2 // Method java/lang/Integer.intValue:()I 4: lookupswitch { // 1 1: 24 default: 34 } 24: getstatic #3 // Field java/lang/System.out:Ljava/io/PrintStream; 27: iconst_1 28: invokevirtual #4 // Method java/io/PrintStream.println:(I)V 31: goto 34 34: return可以看到 1: invokevirtual #2 // Method java/lang/Integer.intValue:()I 调用 intValue 进行自动拆箱。 从字节码层面看下switch是怎么支持枚举类型的。 我们定义如下枚举: /** * 定义性别枚举类 */ public enum SexEnum { MALE(1, "男"), FEMALE(6, "女"); private int key; private String name; SexEnum(int key, String name) { this.key = key; this.name = name; } }从字节码中可以看出枚举SexEnum继承java.lang.Enum
java.lang.Enum类中有如下实例变量: /** * The ordinal of this enumeration constant (its position * in the enum declaration, where the initial constant is assigned * an ordinal of zero). * * Most programmers will have no use for this field. It is designed * for use by sophisticated enum-based data structures, such as * {@link java.util.EnumSet} and {@link java.util.EnumMap}. */ private final int ordinal;表示是一个序数,或者叫序号,定位枚举常量的位置,起始值是0。从源码中可知,ordinal是由final修饰,final修饰实例变量时,有三个地方可以初始化,而且一经初始化后值不能再改变。 (1)定义时就初始化 (2)非静态代码块 (3)构造函数 我们看下结合SexEnum枚举的字节码看下ordinal是在哪里进行赋值的? 就需要先了解下枚举中的 MALE 和 FEMALE是怎么表示的?看下SexEnum生成的字节码,是由两个由static final 修饰的类变量MALE 和 FEMALE来表示的,static final 修饰的类变量是在什么时机进行初始化的?
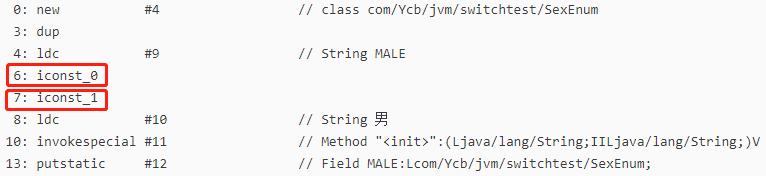
由static final 修饰的类变量在定义的时候进行初始化 或者 在静态代码块中进行初始化。此处定义的时候没进行初始化,所以我们再从字节码的层面看下静态代码块的逻辑 static {}; descriptor: ()V flags: ACC_STATIC Code: stack=6, locals=0, args_size=0 0: new #4 // class com/Ycb/jvm/switchtest/SexEnum 3: dup 4: ldc #9 // String MALE 6: iconst_0 7: iconst_1 8: ldc #10 // String 男 10: invokespecial #11 // Method "":(Ljava/lang/String;IILjava/lang/String;)V 13: putstatic #12 // Field MALE:Lcom/Ycb/jvm/switchtest/SexEnum; 16: new #4 // class com/Ycb/jvm/switchtest/SexEnum 19: dup 20: ldc #13 // String FEMALE 22: iconst_1 23: bipush 6 25: ldc #14 // String 女 27: invokespecial #11 // Method "":(Ljava/lang/String;IILjava/lang/String;)V 30: putstatic #15 // Field FEMALE:Lcom/Ycb/jvm/switchtest/SexEnum; 33: iconst_2 34: anewarray #4 // class com/Ycb/jvm/switchtest/SexEnum 37: dup 38: iconst_0 39: getstatic #12 // Field MALE:Lcom/Ycb/jvm/switchtest/SexEnum; 42: aastore 43: dup 44: iconst_1 45: getstatic #15 // Field FEMALE:Lcom/Ycb/jvm/switchtest/SexEnum; 48: aastore 49: putstatic #1 // Field $VALUES:[Lcom/Ycb/jvm/switchtest/SexEnum; 52: return这一部分就是设置MALE静态变量的值,框住的两个地方 (1)6:iconst_0 感觉就是 MALE 的 ordinal 的赋值 (2)7:iconst_1 应该就是 定义MALE时,MALE(1,:"男") 中的1
