|
Java se 编程题练习题总结(详解过程,代码)
1.Demo17

import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo17 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//数据:体重weight 身高height 身体质量指数BMI = weight / height^2
//1.提示用户输入体重和身高
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter weight:");
double weight = input.nextDouble();
System.out.println("Enter height:");
double height = input.nextDouble();
//2.计算BMI
double BMI = weight * 0.45359237 / Math.pow( height * 0.0254, 2);
//3.判断BMI条件,输出结果
if (BMI < 18.5){
System.out.println("偏瘦");
} else if (BMI < 25.0) {
System.out.println("正常");
} else if (BMI < 30.0) {
System.out.println("超重");
} else {
System.out.println("过胖");
}
}
}
解析:分析题,列出所需要的数据,已经所要求的结果,按照提供的公式和判断条件完成此题。
2.Demo19

import java.util.*;
public class Demo19 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
数据:随机一个两位数彩票(电脑)
用户输入一个两位数彩票(用户)
电脑顺序 = 用户顺序 10000
电脑数字 = 用户数字 3000
电脑一个数字 = 用户的一个数字 1000
*/
//1.提示用户输入一个两位数
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter a number:");
int usr = input.nextInt();
//2.随机产生
Random random = new Random();
int com = random.nextInt(100);
//3.用户和电脑的个位和十位
int usr1 = usr % 10;
int usr2 = usr / 10;
int com1 = com % 10;
int com2 = com / 10;
//4.判断条件
if (usr1 == com1 && usr2 == com2){
System.out.println("奖金为10000美元");
} else if (usr1 == com2 && usr2 == com1) {
System.out.println("奖金为3000美元");
} else if (usr1 == com1 || usr1 == com2 || usr2 == com1 || usr2 == com2) {
System.out.println("奖金为1000美元");
} else {
System.out.println("没有中奖");
}
}
}
解析:分析题,列出所需要的数据,已经所要求的结果,按照提供的公式和判断条件完成此题。
3.Demo21

import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo21 {
public static void main(String[] args){
/*
数据:a,b,c,d,e,f
ax + by = e
cx + dy = f
x = (ed - bf)/(ad - bc)
y = (af - ec)/(ad - bc)
delt = ad - bc
*/
//1.提示用户输入a,b,c,d,e,f
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter a,b,c,d,e,f:");
double a = input.nextDouble();
double b = input.nextDouble();
double c = input.nextDouble();
double d = input.nextDouble();
double e = input.nextDouble();
double f = input.nextDouble();
//2.计算x,y,delt
double x = (e * d - b * f) / (a * d - b * c);
double y = (a * f - e * c) / (a * d - b * c);
double delt = a * b - b * c;
//3.判断条件,输出结果
if (delt != 0){
System.out.println("x is" + x + "and y is" + y);
} else {
System.out.println("The equation has no solution");
}
}
}
4.Demo22
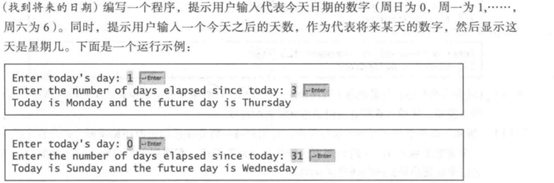
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo22 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.提示用户代表数字日期
String[] arr = {"Sunday", "Monday", "Tuesday", "Wednessday", "Thursday", "Friday","Saturday" };
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
//2.提示用户输入当天天数,将来天数
System.out.print("Enter today's day:");
int today = input.nextInt();
System.out.print("Enter future's day:");
int future = input.nextInt();
//3.输出结果
System.out.println("Today is " + arr[today] + " and the future day is " + arr[future]);
}
}
5.Demo25

