| 使用ansible统一管理修改Linux和Windows管理员密码 | 您所在的位置:网站首页 › ansible批量修改密码 › 使用ansible统一管理修改Linux和Windows管理员密码 |
使用ansible统一管理修改Linux和Windows管理员密码
|
一、ansible安装:
1、选择一台centos 7 2、通过yum安装ansible #安装epel源 yum install epel-release -y #安装ansible yum install -y ansible #安装ansible.windows 模块 ansible-galaxy collection install ansible.windows #安装pip wget https://bootstrap.pypa.io/pip/2.7/get-pip.py python get-pip.py #使用pip安装所需插件 pip install pywinrm 二、Server端配置 #配置远程主机: vim /etc/ansible/hosts [linux] 192.168.83.128 192.168.83.133 [win] 192.168.83.132 ansible_ssh_user=administrator ansible_ssh_pass=2008.Com ansibe_port=5985 ansible_connection="winrm" ansible_winrm_server_cert_validation=ignore ansible_winrm_transport=ntlm 192.168.83.134 ansible_ssh_user=administrator ansible_ssh_pass=2008.Com ansibe_port=5985 ansible_connection="winrm" ansible_winrm_server_cert_validation=ignore ansible_winrm_transport=ntlm #配置Linux免密登录 ssh-keygen -t rsa ssh-copy-id -i ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub [email protected] ssh-copy-id -i ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub [email protected]测试:
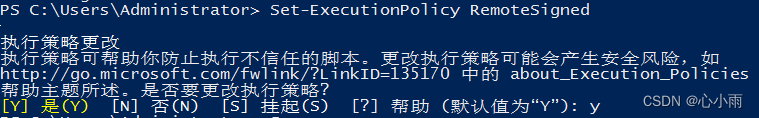
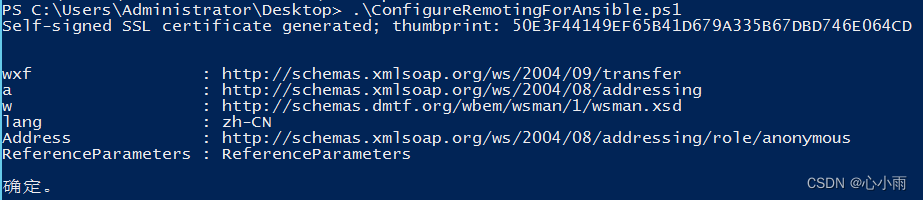
要求:不满足该配置请进行升级 PowerShell 3.0+ .NET 4.0+ Microsoft .NET Framework 4.5下载地址:https://download.microsoft.com/download/B/A/4/BA4A7E71-2906-4B2D-A0E1-80CF16844F5F/dotNetFx45_Full_setup.exe 更新PowerShell 2.0到3.0的脚本:https://github.com/ansible/ansible/blob/devel/examples/scripts/upgrade_to_ps3.ps1 # Powershell script to upgrade a PowerShell 2.0 system to PowerShell 3.0 # based on http://occasionalutility.blogspot.com/2013/11/everyday-powershell-part-7-powershell.html # # some Ansible modules that may use Powershell 3 features, so systems may need # to be upgraded. This may be used by a sample playbook. Refer to the windows # documentation on docs.ansible.com for details. # # - hosts: windows # tasks: # - script: upgrade_to_ps3.ps1 # Get version of OS # 6.0 is 2008 # 6.1 is 2008 R2 # 6.2 is 2012 # 6.3 is 2012 R2 if ($PSVersionTable.psversion.Major -ge 3) { Write-Output "Powershell 3 Installed already; You don't need this" Exit } $powershellpath = "C:\powershell" function download-file { param ([string]$path, [string]$local) $client = new-object system.net.WebClient $client.Headers.Add("user-agent", "PowerShell") $client.downloadfile($path, $local) } if (!(test-path $powershellpath)) { New-Item -ItemType directory -Path $powershellpath } # .NET Framework 4.0 is necessary. #if (($PSVersionTable.CLRVersion.Major) -lt 2) #{ # $DownloadUrl = "http://download.microsoft.com/download/B/A/4/BA4A7E71-2906-4B2D-A0E1-80CF16844F5F/dotNetFx45_Full_x86_x64.exe" # $FileName = $DownLoadUrl.Split('/')[-1] # download-file $downloadurl "$powershellpath\$filename" # ."$powershellpath\$filename" /quiet /norestart #} #You may need to reboot after the .NET install if so just run the script again. # If the Operating System is above 6.2, then you already have PowerShell Version > 3 if ([Environment]::OSVersion.Version.Major -gt 6) { Write-Output "OS is new; upgrade not needed." Exit } $osminor = [environment]::OSVersion.Version.Minor $architecture = $ENV:PROCESSOR_ARCHITECTURE if ($architecture -eq "AMD64") { $architecture = "x64" } else { $architecture = "x86" } if ($osminor -eq 1) { $DownloadUrl = "http://download.microsoft.com/download/E/7/6/E76850B8-DA6E-4FF5-8CCE-A24FC513FD16/Windows6.1-KB2506143-" + $architecture + ".msu" } elseif ($osminor -eq 0) { $DownloadUrl = "http://download.microsoft.com/download/E/7/6/E76850B8-DA6E-4FF5-8CCE-A24FC513FD16/Windows6.0-KB2506146-" + $architecture + ".msu" } else { # Nothing to do; In theory this point will never be reached. Exit } $FileName = $DownLoadUrl.Split('/')[-1] download-file $downloadurl "$powershellpath\$filename" Start-Process -FilePath "$powershellpath\$filename" -ArgumentList /quiet配置ansible远程的脚本:https://github.com/ansible/ansible/blob/devel/examples/scripts/ConfigureRemotingForAnsible.ps1 #Requires -Version 3.0 # Configure a Windows host for remote management with Ansible # ----------------------------------------------------------- # # This script checks the current WinRM (PS Remoting) configuration and makes # the necessary changes to allow Ansible to connect, authenticate and # execute PowerShell commands. # # IMPORTANT: This script uses self-signed certificates and authentication mechanisms # that are intended for development environments and evaluation purposes only. # Production environments and deployments that are exposed on the network should # use CA-signed certificates and secure authentication mechanisms such as Kerberos. # # To run this script in Powershell: # # [Net.ServicePointManager]::SecurityProtocol = [Net.SecurityProtocolType]::Tls12 # $url = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ansible/ansible/devel/examples/scripts/ConfigureRemotingForAnsible.ps1" # $file = "$env:temp\ConfigureRemotingForAnsible.ps1" # # (New-Object -TypeName System.Net.WebClient).DownloadFile($url, $file) # # powershell.exe -ExecutionPolicy ByPass -File $file # # All events are logged to the Windows EventLog, useful for unattended runs. # # Use option -Verbose in order to see the verbose output messages. # # Use option -CertValidityDays to specify how long this certificate is valid # starting from today. So you would specify -CertValidityDays 3650 to get # a 10-year valid certificate. # # Use option -ForceNewSSLCert if the system has been SysPreped and a new # SSL Certificate must be forced on the WinRM Listener when re-running this # script. This is necessary when a new SID and CN name is created. # # Use option -EnableCredSSP to enable CredSSP as an authentication option. # # Use option -DisableBasicAuth to disable basic authentication. # # Use option -SkipNetworkProfileCheck to skip the network profile check. # Without specifying this the script will only run if the device's interfaces # are in DOMAIN or PRIVATE zones. Provide this switch if you want to enable # WinRM on a device with an interface in PUBLIC zone. # # Use option -SubjectName to specify the CN name of the certificate. This # defaults to the system's hostname and generally should not be specified. # Written by Trond Hindenes # Updated by Chris Church # Updated by Michael Crilly # Updated by Anton Ouzounov # Updated by Nicolas Simond # Updated by Dag Wieërs # Updated by Jordan Borean # Updated by Erwan Quélin # Updated by David Norman # # Version 1.0 - 2014-07-06 # Version 1.1 - 2014-11-11 # Version 1.2 - 2015-05-15 # Version 1.3 - 2016-04-04 # Version 1.4 - 2017-01-05 # Version 1.5 - 2017-02-09 # Version 1.6 - 2017-04-18 # Version 1.7 - 2017-11-23 # Version 1.8 - 