| 名词解析(二十一)高危型HPV(high | 您所在的位置:网站首页 › hpv病毒高危和低危哪个好治 › 名词解析(二十一)高危型HPV(high |
名词解析(二十一)高危型HPV(high
|
图1: HPV的基因组结构(以HPV 16为例),其中URR为上游调控序列,即LCR。 E1和E2蛋白是识别复制起点的因子,其中E2蛋白也是病毒基因转录的主要调节因子。虽然按名称来看E4排在前面,在功能上却在病毒复制的晚期发挥作用,E5反而在病毒复制早期和晚期都发挥着重要的作用。E6和E7蛋白的靶点是一些细胞周期的负性调控因子,主要包括Rb和P53。在病毒的复制周期中,E6和E7蛋白负责维持病毒小体的稳定并且促进已经分化的宿主细胞重新进入细胞周期的S期。L1和L2蛋白是在衣壳蛋白中组装的,并最终在子代病毒的基因组周围形成一个二十面体的衣壳。 The E1 and E2 proteins of HPV act as factors that recognize the origin of replication; E2 protein is also the main regulator of viral gene tranion. E4, despite its name, is believed to be involved in the late stages of the life cycle of the virus and E5 may function during both early and late phases. The E6 and E7 proteins target a number of negative regulators of the cell cycle, primarily Rb and p53, respectively. During the viral life cycle, E6 and E7 facilitate stable maintenance of viral episomes and stimulate differentiating cells to re-enter the S phase. The L1 and L2 proteins assemble in capsomers , which form icosahedral capsids around the viral genome during the generation of progeny virions . 贰 | HPV的分型 乳头瘤病毒的分型是按照核苷酸序列的比对进行的,而非血清学分型,因此不同类型的HPV在分类的时候都称某种基因型。L1开放阅读框是HPV基因组中一个最保守的序列,因此在过去15年中被广泛用于新型HPV病毒的鉴定。如果一个HPV的全基因组能被复制,且与已知结构最相近的病毒类型相比,其L1序列的差异超过10%时称为一个新的基因型,如果差异介于2%到10%之间称为一个新的亚型,如果差异小于2%时称为一个变种。我们常用希腊字母标注乳头瘤病的属,并且在后头加上阿拉伯字母表示具体的种类。例如,αPV9(Alphapapillomavirus 9)包括HPV16, 31, 33, 35, 52, 58和67七种。 The classification of papillomaviruses is based on nucleotide sequence comparison rather than on serology, with individual HPVs being referred to as genotypes. The L1 ORF is the most conserved region within the genome and has therefore been used for the identification of new papillomavirus types over the past 15 years. A new papillomavirus isolate is recognized if the complete genome has been cloned and the DNA sequence of the L1 ORF differs by more than 10% from the closest known type. Differences in homology of between 2% and 10% define a subtype and those of less than 2% define a variant. These papillomavirus “types” are grouped into larger phylogenetic groupings or genera, which are categorised with a Greek letter followed by a number that indicates the species. Thus the species Alphapapillomavirus 9 includes HPV types 16, 31, 35, 33, 52, 58 and 67.
