|
大家好,我是微学AI,今天给大家带来机器学习实战4-学生成绩的可视化分析与成绩预测,机器学习在教育中的应用具有很大的潜力,特别是在学生成绩的可视化分析与成绩预测方面。
机器学习可以通过对学生的父母教育情况和学校表现等数据进行分析和挖掘,从而揭示潜在的学习模式和趋势。这种可视化分析可以帮助教师更好地了解学生的学习状况,并针对性地调整教学策略。机器学习还可以利用学生的历史数据、课程表、出勤记录等信息,建立模型来预测学生未来的成绩。这种预测可以帮助教师及时发现学生可能存在的问题并采取相应的措施加以干预,从而提高学生的学习效果和成绩。
一、导入库和数据
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import seaborn as sns
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.svm import SVR
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeRegressor
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestRegressor
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error, r2_score, mean_absolute_error
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei']
df_pre = pd.read_csv('exams.csv')
df_pre[['math score', 'reading score', 'writing score']].agg(['var', 'std'])
correlation_matrix = df_pre.corr()
数据样例:
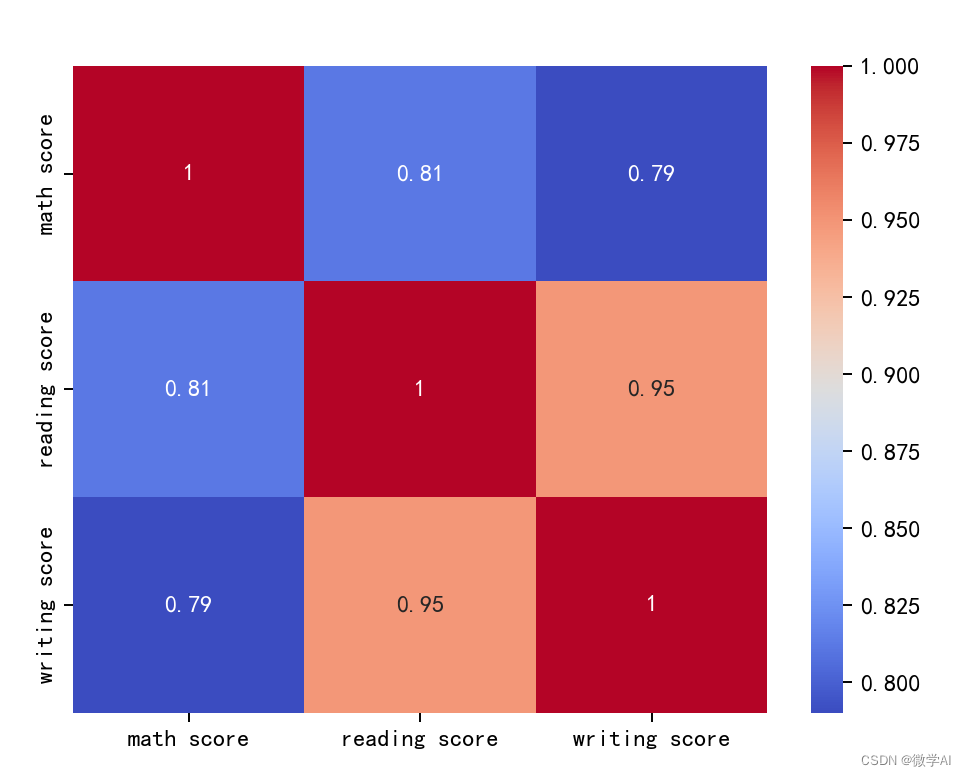
二、创建一个热图的相关矩阵