2018-02-23 # Version 1.9 - 2018-09-21 # Support -Verbose option [CmdletBinding()] Param ( [string]$SubjectName = $env:COMPUTERNAME, [int]$CertValidityDays = 1095, [switch]$SkipNetworkProfileCheck, $CreateSelfSignedCert = $true, [switch]$ForceNewSSLCert, [switch]$GlobalHttpFirewallAccess, [switch]$DisableBasicAuth = $false, [switch]$EnableCredSSP ) Function Write-ProgressLog { $Message = $args[0] Write-EventLog -LogName Application -Source $EventSource -EntryType Information -EventId 1 -Message $Message } Function Write-VerboseLog { $Message = $args[0] Write-Verbose $Message Write-ProgressLog $Message } Function Write-HostLog { $Message = $args[0] Write-Output $Message Write-ProgressLog $Message } Function New-LegacySelfSignedCert { Param ( [string]$SubjectName, [int]$ValidDays = 1095 ) $hostnonFQDN = $env:computerName $hostFQDN = [System.Net.Dns]::GetHostByName(($env:computerName)).Hostname $SignatureAlgorithm = "SHA256" $name = New-Object -COM "X509Enrollment.CX500DistinguishedName.1" $name.Encode("CN=$SubjectName", 0) $key = New-Object -COM "X509Enrollment.CX509PrivateKey.1" $key.ProviderName = "Microsoft Enhanced RSA and AES Cryptographic Provider" $key.KeySpec = 1 $key.Length = 4096 $key.SecurityDescriptor = "D:PAI(A;;0xd01f01ff;;;SY)(A;;0xd01f01ff;;;BA)(A;;0x80120089;;;NS)" $key.MachineContext = 1 $key.Create() $serverauthoid = New-Object -COM "X509Enrollment.CObjectId.1" $serverauthoid.InitializeFromValue("1.3.6.1.5.5.7.3.1") $ekuoids = New-Object -COM "X509Enrollment.CObjectIds.1" $ekuoids.Add($serverauthoid) $ekuext = New-Object -COM "X509Enrollment.CX509ExtensionEnhancedKeyUsage.1" $ekuext.InitializeEncode($ekuoids) $cert = New-Object -COM "X509Enrollment.CX509CertificateRequestCertificate.1" $cert.InitializeFromPrivateKey(2, $key, "") $cert.Subject = $name $cert.Issuer = $cert.Subject $cert.NotBefore = (Get-Date).AddDays(-1) $cert.NotAfter = $cert.NotBefore.AddDays($ValidDays) $SigOID = New-Object -ComObject X509Enrollment.CObjectId $SigOID.InitializeFromValue(([Security.Cryptography.Oid]$SignatureAlgorithm).Value) [string[]] $AlternativeName += $hostnonFQDN $AlternativeName += $hostFQDN $IAlternativeNames = New-Object -ComObject X509Enrollment.CAlternativeNames foreach ($AN in $AlternativeName) { $AltName = New-Object -ComObject X509Enrollment.CAlternativeName $AltName.InitializeFromString(0x3, $AN) $IAlternativeNames.Add($AltName) } $SubjectAlternativeName = New-Object -ComObject X509Enrollment.CX509ExtensionAlternativeNames $SubjectAlternativeName.InitializeEncode($IAlternativeNames) [String[]]$KeyUsage = ("DigitalSignature", "KeyEncipherment") $KeyUsageObj = New-Object -ComObject X509Enrollment.CX509ExtensionKeyUsage $KeyUsageObj.InitializeEncode([int][Security.Cryptography.X509Certificates.X509KeyUsageFlags]($KeyUsage)) $KeyUsageObj.Critical = $true $cert.X509Extensions.Add($KeyUsageObj) $cert.X509Extensions.Add($ekuext) $cert.SignatureInformation.HashAlgorithm = $SigOID $CERT.X509Extensions.Add($SubjectAlternativeName) $cert.Encode() $enrollment = New-Object -COM "X509Enrollment.CX509Enrollment.1" $enrollment.InitializeFromRequest($cert) $certdata = $enrollment.CreateRequest(0) $enrollment.InstallResponse(2, $certdata, 0, "") # extract/return the thumbprint from the generated cert $parsed_cert = New-Object System.Security.Cryptography.X509Certificates.X509Certificate2 $parsed_cert.Import([System.Text.Encoding]::UTF8.GetBytes($certdata)) return $parsed_cert.Thumbprint } Function Enable-GlobalHttpFirewallAccess { Write-Verbose "Forcing global HTTP firewall access" # this is a fairly naive implementation; could be more sophisticated about rule matching/collapsing $fw = New-Object -ComObject HNetCfg.FWPolicy2 # try to find/enable the default rule first $add_rule = $false $matching_rules = $fw.Rules | Where-Object { $_.Name -eq "Windows Remote Management (HTTP-In)" } $rule = $null If ($matching_rules) { If ($matching_rules -isnot [Array]) { Write-Verbose "Editing existing single HTTP firewall rule" $rule = $matching_rules } Else { # try to find one with the All or Public profile first Write-Verbose "Found multiple existing HTTP firewall rules..." $rule = $matching_rules | ForEach-Object { $_.Profiles -band 4 }[0] If (-not $rule -or $rule -is [Array]) { Write-Verbose "Editing an arbitrary single HTTP firewall rule (multiple existed)" # oh well, just pick the first one $rule = $matching_rules[0] } } } If (-not $rule) { Write-Verbose "Creating a new HTTP firewall rule" $rule = New-Object -ComObject HNetCfg.FWRule $rule.Name = "Windows Remote Management (HTTP-In)" $rule.Description = "Inbound rule for Windows Remote Management via WS-Management. [TCP 5985]" $add_rule = $true } $rule.Profiles = 0x7FFFFFFF $rule.Protocol = 6 $rule.LocalPorts = 5985 $rule.RemotePorts = "*" $rule.LocalAddresses = "*" $rule.RemoteAddresses = "*" $rule.Enabled = $true $rule.Direction = 1 $rule.Action = 1 $rule.Grouping = "Windows Remote Management" If ($add_rule) { $fw.Rules.Add($rule) } Write-Verbose "HTTP firewall rule $($rule.Name) updated" } # Setup error handling. Trap { $_ Exit 1 } $ErrorActionPreference = "Stop" # Get the ID and security principal of the current user account $myWindowsID = [System.Security.Principal.WindowsIdentity]::GetCurrent() $myWindowsPrincipal = new-object System.Security.Principal.WindowsPrincipal($myWindowsID) # Get the security principal for the Administrator role $adminRole = [System.Security.Principal.WindowsBuiltInRole]::Administrator # Check to see if we are currently running "as Administrator" if (-Not $myWindowsPrincipal.IsInRole($adminRole)) { Write-Output "ERROR: You need elevated Administrator privileges in order to run this script." Write-Output " Start Windows PowerShell by using the Run as Administrator option." Exit 2 } $EventSource = $MyInvocation.MyCommand.Name If (-Not $EventSource) { $EventSource = "Powershell CLI" } If ([System.Diagnostics.EventLog]::Exists('Application') -eq $False -or [System.Diagnostics.EventLog]::SourceExists($EventSource) -eq $False) { New-EventLog -LogName Application -Source $EventSource } # Detect PowerShell version. If ($PSVersionTable.PSVersion.Major -lt 3) { Write-ProgressLog "PowerShell version 3 or higher is required." Throw "PowerShell version 3 or higher is required." } # Find and start the WinRM service. Write-Verbose "Verifying WinRM service." If (!(Get-Service "WinRM")) { Write-ProgressLog "Unable to find the WinRM service." Throw "Unable to find the WinRM service." } ElseIf ((Get-Service "WinRM").Status -ne "Running") { Write-Verbose "Setting WinRM service to start automatically on boot." Set-Service -Name "WinRM" -StartupType Automatic Write-ProgressLog "Set WinRM service to start automatically on boot." Write-Verbose "Starting WinRM service." Start-Service -Name "WinRM" -ErrorAction Stop Write-ProgressLog "Started WinRM service." } # WinRM should be running; check that we have a PS session config. If (!