import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo25 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.提示用户输入的年月日
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter year:");
int year = input.nextInt();
System.out.print("Enter month:");
int m = input.nextInt();
System.out.print("Enter the day of the month:");
int q =input.nextInt();
//2.判断条件,分别计算m,j,k,h
if (m == 1 || m == 2) {
m = m + 12;
year = year - 1;
}
int j = year / 100;
int k = year % 100;
int h = (q + 26 * (m + 1) / 10 + k + k / 4 + j / 4 + 5 * j) % 7;
//3.输出结果
String[] arr = {"Saturday","Sunday","Monday","Tuesday","Wednesday","Thursday","Friday"};
System.out.println(arr[h]);
}
}
6.Demo27
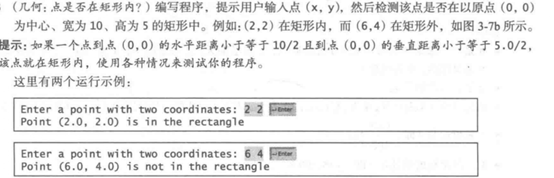
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo27 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.输入一个点
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter a point with two coordinates:");
double x = input.nextDouble();
double y = input.nextDouble();
//2.判断条件,输出结果
if (x = -10 / 2 && y = -5.0 / 2){
System.out.println("In the rectangle");
} else {
System.out.println("Not in the rectangle");
}
}
}
思路过程:
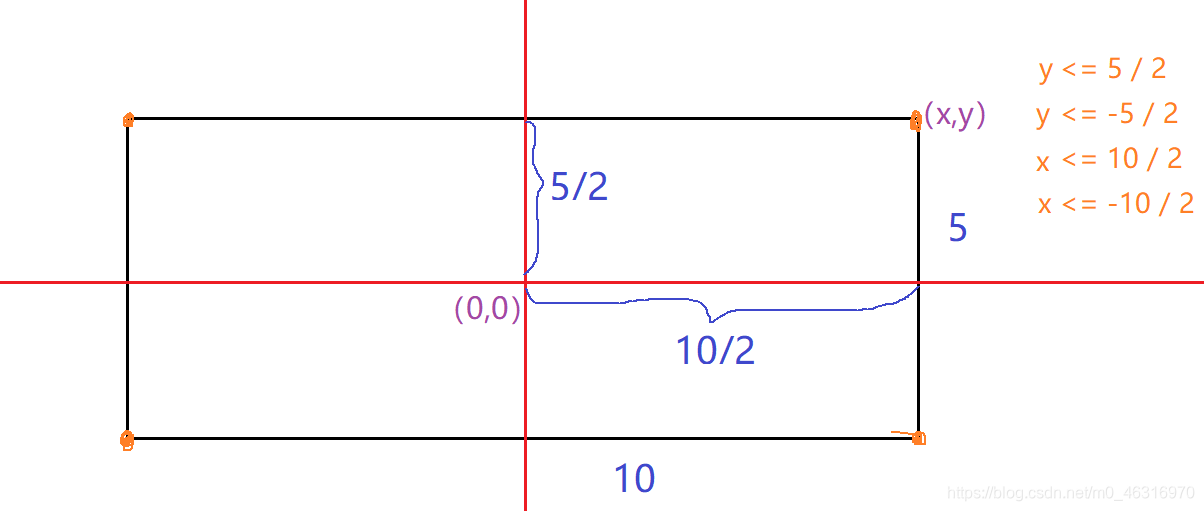
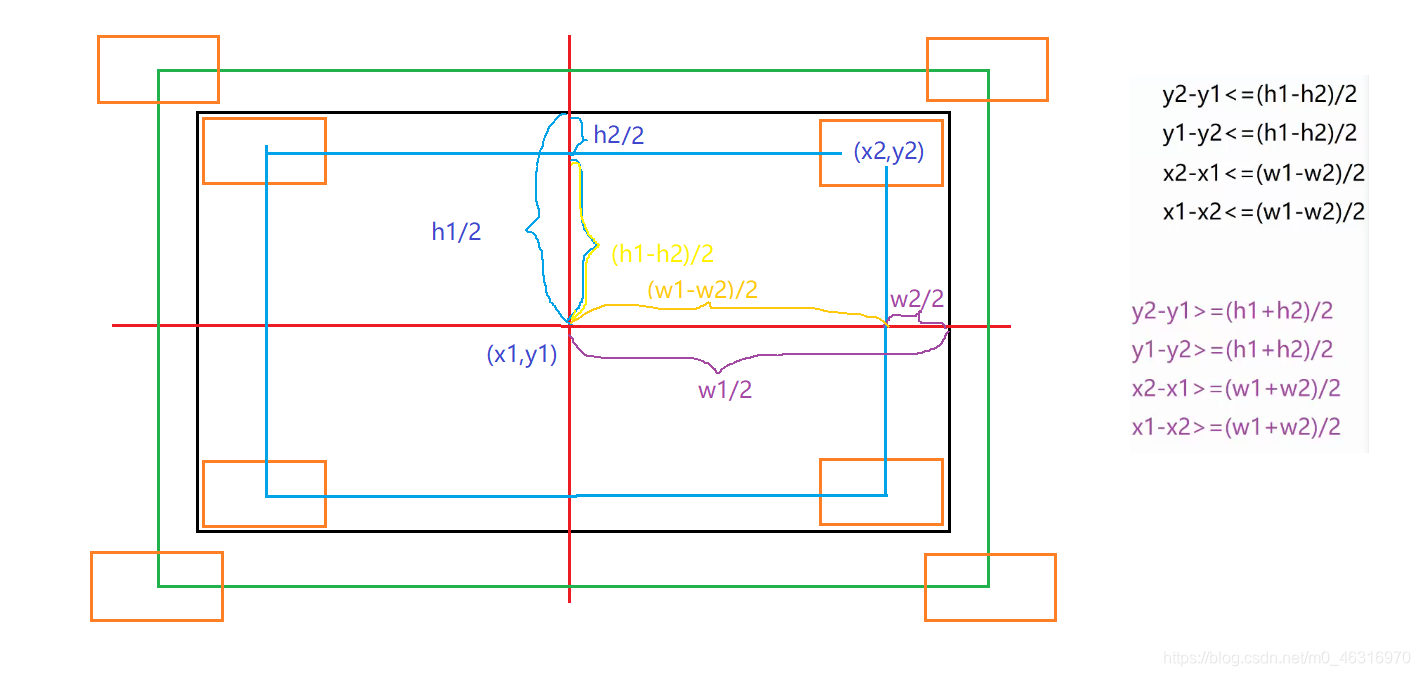
7.Demo29
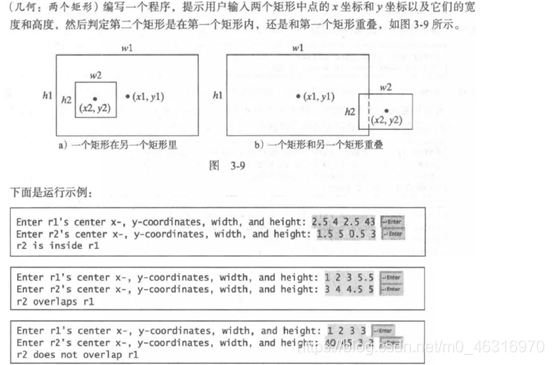
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo29 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.输入两个矩阵的高,宽
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter r1:");
double x1 = input.nextDouble();
double y1 = input.nextDouble();
double w1 = input.nextDouble();
double h1 = input.nextDouble();
System.out.print("Enter r2:");
double x2 = input.nextDouble();
double y2 = input.nextDouble();
double w2 = input.nextDouble();
double h2 = input.nextDouble();
//2.判断条件,输出结果
if (y2 - y1 = (w1 + w2) / 2){
System.out.println("r2 is not in r1");
} else {
System.out.println("r2 overlaps r1");
}
}
}
思路过程:
8.Demo31