sns.heatmap(correlation_matrix, annot=True, cmap='coolwarm')
plt.show()
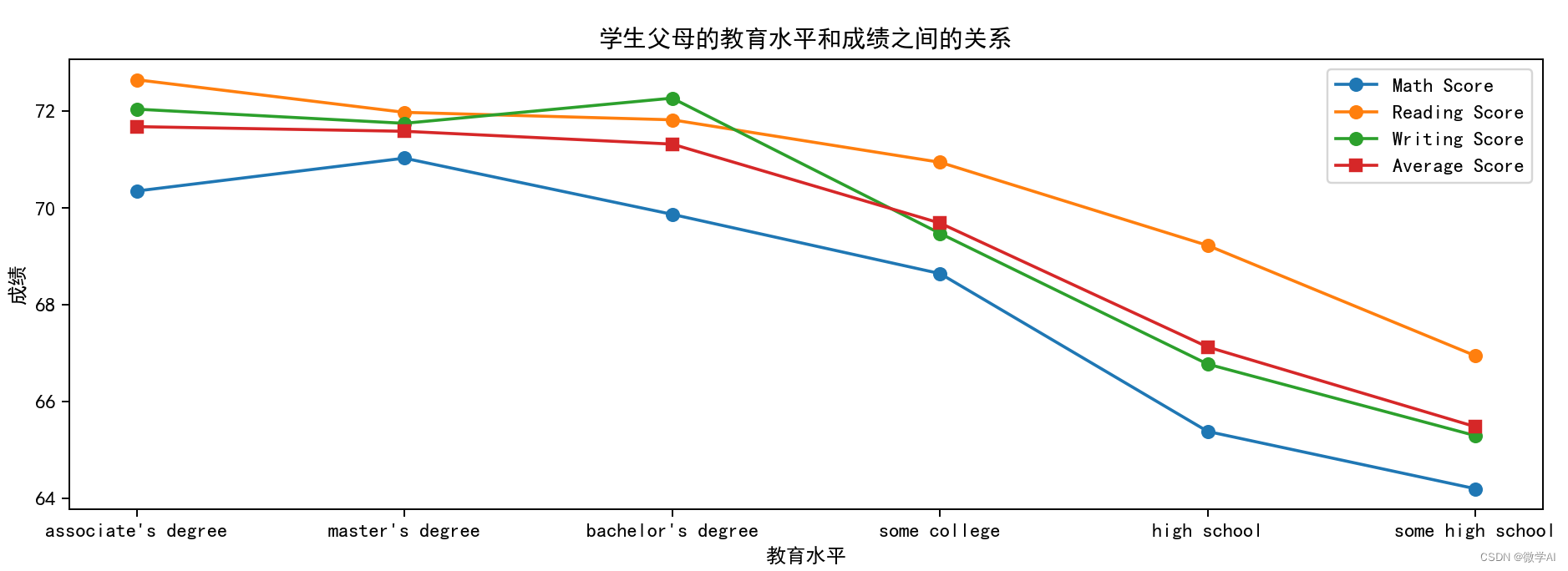
三、学生父母的教育水平和成绩之间的关系
education_score = df_pre.groupby('parental level of education')[['math score', 'reading score', 'writing score']].mean().reset_index()
education_score['average score'] = (education_score['math score']+education_score['reading score']+education_score['writing score'])/3
education_score = education_score.sort_values('average score', ascending=False)
plt.figure(figsize=(13,4))
plt.plot(education_score['parental level of education'], education_score['math score'], marker='o', label='Math Score')
plt.plot(education_score['parental level of education'], education_score['reading score'], marker='o', label='Reading Score')
plt.plot(education_score['parental level of education'], education_score['writing score'], marker='o', label='Writing Score')