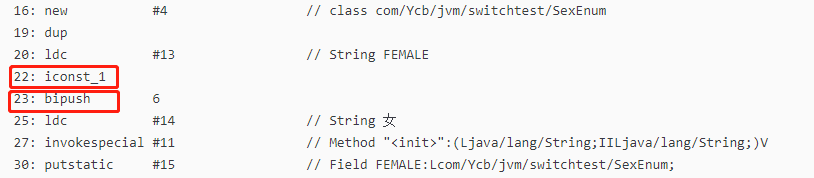
这一部分就是设置FEMALE静态变量的值,框住的两个地方 (1)22:iconst_1 感觉就是 FEMALE 的 ordinal 的赋值 (2)23: bipush 6 应该就是 定义FEMALE时,FEMALE(6,"女") 中的6
知道了ordinal值的定义和赋值时机之后我们看下,switch是怎么只是枚举类型的 定义如下代码: public void enumSwitch(SexEnum sexEnum) { switch (sexEnum) { case MALE: System.out.println("男"); break; case FEMALE: System.out.println("女"); break; default: break; } }反编译生成的class文件,得到如下内容 package com.Ycb.jvm.switchtest; import com.Ycb.jvm.switchtest.SexEnum; import com.Ycb.jvm.switchtest.SexEnumTest.1; public class SexEnumTest { public void enumSwitch(SexEnum sexEnum) { switch(1.$SwitchMap$com$Ycb$jvm$switchtest$SexEnum[sexEnum.ordinal()]) { case 1: System.out.println("MALE"); break; case 2: System.out.println("FEMALE"); } } }核心就是这一句:switch(1.$SwitchMap$com$Ycb$jvm$switchtest$SexEnum[sexEnum.ordinal()]) 1.$SwitchMap$com$Ycb$jvm$switchtest$SexEnum[ ] 这个数组是什么?原来是会自动生成SexEnumTest$1.class文件,我们反编译后看下里面的内容如下: package com.Ycb.jvm.switchtest; import com.Ycb.jvm.switchtest.SexEnum; // $FF: synthetic class class SexEnumTest$1 { // $FF: synthetic field static final int[] $SwitchMap$com$Ycb$jvm$switchtest$SexEnum = new int[SexEnum.values().length]; static { try { $SwitchMap$com$Ycb$jvm$switchtest$SexEnum[SexEnum.MALE.ordinal()] = 1; } catch (NoSuchFieldError var2) { ; } try { $SwitchMap$com$Ycb$jvm$switchtest$SexEnum[SexEnum.FEMALE.ordinal()] = 2; } catch (NoSuchFieldError var1) { ; } } }到这里,对于switch是如何支持枚举类型的,一切迷雾都已经解开了。 接下来我们看下switch是如何支持String类型的。 我们定义如下方法: public void stringSwitch(String key) { switch (key) { case "MALE": System.out.println("MALE"); break; case "FEMALE": System.out.println("FEMALE"); break; default: System.out.println("I Don't NONE"); break; } }反编译.class文件,得到如下的结果 public void stringSwitch(String key) { byte var3 = -1; switch(key.hashCode()) { case 2358797: if(key.equals("MALE")) { var3 = 0; } break; case 2070122316: if(key.equals("FEMALE")) { var3 = 1; } } switch(var3) { case 0: System.out.println("MALE"); break; case 1: System.out.println("FEMALE"); break; default: System.out.println("I Don\'t NONE"); } }从反编译的结果中我们可以看出String使用hashCode实现,本质还是转换为基本类型 int 。从上面的结果中我们可以看出,偶外添加了判断 if ( key.equals("MALE")){ // },原因是hash可能存在冲突。 那传入的key能否为null?答案是肯定不能的,key为null时会报空指针异常,因为switch里面其实使用的是key.hashcode()。所以会报空指针异常,验证结果如下:
|
【本文地址】