(Get-PSSessionConfiguration -Verbose:$false) -or (!(Get-ChildItem WSMan:\localhost\Listener))) { If ($SkipNetworkProfileCheck) { Write-Verbose "Enabling PS Remoting without checking Network profile." Enable-PSRemoting -SkipNetworkProfileCheck -Force -ErrorAction Stop Write-ProgressLog "Enabled PS Remoting without checking Network profile." } Else { Write-Verbose "Enabling PS Remoting." Enable-PSRemoting -Force -ErrorAction Stop Write-ProgressLog "Enabled PS Remoting." } } Else { Write-Verbose "PS Remoting is already enabled." } # Ensure LocalAccountTokenFilterPolicy is set to 1 # https://github.com/ansible/ansible/issues/42978 $token_path = "HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\System" $token_prop_name = "LocalAccountTokenFilterPolicy" $token_key = Get-Item -Path $token_path $token_value = $token_key.GetValue($token_prop_name, $null) if ($token_value -ne 1) { Write-Verbose "Setting LocalAccountTOkenFilterPolicy to 1" if ($null -ne $token_value) { Remove-ItemProperty -Path $token_path -Name $token_prop_name } New-ItemProperty -Path $token_path -Name $token_prop_name -Value 1 -PropertyType DWORD > $null } # Make sure there is a SSL listener. $listeners = Get-ChildItem WSMan:\localhost\Listener If (!($listeners | Where-Object { $_.Keys -like "TRANSPORT=HTTPS" })) { # We cannot use New-SelfSignedCertificate on 2012R2 and earlier $thumbprint = New-LegacySelfSignedCert -SubjectName $SubjectName -ValidDays $CertValidityDays Write-HostLog "Self-signed SSL certificate generated; thumbprint: $thumbprint" # Create the hashtables of settings to be used. $valueset = @{ Hostname = $SubjectName CertificateThumbprint = $thumbprint } $selectorset = @{ Transport = "HTTPS" Address = "*" } Write-Verbose "Enabling SSL listener." New-WSManInstance -ResourceURI 'winrm/config/Listener' -SelectorSet $selectorset -ValueSet $valueset Write-ProgressLog "Enabled SSL listener." } Else { Write-Verbose "SSL listener is already active." # Force a new SSL cert on Listener if the $ForceNewSSLCert If ($ForceNewSSLCert) { # We cannot use New-SelfSignedCertificate on 2012R2 and earlier $thumbprint = New-LegacySelfSignedCert -SubjectName $SubjectName -ValidDays $CertValidityDays Write-HostLog "Self-signed SSL certificate generated; thumbprint: $thumbprint" $valueset = @{ CertificateThumbprint = $thumbprint Hostname = $SubjectName } # Delete the listener for SSL $selectorset = @{ Address = "*" Transport = "HTTPS" } Remove-WSManInstance -ResourceURI 'winrm/config/Listener' -SelectorSet $selectorset # Add new Listener with new SSL cert New-WSManInstance -ResourceURI 'winrm/config/Listener' -SelectorSet $selectorset -ValueSet $valueset } } # Check for basic authentication. $basicAuthSetting = Get-ChildItem WSMan:\localhost\Service\Auth | Where-Object { $_.Name -eq "Basic" } If ($DisableBasicAuth) { If (($basicAuthSetting.Value) -eq $true) { Write-Verbose "Disabling basic auth support." Set-Item -Path "WSMan:\localhost\Service\Auth\Basic" -Value $false Write-ProgressLog "Disabled basic auth support." } Else { Write-Verbose "Basic auth is already