plt.plot(education_score['parental level of education'], education_score['average score'], marker='s', label='Average Score')
plt.title('学生父母的教育水平和成绩之间的关系')
plt.xlabel('教育水平')
plt.ylabel('成绩')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
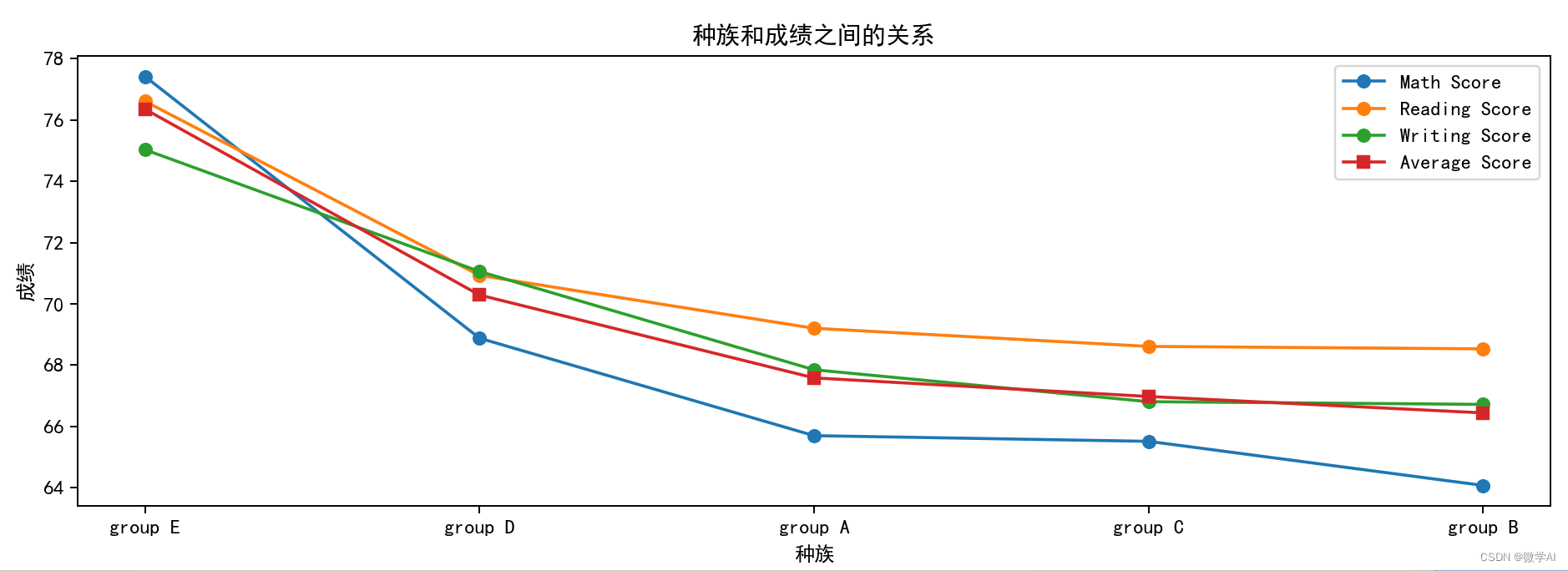
四、种族和成绩之间的关系
race_score = df_pre.groupby('race/ethnicity')[['math score', 'reading score', 'writing score']].mean().reset_index()
race_score['average score'] = (race_score['math score']+race_score['reading score']+race_score['writing score'])/3
race_score = race_score.sort_values('average score', ascending=False)
plt.figure(figsize=(13,4))
plt.plot(race_score['race/ethnicity'], race_score['math score'], marker='o', label='Math Score')
plt.plot(race_score['race/ethnicity'], race_score['reading score'], marker='o', label='Reading Score')
plt.plot(race_score['race/ethnicity'], race_score['writing score'], marker='o', label='Writing Score')