图2: HPV的进化关系图。HPV共分五个属,图中上半部分代表α属,蓝色代表β属,绿色代表γ属,另外两个属分别用深紫色和橘红色代表。其中,α属常常根据它们和癌症发生的关系分为皮肤低危型(浅棕色代表)、黏膜低危型(黄色)和高危型(粉色)三组。红色字体的HPV型别已经被流行病学证据证明与人类癌症发生有关,其余未标红的也是疑似与癌症发生有关。 这种分类方法很宽泛,没有考虑病毒的系统发生、基因组结构和致病性等因素,因此往往分类上很相近的两个型别的HPV会表现出很不一样的致病过程。例如,HPV6和11都属于Alpha papilloma virus 10,而且两者导致的病变外观也很相似,但HPV6往往导致生殖器病变,HPV11却常常导致口腔部位的病变。 叁 | HPV的基因型与致病性 女性HPV相关疾病: 1. 宫颈癌: 世界范围内,宫颈癌是女性第四常见的癌症,每年有大概53万例新发宫颈浸润癌被诊断,26万人因宫颈癌死亡。 HPV与宫颈癌的关系已经被大量研究证实,几乎所有的宫颈癌都和HPV感染有关,其中HPV16感染导致了约50%的宫颈癌,HPV18导致了约20%,HPV31, 33, 45, 52和58被认为导致了其余19%的宫颈癌。高危型HPV的流行病学可以被以下研究说明: Evidence linking HPV to cervical carcinoma is extensive. Virtually all cases of cervical cancer are attributable to HPV infection, with HPV 16 accounting for approximately 50 percent of cases and HPV 18 for 20 percent. HPV types 31, 33, 45, 52, and 58 are estimated to cause an additional 19 percent. The epidemiology of high-risk types can be illustrated by the following observations: 一个包含11个病例对照研究,纳入了9个国家共1918名罹患宫颈鳞癌和1928名对照组人群的系统分析表明,HPV DNA存在于90%的宫颈癌患者和13%的对照组人群中,一共有15种HPV型别被认定为高危型,分别是HPV 16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 45, 51, 52, 56, 58, 59, 68, 73 和82。 A pooled analysis of 11 case-control studies from nine countries involving 1918 women with histologically confirmed squamous-cell cervical cancer and 1928 controls was performed to better determine the risk associated with various HPV genotypes. HPV DNA was found in 90 percent of the women with cervical cancer and 13 percent of controls. Fifteen HPV types were classified as high risk (HPV 16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 45, 51, 52, 56, 58, 59, 68, 73, and 82). 一个包含11个病例对照研究,纳入了9个国家共1918名罹患宫颈鳞癌和1928名对照组人群的系统分析表明,HPV DNA存在于90%的宫颈癌患者和13%的对照组人群中,一共有15种HPV型别被认定为高危型,分别是HPV 16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 45, 51, 52, 56, 58, 59, 68, 73 和82。 A pooled analysis of 11 case-control studies from nine countries involving 1918 women with histologically confirmed squamous-cell cervical cancer and 1928 controls was performed to better determine the risk associated with various HPV genotypes. HPV DNA was found in 90 percent of the women with cervical cancer and 13 percent of controls. Fifteen HPV types were classified as high risk (HPV 16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 45, 51, 52, 56, 58, 59, 68, 73, and 82). 一项研究回顾了5大洲38个国家共10575份宫颈浸润癌患者的石蜡病理标本,结果表明,最常见的HPV型别是16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 45, 52 和 58型,HPV 16和18占所有病例的71%。 A study of paraffin-embedded samples representing 10,575 cases of invasive cervical cancer from 38 countries spanning five continents demonstrated that the most common HPV types were 16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 45, 52 and 58; HPV types 16 and 18 represented 71 percent of the cases overall. 一项研究回顾了5大洲38个国家共10575份宫颈浸润癌患者的石蜡病理标本,结果表明,最常见的HPV型别是16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 45, 52 和 58型,HPV 16和18占所有病例的71%。 