disabled." } } Else { If (($basicAuthSetting.Value) -eq $false) { Write-Verbose "Enabling basic auth support." Set-Item -Path "WSMan:\localhost\Service\Auth\Basic" -Value $true Write-ProgressLog "Enabled basic auth support." } Else { Write-Verbose "Basic auth is already enabled." } } # If EnableCredSSP if set to true If ($EnableCredSSP) { # Check for CredSSP authentication $credsspAuthSetting = Get-ChildItem WSMan:\localhost\Service\Auth | Where-Object { $_.Name -eq "CredSSP" } If (($credsspAuthSetting.Value) -eq $false) { Write-Verbose "Enabling CredSSP auth support." Enable-WSManCredSSP -role server -Force Write-ProgressLog "Enabled CredSSP auth support." } } If ($GlobalHttpFirewallAccess) { Enable-GlobalHttpFirewallAccess } # Configure firewall to allow WinRM HTTPS connections. $fwtest1 = netsh advfirewall firewall show rule name="Allow WinRM HTTPS" $fwtest2 = netsh advfirewall firewall show rule name="Allow WinRM HTTPS" profile=any If ($fwtest1.count -lt 5) { Write-Verbose "Adding firewall rule to allow WinRM HTTPS." netsh advfirewall firewall add rule profile=any name="Allow WinRM HTTPS" dir=in localport=5986 protocol=TCP action=allow Write-ProgressLog "Added firewall rule to allow WinRM HTTPS." } ElseIf (($fwtest1.count -ge 5) -and ($fwtest2.count -lt 5)) { Write-Verbose "Updating firewall rule to allow WinRM HTTPS for any profile." netsh advfirewall firewall set rule name="Allow WinRM HTTPS" new profile=any Write-ProgressLog "Updated firewall rule to allow WinRM HTTPS for any profile." } Else { Write-Verbose "Firewall rule already exists to allow WinRM HTTPS." } # Test a remoting connection to localhost, which should work. $httpResult = Invoke-Command -ComputerName "localhost" -ScriptBlock { $using:env:COMPUTERNAME } -ErrorVariable httpError -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue $httpsOptions = New-PSSessionOption -SkipCACheck -SkipCNCheck -SkipRevocationCheck $httpsResult = New-PSSession -UseSSL -ComputerName "localhost" -SessionOption $httpsOptions -ErrorVariable httpsError -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue If ($httpResult -and $httpsResult) { Write-Verbose "HTTP: Enabled | HTTPS: Enabled" } ElseIf ($httpsResult -and !$httpResult) { Write-Verbose "HTTP: Disabled | HTTPS: Enabled" } ElseIf ($httpResult -and !$httpsResult) { Write-Verbose "HTTP: Enabled | HTTPS: Disabled" } Else { Write-ProgressLog "Unable to establish an HTTP or HTTPS remoting session." Throw "Unable to establish an HTTP or HTTPS remoting session." } Write-VerboseLog "PS Remoting has been successfully configured for Ansible."配置Windows客户端 #查看powershell执行策略: get-executionpolicy #设置powershell执行策略为 remotesigned set-executionpolicy remotesigned #查看powershell版本号,如果低于3.0请执行upgrade_to_ps3.ps1 get-host #配置远程控制(与winrm二选一即可) .\ConfigureRemotingForAnsible.ps1 #启动winrm(与ConfigureRemotingForAnsible.ps1脚本二选一即可) winrm quickconfig #修改winrm配置,启用远程连接认证 winrm set winrm/config/service '@{AllowUnencrypted="true"}' winrm set winrm/config/service/auth '@{Basic="true"}' #查看winrm service启动监听状态 winrm enumerate winrm/config/listener #查看winrm配置信息 winrm get winrm/config防火墙配置5985、5986端口开放或者关闭防火墙
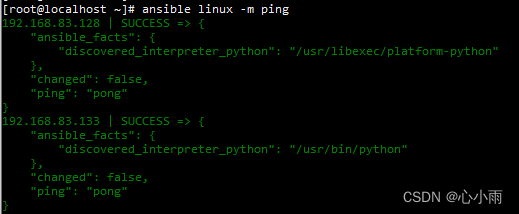
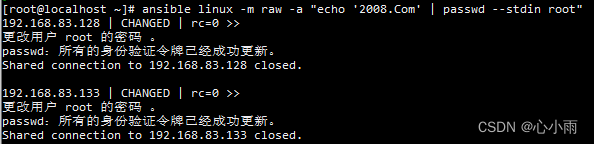
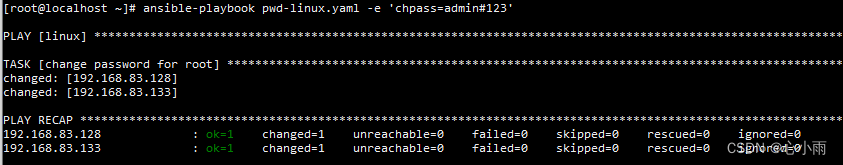
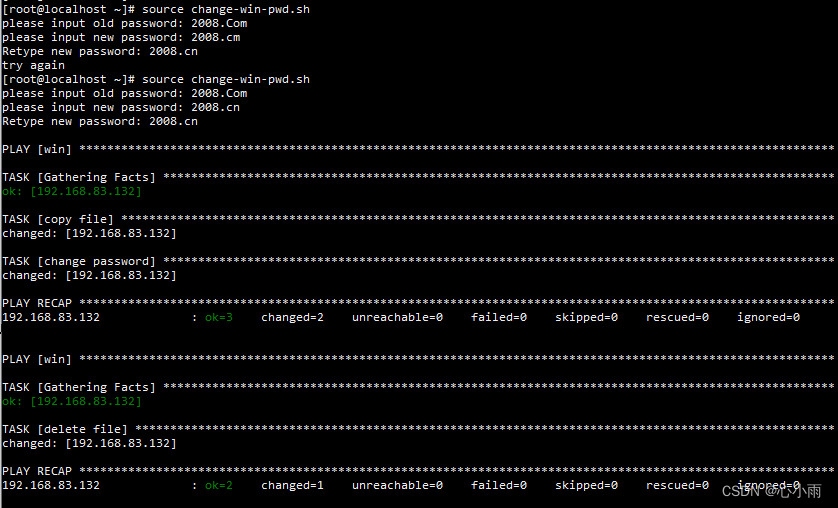
执行效果: |
【本文地址】
公司简介
联系我们