plt.plot(race_score['race/ethnicity'], race_score['average score'], marker='s', label='Average Score')
plt.title('种族和成绩之间的关系')
plt.xlabel('种族')
plt.ylabel('成绩')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
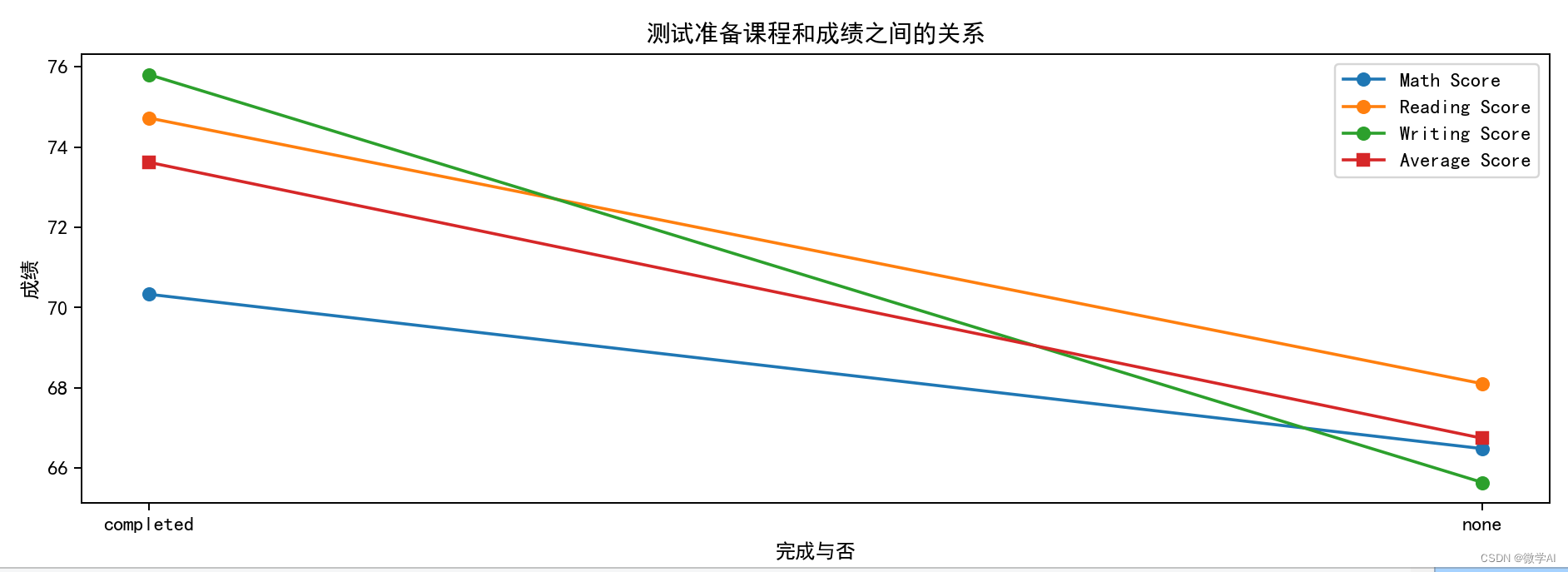
五、测试准备课程和成绩之间的关系
prep_score = df_pre.groupby('test preparation course')[['math score', 'reading score', 'writing score']].mean().reset_index()
prep_score['average score'] = (prep_score['math score']+prep_score['reading score']+prep_score['writing score'])/3
prep_score = prep_score.sort_values('average score', ascending=False)
plt.figure(figsize=(13,4))
plt.plot(prep_score['test preparation course'], prep_score['math score'], marker='o', label='Math Score')
plt.plot(prep_score['test preparation course'], prep_score['reading score'], marker='o', label='Reading Score')
plt.plot(prep_score['test preparation course'], prep_score['writing score'], marker='o', label='Writing Score')