A study of paraffin-embedded samples representing 10,575 cases of invasive cervical cancer from 38 countries spanning five continents demonstrated that the most common HPV types were 16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 45, 52 and 58; HPV types 16 and 18 represented 71 percent of the cases overall. 2. 外阴和阴道癌: 外阴和阴道癌在全球范围内比较少见。不像宫颈癌和肛门癌,并非所有的外生殖器癌症都与HPV感染相关。据估计,有29-43%的外阴癌与HPV感染相关,87%的外阴上皮内病变(VIN)和70%的阴道癌与HPV感染相关。HPV 16和18型感染在HPV阳性的外阴癌中大约占35-77%,在HPV阳性的外阴癌前病变中占75-80%,在HPV阳性的阴道癌和阴道癌前病变中占60%。 Vulvar and vaginal cancer are uncommon globally. Unlike cervical and anal cancer, not all cancers of the external genitalia are associated with HPV infection. The attributable fraction due to HPV infection has been estimated to be 29 to 43 percent for vulvar cancer, 87 percent for vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia (VIN), and 70 percent for vaginal cancer. HPV types 16 and 18 cause approximately 35 to 77 percent of HPV-positive vulvar cancer, 75 to 80 percent of HPV-positive precancerous vulvar lesions, and 60 percent of HPV-positive vaginal cancer and precancerous vaginal lesions. 不同于HPV阴性的外生殖器癌症,HPV阳性的外阴癌有以下特点:往往发生在更年轻的患者中;在病理学上呈现出基底细胞样变而非角化型;较少出现p53突变;与性行为风险相关。 In contrast to HPV-negative cancers of the external genitalia, HPV-associated vulvar cancers occur at a younger age, exhibit basaloid instead of keratinizing pathology, do not have p53 mutations, and are associated with sexual risk factors. 3. 除此之外,HPV感染还会导致非生殖器疣、生殖器疣、肛门癌、口咽癌、青少年喉乳头状瘤病、阴茎癌及癌前病变、鲍温病(Bowen Disease)等疾病。各种疾病与其相关的HPV型别如下表。
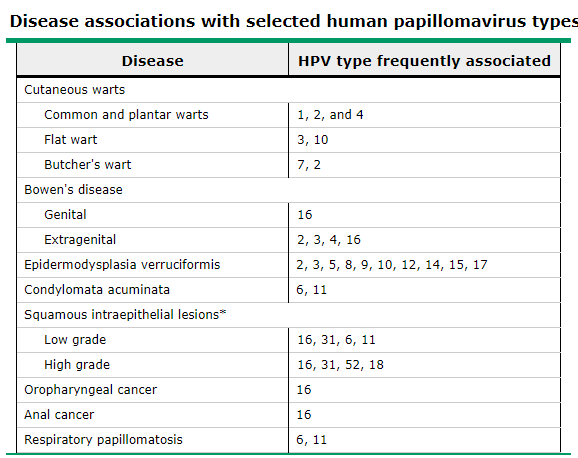
图3 不同疾病及其相关HPV的基因型。 肆 | 高危型HPV和疑似高危型 HPV 看了上面这么多内容,那到底什么是高危型HPV呢? 根据定义,40余种黏膜型HPV亚型与生殖道感染有关,这些HPV亚型按照致病力的大小不同分为高危型和低危型。 Of the mucosal subtypes, 40 subtypes are associated with infections of the genital tract. HPV infections of the genital tract have been subclassied into those associated with benign (low risk) and malignant (high risk) genital tract disease. 凡是和恶性生殖道疾病(例如:宫颈癌等)发病相关的HPV型别均为高危型HPV,一些证据尚不充分的被称作疑似高危型HPV,而与良性生殖道疾病(例如:生殖器疣等)发病相关的被称作低危型HPV。 根据2005年IARC(世界癌症研究机构)专题讨论会的结果规定,HPV16、18、31、33、35、39、45、51、52、56、58、59、68、73和82这15种型别为高危型,HPV26、53和66为疑似高危型。 不同HPV检测方法的检测内容有所差别。HC-2(第二代杂交捕获法)检测13种高危型HPV,包括HPV16、18、31、33、35、39、45、51、52、56、58、59和68,最后的报告结果是所有型别HPV的总和,因而阴性预测值较高。Rt-qPCR(实时荧光定量PCR)的检测内容与HC-2相同,但是检测结果是分型的,能具体到每个型别的病毒拷贝数,因而阳性预测值较高。透景流式液态芯片的检测内容包括所有15种高危型HPV、3种疑似高危型HPV、7种低危型HPV和HPV55(在检测内容中归为高危型)。除此之外,还有很多种HPV基因的检测方法,因此具体到不同医院的检查结果也略有不同。 参考文献 1. Joel M Palefsky, Ross D Cranston. Virology of human papillomavirus infections and the link to cancer. UpToDate. 2. Joel M Palefsky. Human papillomavirus infections: Epidemiology and disease associations. UpToDate. 3. Egawa N, Egawa K, Griffin H, et al. Human Papillomaviruses; Epithelial Tropisms, and the Development of Neoplasia. Viruses. 2015;7(7):3863-90. 4. IARC Working Group on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans VOLUME 90: Human Papillomaviruses. 2007: 47-78. 5. Goodman A. HPV testing as a screen for cervical cancer. BMJ, 2015, 350(jun30 1):h2372. 6. 人乳头瘤病毒(HPV)分型检测及临床意义, 丁香园. 撰稿 | 江路 编辑 | 魏绮珮 校对 | 刘应南 王银浩 审核 | 陶霞 江路
|
【本文地址】