import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo31 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.提示用户输入一个整数值
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter a integer:");
int num = input.nextInt();
//2.判断条件
if ( num % 5 == 0 && num % 6 == 0){
System.out.println("Is" + num + "divisible by 5 and 6? true");
System.out.println("Is" + num + "divisible by 5 or 6? false");
System.out.println("Is" + num + "divisible by 5 or 6,but not both? false");
} else if (num % 5 == 0 || num % 6 == 0) {
System.out.println("Is" + num + "divisible by 5 and 6? false");
System.out.println("Is" + num + "divisible by 5 or 6? true");
System.out.println("Is" + num + "divisible by 5 or 6,but not both? false");
} else if(num % 5 == 0 ^ num % 6 == 0){
System.out.println("Is" + num + "divisible by 5 and 6? false");
System.out.println("Is" + num + "divisible by 5 or 6? false");
System.out.println("Is" + num + "divisible by 5 or 6,but not both? true");
}
}
}
9.Demo34
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo34 {
public static void main(String[] args){
/*
10324 / 16 = 645 ~ 4
645 / 16 = 40 ~ 5
40 / 16 = 2 ~ 8
2 / 16 = 0 ~ 2
hexStr
"" + 2 = 2
2 + "8" = 28
28 + "5" = 285
285 + "4" = 2854
*/
//1.提示用户输入一个十进制数
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter a bin number:");
int num = input.nextInt();
//2.判断
String hexStr = "";
while (num != 0) {
hexStr = num % 16 + hexStr;
num /= 16;
}
System.out.print("hex number:" + hexStr);
}
}
13.Demo40
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo40 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
120 2~60 2
60 2~30 2
30 2~15 2
15 2~7 3
5 2~2 5
*/
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter a number:");
int number = input.nextInt();
while (true) {
boolean flag = true;
for (int i = 2; i |