plt.plot(prep_score['test preparation course'], prep_score['average score'], marker='s', label='Average Score')
plt.title('测试准备课程和成绩之间的关系')
plt.xlabel('完成与否')
plt.ylabel('成绩')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
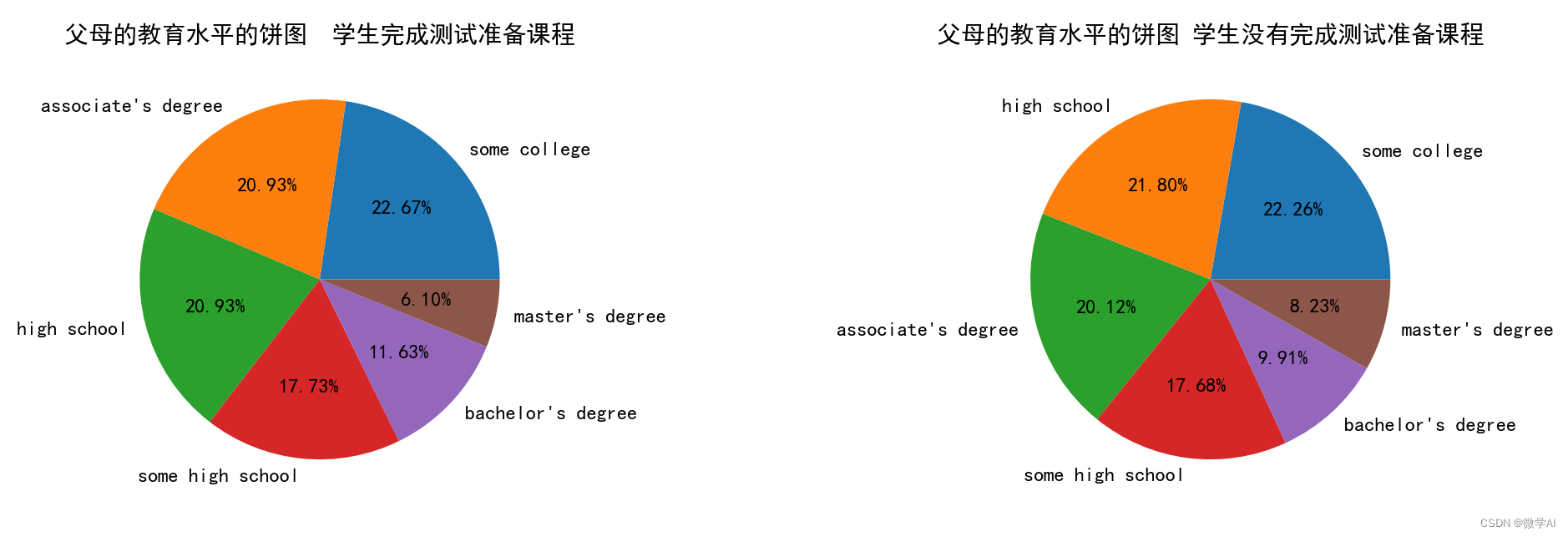
六、父母的教育水平/学生是否完成测试准备课程的饼图
df_pre.groupby('test preparation course')[['math score', 'reading score', 'writing score']].agg(['var', 'std'])
par_test_count = df_pre[['parental level of education', 'test preparation course']].value_counts().to_frame().reset_index().rename(columns={0:'Count'}).sort_values('Count', ascending=False)
# Create a figure with two subplots
fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(15,4))
# Create the first pie chart for the count of students who completed the test preparation course
ax1.pie(par_test_count[par_test_count['test preparation course']=='completed']['Count'],
labels=par_test_count[par_test_count['test preparation course']=='completed']['parental level of education'],
autopct='%1.2f%%')
ax1.set_title('父母的教育水平的饼图 学生完成测试准备课程')
# Create the second pie chart for the count of students who did not complete the test preparation course
ax2.pie(par_test_count[par_test_count['test preparation course']=='none']['Count'],
labels=par_test_count[par_test_count['test preparation course']=='none']['parental level of education'],
autopct='%1.2f%%')
ax2.set_title('父母的教育水平的饼图 学生没有完成测试准备课程')
# Show the plot
plt.show()
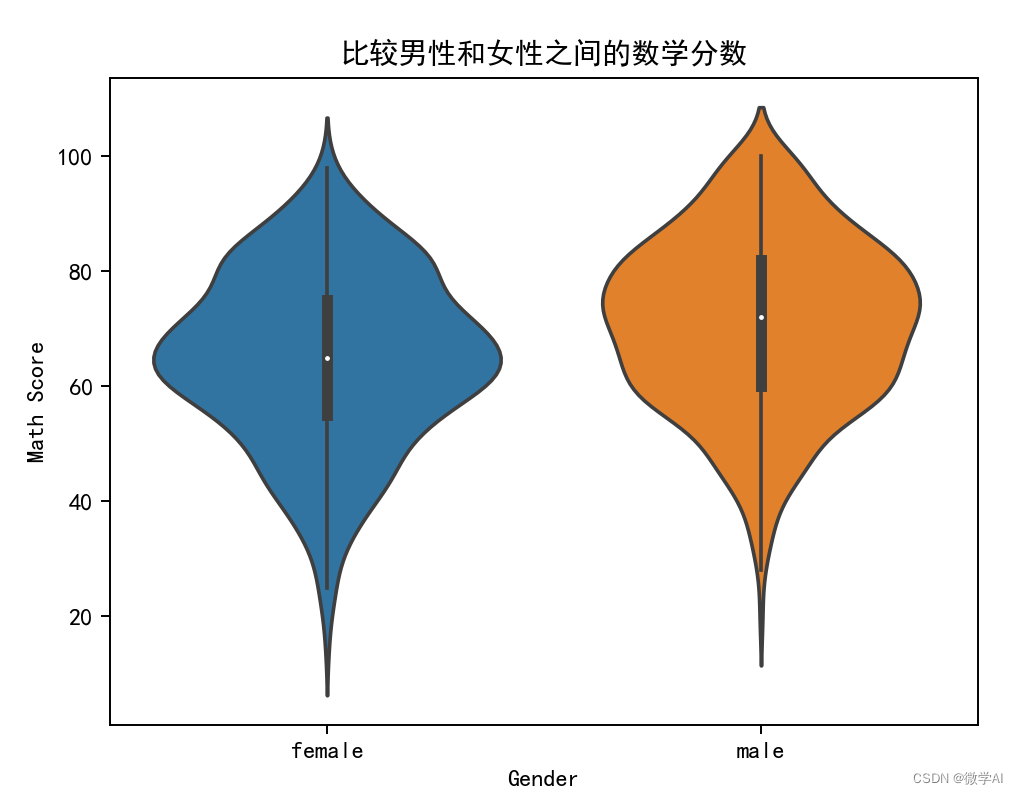
七、比较男性和女性之间的数学分数
df_pre.groupby('gender').mean()
sns.violinplot(x='gender', y='math score', data=df_pre)
# Add labels and title
plt.xlabel('Gender')
plt.ylabel('Math Score')
plt.title('比较男性和女性之间的数学分数')
# Show the plot
plt.show()
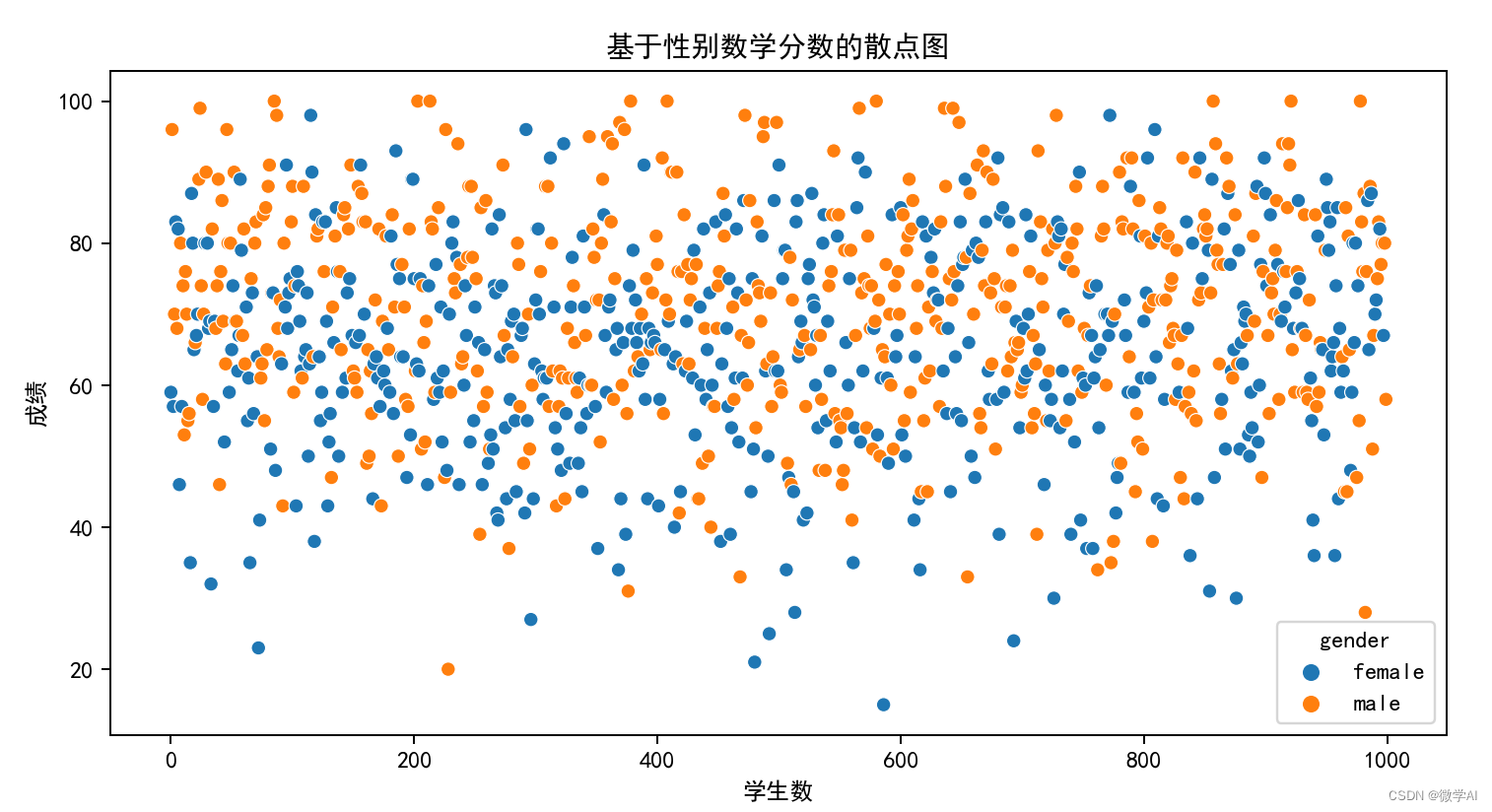
八、基于性别数学分数的散点图
plt.figure(figsize=(10,5))
sns.scatterplot(x=range(0, len(df_pre)), y="math score", hue="gender", data=df_pre)
# Add labels and title
plt.title('基于性别数学分数的散点图')
plt.xlabel('学生数')
plt.ylabel('成绩')
# Show the plot
plt.show()
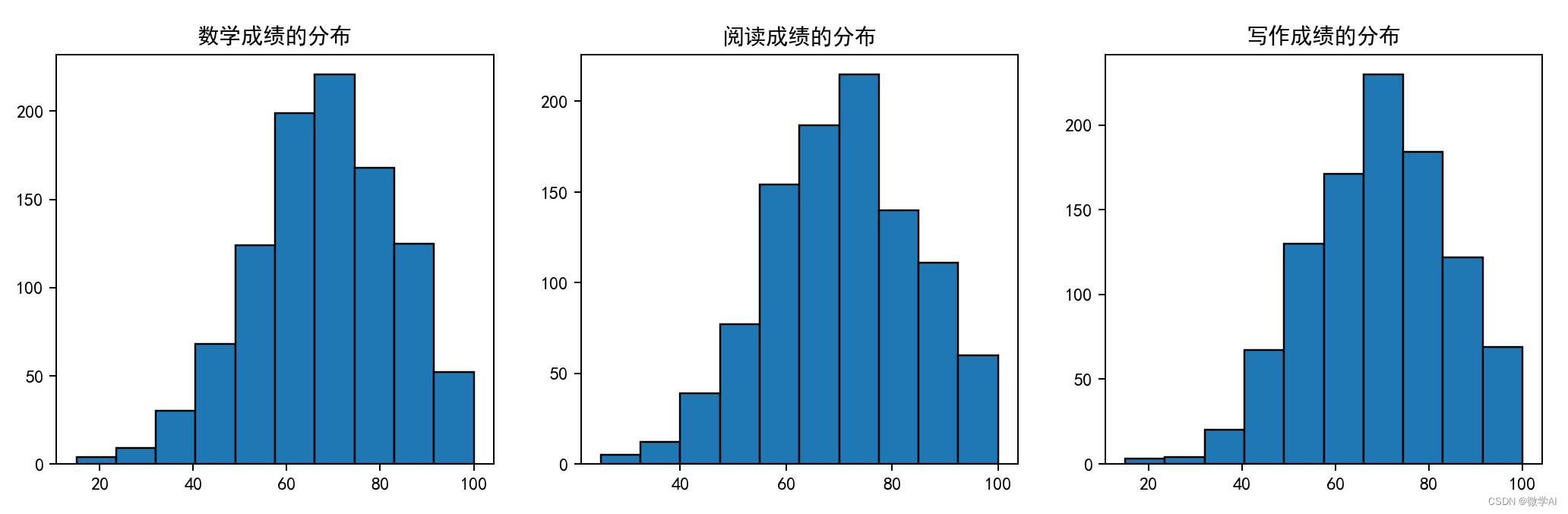
九、学生各科成绩分布图
fig, (ax1, ax2, ax3) = plt.subplots(1, 3, figsize=(20, 4))
# Plot for math
ax1.set_title('数学成绩的分布')
ax1.hist(df_pre['math score'], edgecolor='black')
# Plot for reading
ax2.set_title('阅读成绩的分布')
ax2.hist(df_pre['reading score'], edgecolor='black')
# Plot for writing
ax3.hist(df_pre['writing score'], edgecolor='black')
ax3.set_title('写作成绩的分布')
# Show plots
plt.show()
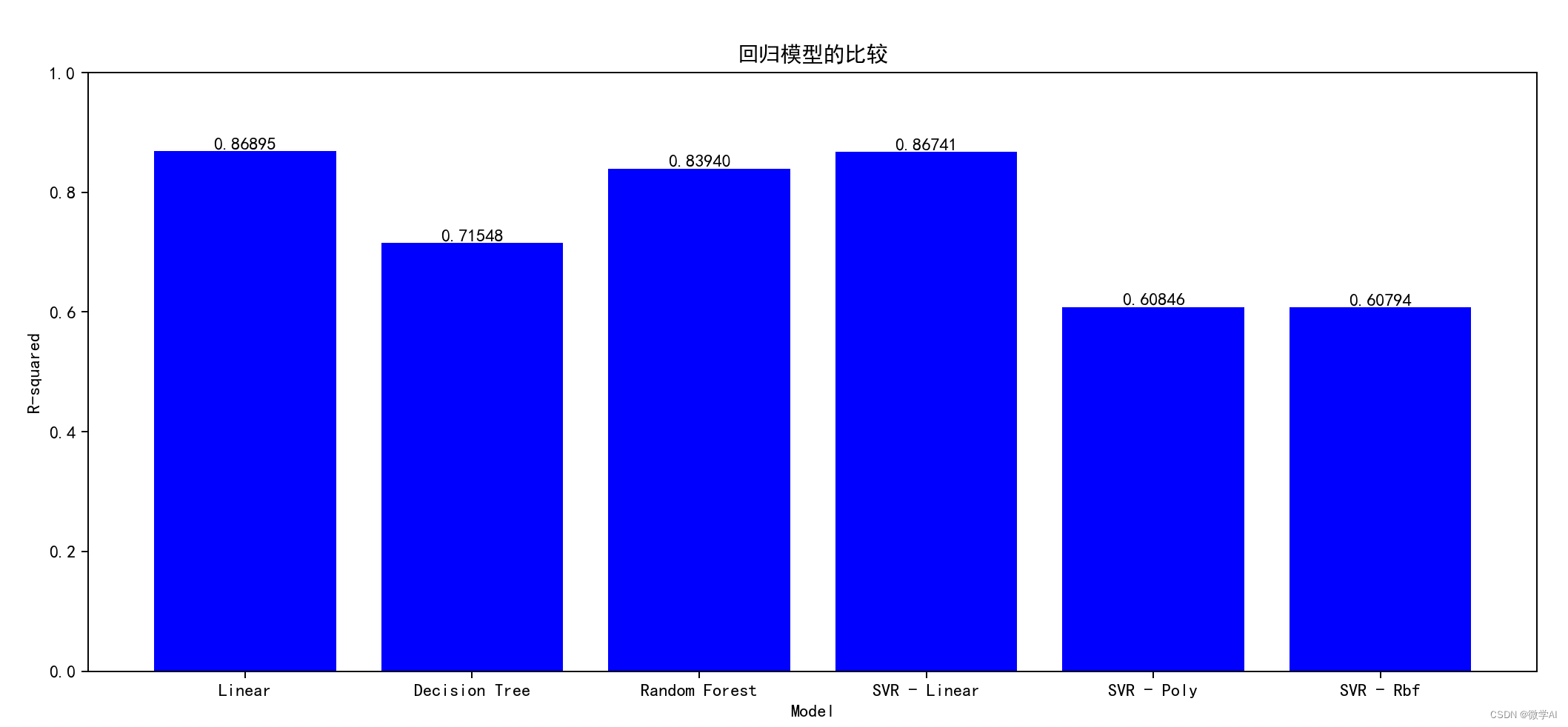
十、机器学习模型比较
df = pd.get_dummies(df_pre)
# Assign variables
X = df.drop('math score', axis=1)
y = df['math score']
# Split the data into training and testing sets
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.4, random_state=42)
models = [LinearRegression(), DecisionTreeRegressor(), RandomForestRegressor(), SVR(kernel='linear'), SVR(kernel='poly'), SVR(kernel='rbf')]
# Use cross-validation to compute the R-squared score for each model
cv_scores = []
for model in models:
scores = cross_val_score(model, X_train, y_train, cv=5, scoring='r2', n_jobs=-1)
cv_scores.append(scores.mean())
# Plot the results
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(15, 6))
rects = ax.bar(['Linear', 'Decision Tree', 'Random Forest', 'SVR - Linear', 'SVR - Poly', 'SVR - Rbf'], cv_scores, color='orange')
ax.set_ylim(0, 1)
ax.set_title('回归模型的比较')
ax.set_xlabel('Model')
ax.set_ylabel('R-squared')
# Add labels above each bar
for rect in rects:
height = rect.get_height()
ax.text(rect.get_x() + rect.get_width()/2., height, f'{height:.5f}', ha='center', va='bottom')
# Show the plot
plt.show()
欢迎大家持续关注,更多机器学习与深度学习的实战案例。
|









